Amidations of Rosin with Isocyanates
... for the addition amounts of the catalysts between 10 and 20 mg/g abietic acid. The results demonstrate that the tertiary amines can greatly accelerate the reaction rate of abietic acid with phenyl isocyanate. Amidation of rosin with phenyl isocyanate Table 3 shows the results of amidation of rosin w ...
... for the addition amounts of the catalysts between 10 and 20 mg/g abietic acid. The results demonstrate that the tertiary amines can greatly accelerate the reaction rate of abietic acid with phenyl isocyanate. Amidation of rosin with phenyl isocyanate Table 3 shows the results of amidation of rosin w ...
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 10 – Alkyl Halides II Chem 2310 I
... In the E1 reaction, there are multiple steps. However, the first step, in which the carbocation is formed, controls the reaction because it is the rate limiting step. ◦ In the rate limiting step, the bond between the halide and the carbon is being broken. ◦ Since only the alkyl halide is part of the ...
... In the E1 reaction, there are multiple steps. However, the first step, in which the carbocation is formed, controls the reaction because it is the rate limiting step. ◦ In the rate limiting step, the bond between the halide and the carbon is being broken. ◦ Since only the alkyl halide is part of the ...
ETHERS
... Mechanism of Cleavage — As seen below, the reaction is basically SN2 in base promoted cleavage. This means that the nucleophile attacks the backside (opposite the oxygen) of the less sterically hindered carbon preferentially – typical SN2 ...
... Mechanism of Cleavage — As seen below, the reaction is basically SN2 in base promoted cleavage. This means that the nucleophile attacks the backside (opposite the oxygen) of the less sterically hindered carbon preferentially – typical SN2 ...
Review
... Chapter 17 is all about reactions that happen at the position one away from an aromatic ring, or one away from a double bond. These are called the benzylic and allylic positions respectively. Benzyl and allyl are the names of the corresponding R groups, and you can use these names as part of the IUP ...
... Chapter 17 is all about reactions that happen at the position one away from an aromatic ring, or one away from a double bond. These are called the benzylic and allylic positions respectively. Benzyl and allyl are the names of the corresponding R groups, and you can use these names as part of the IUP ...
Studies toward the Stereoselective Synthesis of the
... the diseases, commonly called mycotoxicoses through the ingestion of foods or feeds contaminated by these toxic fungal metabolites. The outbreak of a mycotoxicosis that caused the death of 100 000 turkeys, 14 000 ducklings and thousands of partridge and pheasant poults in 1960 in England resulted in ...
... the diseases, commonly called mycotoxicoses through the ingestion of foods or feeds contaminated by these toxic fungal metabolites. The outbreak of a mycotoxicosis that caused the death of 100 000 turkeys, 14 000 ducklings and thousands of partridge and pheasant poults in 1960 in England resulted in ...
File
... group attached to an aromatic carbon. Although they share the same functional group with alcohols, where the –OH group is attached to an aliphatic carbon, the chemistry of phenols is very different from that of alcohols. ...
... group attached to an aromatic carbon. Although they share the same functional group with alcohols, where the –OH group is attached to an aliphatic carbon, the chemistry of phenols is very different from that of alcohols. ...
Alcohol
... Meanwhile, the oxygen atom has lone pairs of nonbonded electrons that render it weakly basic in the presence of strong acids such as sulfuric acid. For example, with methanol: ...
... Meanwhile, the oxygen atom has lone pairs of nonbonded electrons that render it weakly basic in the presence of strong acids such as sulfuric acid. For example, with methanol: ...
Ch14b: Carboxylic Acids
... are produced by simple substances of the carboxylic acid family of organic substances. ‣ These organic molecules are acids. Like the simple binary acids you’re already familiar with (HCl, HBr) they release free protons (H+). ‣ These substances have high acidity (low pH). ‣ They neutralize bases like ...
... are produced by simple substances of the carboxylic acid family of organic substances. ‣ These organic molecules are acids. Like the simple binary acids you’re already familiar with (HCl, HBr) they release free protons (H+). ‣ These substances have high acidity (low pH). ‣ They neutralize bases like ...
