12. 16 Physical Properties of Alkanes and Cycloalkanes.
... reactions (Like key reactions given in page 137). Know the products of electrophilic addition to an alkene depending on the reagents ((Like key reactions given in page 137 and stability of carbocation) Be able to recognize the correctly written mechanism for hydration of an alkene to an alcohol (Lik ...
... reactions (Like key reactions given in page 137). Know the products of electrophilic addition to an alkene depending on the reagents ((Like key reactions given in page 137 and stability of carbocation) Be able to recognize the correctly written mechanism for hydration of an alkene to an alcohol (Lik ...
CHAPTER 13 Approaches to the Asymmetric Synthesis of Unusual
... for the preparation of a-amino acids. Since glycine is the simplest amino acid, derivatization of glycine (including “double derivatization” to make a, a’-disubstituted a-amino acids) can, in principle, provide an infinite variety of a-amino acids. Numerous approaches have been devised and previousl ...
... for the preparation of a-amino acids. Since glycine is the simplest amino acid, derivatization of glycine (including “double derivatization” to make a, a’-disubstituted a-amino acids) can, in principle, provide an infinite variety of a-amino acids. Numerous approaches have been devised and previousl ...
Amide bond formation and peptide coupling
... fluoride 1230 in the presence of pyridine and react in a similar way to cyanuric chloride 6 (Scheme 12). Alternatively, N,N-tetramethylfluoroformamidinium hexafluorophosphate (TFFH) 13 can be used in the presence of Hünig’s base.31 This salt is advantageous in being nonhygroscopic and stable to han ...
... fluoride 1230 in the presence of pyridine and react in a similar way to cyanuric chloride 6 (Scheme 12). Alternatively, N,N-tetramethylfluoroformamidinium hexafluorophosphate (TFFH) 13 can be used in the presence of Hünig’s base.31 This salt is advantageous in being nonhygroscopic and stable to han ...
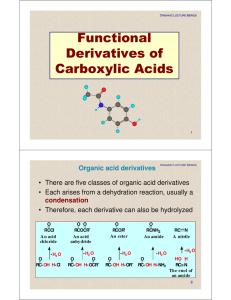
Functional Derivatives of Carboxylic Acids
... the cephalosporins are also β-lactam antibiotics The cephalosporins d iffer in the group bonded to the acyl carbon an d the s ide chain of the thiazin e rin g O NH2 ...
... the cephalosporins are also β-lactam antibiotics The cephalosporins d iffer in the group bonded to the acyl carbon an d the s ide chain of the thiazin e rin g O NH2 ...
Mock Exam One
... a.) The bond angle around the oxygen of an alcohol is < 109.5°. b.) Alcohols contain a polar covalent bond that an alkane does not have. c.) The strongest intermolecular force present in an alcohol is hydrogen bonding while the strongest intermolecular force present in alkanes is London dispersion. ...
... a.) The bond angle around the oxygen of an alcohol is < 109.5°. b.) Alcohols contain a polar covalent bond that an alkane does not have. c.) The strongest intermolecular force present in an alcohol is hydrogen bonding while the strongest intermolecular force present in alkanes is London dispersion. ...
Synthetic applications of ortho esters
... In contrast to acetal derivatives of carbonyl compounds, ortho esters have found surprisingly limited use in organic synthesis [1]. Since ortho esters are among the few carboxylic acid protective groups that demonstrate a high level of stability toward strong nucleophiles and bases, most current app ...
... In contrast to acetal derivatives of carbonyl compounds, ortho esters have found surprisingly limited use in organic synthesis [1]. Since ortho esters are among the few carboxylic acid protective groups that demonstrate a high level of stability toward strong nucleophiles and bases, most current app ...
Coordination Numbers and Structures
... atom is surrounded by neutral or anionic ligands. For example, it was known that cobalt forms a "complex" with formula CoCl3•6NH3, but the nature of the association indicated by the dot was mysterious. Werner proposed the structure [Co(NH3)6]Cl3, with the Co3+ ion surrounded by six NH3 at the vertic ...
... atom is surrounded by neutral or anionic ligands. For example, it was known that cobalt forms a "complex" with formula CoCl3•6NH3, but the nature of the association indicated by the dot was mysterious. Werner proposed the structure [Co(NH3)6]Cl3, with the Co3+ ion surrounded by six NH3 at the vertic ...
Lecture 4 - Sugars, ring structures
... The substituent groups on the molecule are either in an axial or equatorial position depending on what gives the most stable molecule. ...
... The substituent groups on the molecule are either in an axial or equatorial position depending on what gives the most stable molecule. ...
Boron and Metal Catalyzed CC and CH Bond Formation
... dialkynylation of aryl aldehydes using dialkynylboron chloride. Numerous applications of these novel reactions have been developed. These include alternate routes to diphenylmethanes and 1,4-diynes from easily prepared dialkynylboron chlorides. In addition, E and Z alkenyl halides can now be prepare ...
