Chapter 3. The Concept of Protecting Functional Groups
... AcOH-THF, TsOH, Dowex-H (cation exchange resin) ...
... AcOH-THF, TsOH, Dowex-H (cation exchange resin) ...
Carboxylic Acid Questions 1.-Arrange the following in order of (i
... LiAlH4 is a source of H- (a nucleophile) which functions as a reducing agent. ...
... LiAlH4 is a source of H- (a nucleophile) which functions as a reducing agent. ...
11 - DR CLEM KUEK
... 1-chloropropane can be prepared by reacting propane with chlorine. The substitution reaction of propane is preferable to an addition reaction of propene because the addition of HCl to propene will result in the formation of unwanted 2-chloropropane. ...
... 1-chloropropane can be prepared by reacting propane with chlorine. The substitution reaction of propane is preferable to an addition reaction of propene because the addition of HCl to propene will result in the formation of unwanted 2-chloropropane. ...
A-level Paper 2 Practice Paper 1 - A
... U and V are other isomers of P, Q, R, S and T. The 1H n.m.r. spectrum of U consists of two singlets. V is a cyclic alcohol that exists as optical isomers. Draw the structure of U and the structure of V. ...
... U and V are other isomers of P, Q, R, S and T. The 1H n.m.r. spectrum of U consists of two singlets. V is a cyclic alcohol that exists as optical isomers. Draw the structure of U and the structure of V. ...
C h e m g u i d e ... ALCOHOLS: REPLACING THE -OH GROUP BY A HALOGEN
... 1. a) Describe what you would see if you added a small amount of phosphorus(V) chloride to an alcohol. b) This can only be used as a test for an alcohol if you first eliminate other compounds which also contain an -OH group. Give two completely different examples of something which would react with ...
... 1. a) Describe what you would see if you added a small amount of phosphorus(V) chloride to an alcohol. b) This can only be used as a test for an alcohol if you first eliminate other compounds which also contain an -OH group. Give two completely different examples of something which would react with ...
Final Exam, Chem 111 2012 Study Guide (labs)
... a. Explain the origin of steric repulsion, with examples (e.g., eclipsed vs staggered) b. Explain how to tell when two structures are different conformations of the same molecule, vs when they are different constitutional isomers. c. Draw distinct constitutional isomers for given alkanes and alkenes ...
... a. Explain the origin of steric repulsion, with examples (e.g., eclipsed vs staggered) b. Explain how to tell when two structures are different conformations of the same molecule, vs when they are different constitutional isomers. c. Draw distinct constitutional isomers for given alkanes and alkenes ...
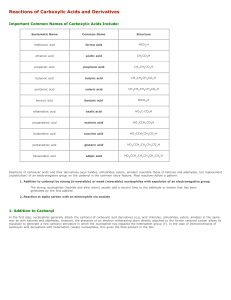
Reactions of Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives
... In the first step, nucleophiles generally attack the carbonyl of carboxylic acid derivatives (e.g. acid chlorides, anhydrides, esters, amides) in the same way as with ketones and aldehydes. However, the presence of an electron withdrawing atom directly attached to the former carbonyl carbon allows i ...
... In the first step, nucleophiles generally attack the carbonyl of carboxylic acid derivatives (e.g. acid chlorides, anhydrides, esters, amides) in the same way as with ketones and aldehydes. However, the presence of an electron withdrawing atom directly attached to the former carbonyl carbon allows i ...
Homework Set #1
... D-2-deoxyribose is found in DNA. Draw the structure. Deoxyribose and ribose form esters with phosphoric acid in DNA and RNA. Can both monosaccharides react to form the same number of ester combinations? Show the reactive sites for esterfication. CH2OH O ...
... D-2-deoxyribose is found in DNA. Draw the structure. Deoxyribose and ribose form esters with phosphoric acid in DNA and RNA. Can both monosaccharides react to form the same number of ester combinations? Show the reactive sites for esterfication. CH2OH O ...
SYNOPSIS OF CHEMISTRY
... 3. Acid-base reactions à la Brønsted. Conjugate pairs. 4. Autoprotolysis. Ampholytes. 5. Lewis acids and bases.Protons and electron-pairs. Acid-base reactions without protons. 6. Dissociation of water. Ion product of water. 7. pH. pH scale. pH indicators. Тitration. 8. Oxidation-reduction reaction. ...
... 3. Acid-base reactions à la Brønsted. Conjugate pairs. 4. Autoprotolysis. Ampholytes. 5. Lewis acids and bases.Protons and electron-pairs. Acid-base reactions without protons. 6. Dissociation of water. Ion product of water. 7. pH. pH scale. pH indicators. Тitration. 8. Oxidation-reduction reaction. ...
