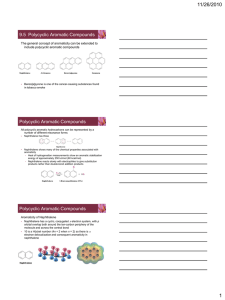
(General Equilibrium) Part 1
... With time, the concentration of reactant decreases and the concentration of product increases until both concentrations level off at constant, equilibrium values. Reactants start high and go ___________ . Products start low and go ...
... With time, the concentration of reactant decreases and the concentration of product increases until both concentrations level off at constant, equilibrium values. Reactants start high and go ___________ . Products start low and go ...
Communications to the Editor - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... also be converted to a mixture in which 6b predominated by base treatment. We assumed that 6a and 6b are the endo (syn to carbonyl) and exo (anti to carbonyl) isomers, respectively. However, the correctness of this assignment was not proven until the completion of the synthesis when the synthetic pr ...
... also be converted to a mixture in which 6b predominated by base treatment. We assumed that 6a and 6b are the endo (syn to carbonyl) and exo (anti to carbonyl) isomers, respectively. However, the correctness of this assignment was not proven until the completion of the synthesis when the synthetic pr ...
Descriptive Chemistry for the Final Exam
... Name two allotropes of carbon in addition to graphite and diamond. Explain the term roasting as it is applied to the industrial production of metals from their ores. Why is the roasting process a major source of pollution? ...
... Name two allotropes of carbon in addition to graphite and diamond. Explain the term roasting as it is applied to the industrial production of metals from their ores. Why is the roasting process a major source of pollution? ...
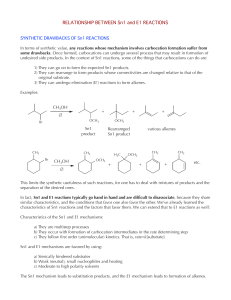
Chapter 12 –Part 2 Reaction of Carbonyl Compounds with
... Reactions of Grignard Reagents with Oxiranes (Epoxides) Grignard reagents are very powerful nucleophiles React react with the δ+ carbons of oxiranes l The reaction results in ring opening and formation of an alcohol l Reaction occurs at the less-substituted ring carbon of the oxirane l Net result is ...
... Reactions of Grignard Reagents with Oxiranes (Epoxides) Grignard reagents are very powerful nucleophiles React react with the δ+ carbons of oxiranes l The reaction results in ring opening and formation of an alcohol l Reaction occurs at the less-substituted ring carbon of the oxirane l Net result is ...
Topic 15 specification content - A
... I can explain how in aqueous solution the following metal-aqua ions are formed: [M(H2O)6]2+, limited to M = Fe and Cu, and [M(H2O)6]3+, limited to M = Al and Fe ...
... I can explain how in aqueous solution the following metal-aqua ions are formed: [M(H2O)6]2+, limited to M = Fe and Cu, and [M(H2O)6]3+, limited to M = Al and Fe ...
24.7 Urea Cycle
... The ammonium ion, the end product of amino acid degradation, is toxic if it is allowed to accumulate. The urea cycle converts ammonium ions to urea, which is transported to the kidneys to form urine. ...
... The ammonium ion, the end product of amino acid degradation, is toxic if it is allowed to accumulate. The urea cycle converts ammonium ions to urea, which is transported to the kidneys to form urine. ...
Chemical Reactions
... 2. To a 250-mL beaker add 30 mL of 0.1 M sulfuric acid. 3. To the beaker add 50 mL of water and 2 drops of phenolphthalein. 4. Ask the student for their opinion as why the water you just added should not make a difference in our reaction. (Point out to them that it is the sulfuric acid reacting with ...
... 2. To a 250-mL beaker add 30 mL of 0.1 M sulfuric acid. 3. To the beaker add 50 mL of water and 2 drops of phenolphthalein. 4. Ask the student for their opinion as why the water you just added should not make a difference in our reaction. (Point out to them that it is the sulfuric acid reacting with ...
Chemistry 210 - MiraCosta College
... IV. Alcohols and alkyl halides A. IUPAC nomenclature of alkyl halides B. IUPAC nomenclature of alcohols C. Classes of alcohols and alkyl halides D. Bonding in alcohols and alkyl halides E. Physical properties of alcohols and alkyl halides F. Acids and bases: general principles G. Acid-base reactions ...
... IV. Alcohols and alkyl halides A. IUPAC nomenclature of alkyl halides B. IUPAC nomenclature of alcohols C. Classes of alcohols and alkyl halides D. Bonding in alcohols and alkyl halides E. Physical properties of alcohols and alkyl halides F. Acids and bases: general principles G. Acid-base reactions ...
Aromatic Compounds
... Rings: The Friedel-Crafts Reaction Alkylation • The introduction of an alkyl group onto the benzene ring • Called the Friedel-Crafts reaction after its discoverers • Among the most useful electrophilic aromatic substitution ...
... Rings: The Friedel-Crafts Reaction Alkylation • The introduction of an alkyl group onto the benzene ring • Called the Friedel-Crafts reaction after its discoverers • Among the most useful electrophilic aromatic substitution ...
Studies of Carbon-Sulfur Bond Cleavage by Homogeneous
... carbon-sulfur bond breaking step. The structures of the intermediates involved were elucidated and the kinetic and thermodynamic parameters that control the reactivity and selectivity were determined. New complexes were found that not only break C-S bonds, but also do further chemistry resulting in ...
... carbon-sulfur bond breaking step. The structures of the intermediates involved were elucidated and the kinetic and thermodynamic parameters that control the reactivity and selectivity were determined. New complexes were found that not only break C-S bonds, but also do further chemistry resulting in ...
Ring-closing metathesis

Ring-closing metathesis, or RCM, is a widely used variation of olefin metathesis in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various unsaturated rings via the intramolecular metathesis of two terminal alkenes, which forms the cycloalkene as the E- or Z- isomers and volatile ethylene.The most commonly synthesized ring sizes are between 5-7 atoms; however, reported syntheses include 45- up to 90- membered macroheterocycles. These reactions are metal-catalyzed and proceed through a metallacyclobutane intermediate. It was first published by Dider Villemin in 1980 describing the synthesis of an Exaltolide precursor, and later become popularized by Robert H. Grubbs and Richard R. Schrock, who shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, along with Yves Chauvin, in 2005 for their combined work in olefin metathesis. RCM is a favorite among organic chemists due to its synthetic utility in the formation of rings, which were previously difficult to access efficiently, and broad substrate scope. Since the only major by-product is ethylene, these reactions may also be considered atom economic, an increasingly important concern in the development of green chemistry.There are several reviews published on ring-closing metathesis.