Elimination Reactions
... base (H2SO4, H3PO4). To favour SN1 over E1, use a good nucleophile. •To favour E2 over SN2, use a strong, bulky non-nucleophilic base. To favour SN2 over E2, use good nucleophiles that are relatively weak bases. •It is important to keep in mind that although you might choose reaction conditions that ...
... base (H2SO4, H3PO4). To favour SN1 over E1, use a good nucleophile. •To favour E2 over SN2, use a strong, bulky non-nucleophilic base. To favour SN2 over E2, use good nucleophiles that are relatively weak bases. •It is important to keep in mind that although you might choose reaction conditions that ...
Elimination Reactions
... base (H2SO4, H3PO4). To favour SN1 over E1, use a good nucleophile. •To favour E2 over SN2, use a strong, bulky non-nucleophilic base. To favour SN2 over E2, use good nucleophiles that are relatively weak bases. •It is important to keep in mind that although you might choose reaction conditions that ...
... base (H2SO4, H3PO4). To favour SN1 over E1, use a good nucleophile. •To favour E2 over SN2, use a strong, bulky non-nucleophilic base. To favour SN2 over E2, use good nucleophiles that are relatively weak bases. •It is important to keep in mind that although you might choose reaction conditions that ...
A-level Chemistry Question paper Unit 3/W - Introduction to
... (a) The empirical formula and the molecular formula of undecane are both C11H24 ...
... (a) The empirical formula and the molecular formula of undecane are both C11H24 ...
Chapter 23: Substituted Hydrocarbons and Their Reactions
... hydrocarbons of similar shape and size. Also, because of polarity and hydrogen bonding, ethanol is completely miscible with water. In fact, once they are mixed, it is difficult to separate water and ethanol completely. Distillation is used to remove ethanol from water, but even after that process is ...
... hydrocarbons of similar shape and size. Also, because of polarity and hydrogen bonding, ethanol is completely miscible with water. In fact, once they are mixed, it is difficult to separate water and ethanol completely. Distillation is used to remove ethanol from water, but even after that process is ...
Development of Catalytic Ester Condensations and Hydrolysis of
... purification method for ester condensation catalyzed by sulfonic acids might be easier than that with N,N-diarylammonium salts because sulfonic acids can be separated by washing the crude product with a small amount of water. However, sulfonic acids are easily deactivated by water since they have hi ...
... purification method for ester condensation catalyzed by sulfonic acids might be easier than that with N,N-diarylammonium salts because sulfonic acids can be separated by washing the crude product with a small amount of water. However, sulfonic acids are easily deactivated by water since they have hi ...
organic problems - St. Olaf College
... A) C8H14O2Cl B) C6H14Br2 C) C7H10NF D) C30H54N2Cl 26 What formal charges are present in the molecule C6H5C≡N-O? ( all heavy atoms have a valence shell octet, and C6H5- is a phenyl group) A) N is -1 and C is +1 B) N is +1 and C is -1 C) O is -1 and C is +1 D) O is -1 and N is +1 27 Which statement ab ...
... A) C8H14O2Cl B) C6H14Br2 C) C7H10NF D) C30H54N2Cl 26 What formal charges are present in the molecule C6H5C≡N-O? ( all heavy atoms have a valence shell octet, and C6H5- is a phenyl group) A) N is -1 and C is +1 B) N is +1 and C is -1 C) O is -1 and C is +1 D) O is -1 and N is +1 27 Which statement ab ...
幻灯片 1
... • The stereochemistry of E2 reaction • As shown by a large number of experiments, E2 reactions always occur with a periplanar geometry, meaning that all four reacting atoms-the hydrogen, the two carbons, and the leaving group- lie in the same plane. Two such geometries are possible: syn periplanar g ...
