4 Organic Chemistry
... What we have done is introduce a branch in the carbon chain. Now we must be able to distinguish between these two compounds by giving them different names. In this case it is quite straightforward. We call the straight-chain molecule n-butane and the branched molecule iso-butane. However, when alkan ...
... What we have done is introduce a branch in the carbon chain. Now we must be able to distinguish between these two compounds by giving them different names. In this case it is quite straightforward. We call the straight-chain molecule n-butane and the branched molecule iso-butane. However, when alkan ...
Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... Precipitation Reactions SOLUBILITY RULES: for Ionic Compounds (Salts) 1. All salts of alkali metals (IA) are soluble. 2. All NH4+ salts are soluble. 3. All salts containing the anions: NO3-, ClO3-, ClO4-, (C2H3O2-) are soluble. 4. All Cl-, Br-, and I- are soluble except for Hg22+, Ag+, and Pb2+ sal ...
... Precipitation Reactions SOLUBILITY RULES: for Ionic Compounds (Salts) 1. All salts of alkali metals (IA) are soluble. 2. All NH4+ salts are soluble. 3. All salts containing the anions: NO3-, ClO3-, ClO4-, (C2H3O2-) are soluble. 4. All Cl-, Br-, and I- are soluble except for Hg22+, Ag+, and Pb2+ sal ...
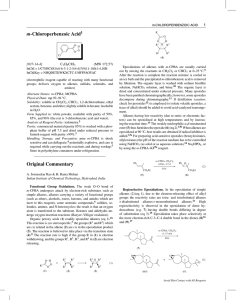
Chloroperbenzoic_aci..
... Diastereoselective Epoxidation of Cyclic Alkenes. π-Facial stereoselectivity (75% anti) is observed in the epoxidation of the allyl ether (10a) since reagent approach from the α-face is blocked by the allylic substituent; a higher diastereoselectivity (90% anti epoxidation) is observed when the bulk ...
... Diastereoselective Epoxidation of Cyclic Alkenes. π-Facial stereoselectivity (75% anti) is observed in the epoxidation of the allyl ether (10a) since reagent approach from the α-face is blocked by the allylic substituent; a higher diastereoselectivity (90% anti epoxidation) is observed when the bulk ...
Anionic rearrangement of 2-benzyloxypyridine derivatives and a synthetic approach to aldingenin B
... synthesis of the tricyclic core of aldingenin B from a key internal alkyne was completed. Synthesis of alkynes by fragmentation is an on-going interest of the Dudley lab. One current goal is to apply our methodology in conjunction with an innovative oxidative alkyne ketalization to achieve a short a ...
... synthesis of the tricyclic core of aldingenin B from a key internal alkyne was completed. Synthesis of alkynes by fragmentation is an on-going interest of the Dudley lab. One current goal is to apply our methodology in conjunction with an innovative oxidative alkyne ketalization to achieve a short a ...
Lecture 11 – Reaction Types and Mechanisms for Inorganic
... enthalpy for the following reaction, so both complexes are thermodynamically capable of undergoing ligand exchange with water. [M(NH3)6]n+ + 6 H3O+ ---> [M(H2O)6]n+ + 6 NH4+ ...
... enthalpy for the following reaction, so both complexes are thermodynamically capable of undergoing ligand exchange with water. [M(NH3)6]n+ + 6 H3O+ ---> [M(H2O)6]n+ + 6 NH4+ ...
Reactions of Acyl Chlorides
... Acyl chlorides react with water to give carboxylic acids (carboxylate ion in base): O RCCl + H2O ...
... Acyl chlorides react with water to give carboxylic acids (carboxylate ion in base): O RCCl + H2O ...
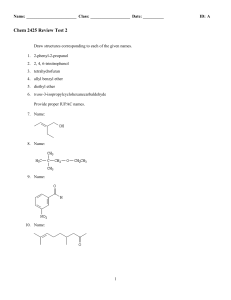
Chem 2425-Test 2 Review
... 13. How do you account for the difference in acidity between meta and para-nitrophenol? ...
... 13. How do you account for the difference in acidity between meta and para-nitrophenol? ...
Chemistry of Fatty Acids
... and double bonds, methylenes adjacent to them are activated, increasing their reactivity. Only rarely do saturated chains show reactivity. Carboxyl groups and unsaturated centers usually react independently, but when in close proximity, both may react through neighboring group participation. In enzy ...
... and double bonds, methylenes adjacent to them are activated, increasing their reactivity. Only rarely do saturated chains show reactivity. Carboxyl groups and unsaturated centers usually react independently, but when in close proximity, both may react through neighboring group participation. In enzy ...
Anionic polymerization
... 3. Anionic Polymerization - Initiators, monomers and mechanism - “Living” polymers, copolymerization ...
... 3. Anionic Polymerization - Initiators, monomers and mechanism - “Living” polymers, copolymerization ...
Introduction - University of Pretoria
... different methods: (i) transformation of a non-carbene ligand and (ii) addition of a carbene ligand precursor to a metal complex from pre-existing carbene complexes, of which five reactions are possible. They are (i) the transfer of a carbene ligand from one metal to another, (ii) modification of th ...
... different methods: (i) transformation of a non-carbene ligand and (ii) addition of a carbene ligand precursor to a metal complex from pre-existing carbene complexes, of which five reactions are possible. They are (i) the transfer of a carbene ligand from one metal to another, (ii) modification of th ...
Chapter Seven - U of L Class Index
... Both these reactions operate on the principal of converting OH into a better leaving ...
... Both these reactions operate on the principal of converting OH into a better leaving ...
Ring-closing metathesis

Ring-closing metathesis, or RCM, is a widely used variation of olefin metathesis in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various unsaturated rings via the intramolecular metathesis of two terminal alkenes, which forms the cycloalkene as the E- or Z- isomers and volatile ethylene.The most commonly synthesized ring sizes are between 5-7 atoms; however, reported syntheses include 45- up to 90- membered macroheterocycles. These reactions are metal-catalyzed and proceed through a metallacyclobutane intermediate. It was first published by Dider Villemin in 1980 describing the synthesis of an Exaltolide precursor, and later become popularized by Robert H. Grubbs and Richard R. Schrock, who shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, along with Yves Chauvin, in 2005 for their combined work in olefin metathesis. RCM is a favorite among organic chemists due to its synthetic utility in the formation of rings, which were previously difficult to access efficiently, and broad substrate scope. Since the only major by-product is ethylene, these reactions may also be considered atom economic, an increasingly important concern in the development of green chemistry.There are several reviews published on ring-closing metathesis.