... dialkynylation of aryl aldehydes using dialkynylboron chloride. Numerous applications of these novel reactions have been developed. These include alternate routes to diphenylmethanes and 1,4-diynes from easily prepared dialkynylboron chlorides. In addition, E and Z alkenyl halides can now be prepare ...
Alcohols phenols ethers
... (R–O/Ar–O) yields another class of compounds known as ‘ethers’, for example, CH3OCH3 (dimethyl ether). ethers as compounds formed by substituting the hydrogen atom of hydroxyl group of an alcohol or phenol by an alkyl or aryl group. Alcohols are organic compounds that have one or more hydroxy (-OH) ...
... (R–O/Ar–O) yields another class of compounds known as ‘ethers’, for example, CH3OCH3 (dimethyl ether). ethers as compounds formed by substituting the hydrogen atom of hydroxyl group of an alcohol or phenol by an alkyl or aryl group. Alcohols are organic compounds that have one or more hydroxy (-OH) ...
Chemical Properties of Monocyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons(5)
... particularly valuable in the synthesis of substituted aromatic rings, where the introduction of a new substituent is strongly affected by the directing effects of other substituents. Planning synthesis of substituted aromatic compounds is therefore an excellent way to gain facility with the many rea ...
... particularly valuable in the synthesis of substituted aromatic rings, where the introduction of a new substituent is strongly affected by the directing effects of other substituents. Planning synthesis of substituted aromatic compounds is therefore an excellent way to gain facility with the many rea ...
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE General Organic Chemistry I
... bonding, structure and properties of organic compounds, stereochemistry, overview of organic reactions, kinetics and thermodynamics, structure, synthesis, and reaction of alkenes, alkynes, and alkyl halides, nucleophilic substitution and elimination reactions, structure determination using Mass Spec ...
... bonding, structure and properties of organic compounds, stereochemistry, overview of organic reactions, kinetics and thermodynamics, structure, synthesis, and reaction of alkenes, alkynes, and alkyl halides, nucleophilic substitution and elimination reactions, structure determination using Mass Spec ...
Reactions of Alkenes: Addition Reactions
... The solvent used in catalytic hydrogenation is chosen for its ability to dissolve the alkene and is typically ethanol, hexane, or acetic acid. The metal catalysts are insoluble in these solvents (or, indeed, in any solvent). Two phases, the solution and the metal, are present, and the reaction takes ...
... The solvent used in catalytic hydrogenation is chosen for its ability to dissolve the alkene and is typically ethanol, hexane, or acetic acid. The metal catalysts are insoluble in these solvents (or, indeed, in any solvent). Two phases, the solution and the metal, are present, and the reaction takes ...
Ch. 17Notes - U of L Class Index
... Nucleophilic addition of alcohols: formation of Acetals (sometimes called Ketals) ...
... Nucleophilic addition of alcohols: formation of Acetals (sometimes called Ketals) ...
PDF - Nanyang Technological University
... For reactions that were carried out in DMF (Table 1, entry 6), the low ee values were largely caused by the racemic background reaction that is not catalyzed by the amine. To suppress the racemic background reaction, we screened solvents for this cooperative system with catalyst C (Table 1, entries ...
... For reactions that were carried out in DMF (Table 1, entry 6), the low ee values were largely caused by the racemic background reaction that is not catalyzed by the amine. To suppress the racemic background reaction, we screened solvents for this cooperative system with catalyst C (Table 1, entries ...
ug chemistry - Krishna University
... enantiomers and mesomers- calculation. D,L and R,S configuration for asymmetric and disymmetric molecules. Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rules. Racemic mixture- racemisation and resolution techniques. Diastereomers- definitionGeometrical isomerism with reference to alkenes- cis, trans and E,Z- configuration UN ...
... enantiomers and mesomers- calculation. D,L and R,S configuration for asymmetric and disymmetric molecules. Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rules. Racemic mixture- racemisation and resolution techniques. Diastereomers- definitionGeometrical isomerism with reference to alkenes- cis, trans and E,Z- configuration UN ...
Ring-closing metathesis

Ring-closing metathesis, or RCM, is a widely used variation of olefin metathesis in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various unsaturated rings via the intramolecular metathesis of two terminal alkenes, which forms the cycloalkene as the E- or Z- isomers and volatile ethylene.The most commonly synthesized ring sizes are between 5-7 atoms; however, reported syntheses include 45- up to 90- membered macroheterocycles. These reactions are metal-catalyzed and proceed through a metallacyclobutane intermediate. It was first published by Dider Villemin in 1980 describing the synthesis of an Exaltolide precursor, and later become popularized by Robert H. Grubbs and Richard R. Schrock, who shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, along with Yves Chauvin, in 2005 for their combined work in olefin metathesis. RCM is a favorite among organic chemists due to its synthetic utility in the formation of rings, which were previously difficult to access efficiently, and broad substrate scope. Since the only major by-product is ethylene, these reactions may also be considered atom economic, an increasingly important concern in the development of green chemistry.There are several reviews published on ring-closing metathesis.