... • The stereochemistry of E2 reaction • As shown by a large number of experiments, E2 reactions always occur with a periplanar geometry, meaning that all four reacting atoms-the hydrogen, the two carbons, and the leaving group- lie in the same plane. Two such geometries are possible: syn periplanar g ...
An Oxidation-Reduction Scheme: Borneol, Camphor, Isoborneol1
... It is expected, therefore, that isoborneol, the alcohol produced from the attack at the least-hindered position, will predominate but will not be the exclusive product in the final reaction mixture. The percentage composition of the mixture can be determined by spectroscopy. It is interesting to not ...
... It is expected, therefore, that isoborneol, the alcohol produced from the attack at the least-hindered position, will predominate but will not be the exclusive product in the final reaction mixture. The percentage composition of the mixture can be determined by spectroscopy. It is interesting to not ...
15_12_13rw
... in alcohols (S—H bond is less polar than O—H). 2. Low molecular weight thiols have foul odors. 3. Thiols are stronger acids than alcohols. 4. Thiols are more easily oxidized than alcohols; ...
... in alcohols (S—H bond is less polar than O—H). 2. Low molecular weight thiols have foul odors. 3. Thiols are stronger acids than alcohols. 4. Thiols are more easily oxidized than alcohols; ...
Definition: the term “alkaloid” (alkali
... the exact nature of the aromatic or heterocyclic system in the new compound. (b) Infra‐red spectroscopy: ¾ In alkaloid chemistry, it is mainly used to ascertain the presence and sometimes the absence of particular functional group. ...
... the exact nature of the aromatic or heterocyclic system in the new compound. (b) Infra‐red spectroscopy: ¾ In alkaloid chemistry, it is mainly used to ascertain the presence and sometimes the absence of particular functional group. ...
Synthesis of Novel Steroid-Peptoid Hybrid Macrocycles by
... As depicted in Scheme 4 (top), an unidirectional Ugi-MiB approach can be implemented easily by utilizing the lithocholic acid derivative 17 functionalized with an amino group at C-3. This compound was readily prepared from methyl lithocholate according to reported procedures [13,24]. The 3α-OH is re ...
... As depicted in Scheme 4 (top), an unidirectional Ugi-MiB approach can be implemented easily by utilizing the lithocholic acid derivative 17 functionalized with an amino group at C-3. This compound was readily prepared from methyl lithocholate according to reported procedures [13,24]. The 3α-OH is re ...
Chapter 11: Sugars and Polysaccharides
... anomer : anomeric carbon OH is on the same side of the ring as the CH2OH of the chiral center defining D- or L- ...
... anomer : anomeric carbon OH is on the same side of the ring as the CH2OH of the chiral center defining D- or L- ...
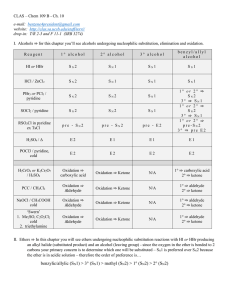
Chapter 10 - UCSB CLAS
... V. Amines ⇒ In this chapter you will see amines primarily acting as bases or nucleophiles – since the leaving group of amines are such a strong bases they cannot undergo substitution or elimination reactions VI. Quaternary ammonium hydroxides ⇒ In this chapter you will see quaternary ammonium hydrox ...
... V. Amines ⇒ In this chapter you will see amines primarily acting as bases or nucleophiles – since the leaving group of amines are such a strong bases they cannot undergo substitution or elimination reactions VI. Quaternary ammonium hydroxides ⇒ In this chapter you will see quaternary ammonium hydrox ...
5 organic chemistry: functional groups
... The longest chain contains the OOH group, which means the compound is named as a derivative of octane. Because it is an alcohol, it would be tempting to name it as an octanol. But it contains a CPC double bond, which means it must be an octenol. We now have to indicate that the OOH group is on one e ...
... The longest chain contains the OOH group, which means the compound is named as a derivative of octane. Because it is an alcohol, it would be tempting to name it as an octanol. But it contains a CPC double bond, which means it must be an octenol. We now have to indicate that the OOH group is on one e ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.