AlCl3 heat HCl
... 11. (3 points) How many stereoisomers would be obtained from the following SN1 reactions? Explain. ...
... 11. (3 points) How many stereoisomers would be obtained from the following SN1 reactions? Explain. ...
Reading Guide Organic Chemistry
... What is the fewest number of carbons needed for an alkane to have structural isomers? As the number of carbon atoms increases, what happens to the number of possible structural isomers? ...
... What is the fewest number of carbons needed for an alkane to have structural isomers? As the number of carbon atoms increases, what happens to the number of possible structural isomers? ...
Name (Last, First):
... The organic chemist uses the term “oxidize” to refer to either of two processes: 1. The removal of two hydrogen atoms, with the formation of water (as in 2 a above) OR 2. The addition of an oxygen atom into the molecule. How would either of these two processes affect the “oxidation number” of the ca ...
... The organic chemist uses the term “oxidize” to refer to either of two processes: 1. The removal of two hydrogen atoms, with the formation of water (as in 2 a above) OR 2. The addition of an oxygen atom into the molecule. How would either of these two processes affect the “oxidation number” of the ca ...
Chemical Equations and Reaction Types Lab
... 3) Determine the products and write the correct formula for each product. Once the correct formula is written it must not be changed during the subsequent balancing operation. 4) Balance the chemical equation. Do NOT change any chemical formulas while balancing. a) Choose the compound with the great ...
... 3) Determine the products and write the correct formula for each product. Once the correct formula is written it must not be changed during the subsequent balancing operation. 4) Balance the chemical equation. Do NOT change any chemical formulas while balancing. a) Choose the compound with the great ...
Ch. 7 & 8 Notes (Chemical Reactions) teacher
... cross must look up the ___________ them if they are different!! Balance it _________ AFTER you get all the correct formulas written first! Don’t forget about the HONClBrIF’s! ...
... cross must look up the ___________ them if they are different!! Balance it _________ AFTER you get all the correct formulas written first! Don’t forget about the HONClBrIF’s! ...
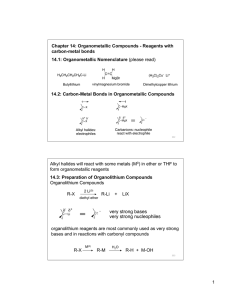
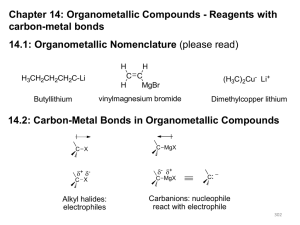
Organometallic Compounds - Reagents
... 14.9: Retrosynthetic Analysis - the process of planning a synthesis by reasoning backward from the the target molecule to a starting compound using known and reliable reactions. “it is a problem solving technique for transforming the structure of a synthetic target molecule (TM) to a sequence of pr ...
... 14.9: Retrosynthetic Analysis - the process of planning a synthesis by reasoning backward from the the target molecule to a starting compound using known and reliable reactions. “it is a problem solving technique for transforming the structure of a synthetic target molecule (TM) to a sequence of pr ...
Reaction types and Stoichiometry
... If 6 liters of hydrogen gas are used, how many liters of nitrogen gas will be needed for the above reaction at STP? A 2 liters B 3 liters C 4 liters D 12 liters ...
... If 6 liters of hydrogen gas are used, how many liters of nitrogen gas will be needed for the above reaction at STP? A 2 liters B 3 liters C 4 liters D 12 liters ...
chemical reaction
... (aq) – aqueous (dissolved in water, exists as ions) ↓ - a precipitate has formed ...
... (aq) – aqueous (dissolved in water, exists as ions) ↓ - a precipitate has formed ...
Sample
... Write the chemical structure for: a) Compound (A) b) Compound (B) 40- Given the following entropy values (Al2O3 is 51.00; Al(s) is 28.32; H2O(g) is 188.7; H2(g) is 130.6) Determine the standard entropy change (ΔS) for the reaction: Al2O3(s) + 3H2(g) ...
... Write the chemical structure for: a) Compound (A) b) Compound (B) 40- Given the following entropy values (Al2O3 is 51.00; Al(s) is 28.32; H2O(g) is 188.7; H2(g) is 130.6) Determine the standard entropy change (ΔS) for the reaction: Al2O3(s) + 3H2(g) ...
Organic Chemistry
... therefore they have higher melting and boiling points than hydrocarbons or alkyl halides of similar mass. Tertiary amines cannot form H bonds between their molecules because they lack a polar N–H bond. Amines of low molar mass are fishy smelling, water soluble, and weakly basic. ...
... therefore they have higher melting and boiling points than hydrocarbons or alkyl halides of similar mass. Tertiary amines cannot form H bonds between their molecules because they lack a polar N–H bond. Amines of low molar mass are fishy smelling, water soluble, and weakly basic. ...
Grignard Reagents
... 14.9: Retrosynthetic Analysis - the process of planning a synthesis by reasoning backward from the the target molecule to a starting compound using known and reliable reactions. “it is a problem solving technique for transforming the structure of a synthetic target molecule (TM) to a sequence of pr ...
... 14.9: Retrosynthetic Analysis - the process of planning a synthesis by reasoning backward from the the target molecule to a starting compound using known and reliable reactions. “it is a problem solving technique for transforming the structure of a synthetic target molecule (TM) to a sequence of pr ...
Structure and Bonding
... The cis and trans isomers of an alkene are configurational isomers (also called geometric isomers) because they have different shapes and cannot interconvert since the double bond of an alkene cannot rotate. Therefore, the substituents are ‘fixed’ in space relative to each other. The methyl groups c ...
... The cis and trans isomers of an alkene are configurational isomers (also called geometric isomers) because they have different shapes and cannot interconvert since the double bond of an alkene cannot rotate. Therefore, the substituents are ‘fixed’ in space relative to each other. The methyl groups c ...
Esters are reduced by hydride reagents to give alcohols or aldehydes.
... Long-chain carboxylic acids and phospholipids are termed amphipathic: they have hydrophobic and hydrophilic ends. When dissolved in water, fatty acids and some phospholipids form structures called “micelles.” Most phospholipids form a more complicated structure called a “lipid bilayer” when dissolv ...
... Long-chain carboxylic acids and phospholipids are termed amphipathic: they have hydrophobic and hydrophilic ends. When dissolved in water, fatty acids and some phospholipids form structures called “micelles.” Most phospholipids form a more complicated structure called a “lipid bilayer” when dissolv ...
Practice: Chapter 21
... 15.Yes; both compounds have the molecular formula C5H8, but they have different carbon chains. 16.The aromatic compounds are 1-methyl-4-propylbenzene and anthracene because these compounds contain benzene rings as part of their molecular structures. 17. Halocarbons are named by use of the prefixes f ...
... 15.Yes; both compounds have the molecular formula C5H8, but they have different carbon chains. 16.The aromatic compounds are 1-methyl-4-propylbenzene and anthracene because these compounds contain benzene rings as part of their molecular structures. 17. Halocarbons are named by use of the prefixes f ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.