NCEA Level 2 Chemistry (91165) 2012 Assessment Schedule
... links between the structure, functional groups and the chemical properties of selected organic compounds. This requires the consistent use of chemistry vocabulary, symbols and conventions. ...
... links between the structure, functional groups and the chemical properties of selected organic compounds. This requires the consistent use of chemistry vocabulary, symbols and conventions. ...
NCEA Level 2 Chemistry (91165) 2012
... links between the structure, functional groups and the chemical properties of selected organic compounds. This requires the consistent use of chemistry vocabulary, symbols and conventions. ...
... links between the structure, functional groups and the chemical properties of selected organic compounds. This requires the consistent use of chemistry vocabulary, symbols and conventions. ...
Subject Description Form
... Upon completion of the subject, students will be able to: 1. understand the properties and reactivity of important functional groups including aromatic compounds, alcohols, amines, and carbonyl compounds; 2. be able to recognize important spectroscopic signatures of aromatic compounds, alcohols, ami ...
... Upon completion of the subject, students will be able to: 1. understand the properties and reactivity of important functional groups including aromatic compounds, alcohols, amines, and carbonyl compounds; 2. be able to recognize important spectroscopic signatures of aromatic compounds, alcohols, ami ...
formic (methanoic) acid
... The most important acyl transfer agent in living organisms is acetyl coenzyme A. This compound is the ester of acetic acid and coenzyme A, a thiol. ...
... The most important acyl transfer agent in living organisms is acetyl coenzyme A. This compound is the ester of acetic acid and coenzyme A, a thiol. ...
File
... Write a structural formula equation for the preparation of but-2-ene from 2-chlorobutane, in the presence of a strong base. ...
... Write a structural formula equation for the preparation of but-2-ene from 2-chlorobutane, in the presence of a strong base. ...
The Liver cont…..
... • Transamination (or aminotransfer) is the reaction between an amino acid and an alphaketo acid. • The amino group is transferred from the former to the latter; this results in the amino acid being converted to the corresponding α-keto acid, while the reactant α-keto acid is converted to the corresp ...
... • Transamination (or aminotransfer) is the reaction between an amino acid and an alphaketo acid. • The amino group is transferred from the former to the latter; this results in the amino acid being converted to the corresponding α-keto acid, while the reactant α-keto acid is converted to the corresp ...
Discuss on Reactions of Alcohols
... Carboxylic acid formation. Upon oxidation with strong oxidizing agents and high temperatures, primary alcohols completely oxidize to form carboxylic acids. The common oxidizing agents used for these conversions are concentrated potassium permanganate or concentrated potassium dichromate. Following ...
... Carboxylic acid formation. Upon oxidation with strong oxidizing agents and high temperatures, primary alcohols completely oxidize to form carboxylic acids. The common oxidizing agents used for these conversions are concentrated potassium permanganate or concentrated potassium dichromate. Following ...
Organic Reactions Worksheet
... ii Gives aldehyde after mild heat and distilling immediately; gives carboxylic acid after refluxing with excess oxidising agent. iii aldehydes; then carboxylic acids iv e.g. CH3CH2OH + [O] → CH3CHO + H2O e.g. CH3CH2OH + 2[O] → CH3COOH + H2O c i displayed formula with >C=O group (ketone) ii ketones i ...
... ii Gives aldehyde after mild heat and distilling immediately; gives carboxylic acid after refluxing with excess oxidising agent. iii aldehydes; then carboxylic acids iv e.g. CH3CH2OH + [O] → CH3CHO + H2O e.g. CH3CH2OH + 2[O] → CH3COOH + H2O c i displayed formula with >C=O group (ketone) ii ketones i ...
Diol Oxidation Handout
... Diol Oxidation Puzzle Introduction: In this experiment, you will use household bleach, a mild oxidizing agent, to oxidize a diol containing compound. You may either use 2-ethyl-1,3-hexanediol or 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol for your reaction. HO ...
... Diol Oxidation Puzzle Introduction: In this experiment, you will use household bleach, a mild oxidizing agent, to oxidize a diol containing compound. You may either use 2-ethyl-1,3-hexanediol or 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol for your reaction. HO ...
Chemistry - NTU.edu - Nanyang Technological University
... (a) Ease of hydrolysis compared with alkyl and aryl chlorides (b) Reaction with alcohols, phenols and primary amines ...
... (a) Ease of hydrolysis compared with alkyl and aryl chlorides (b) Reaction with alcohols, phenols and primary amines ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.