11. Oxidation of alcohols, hydrolysis of halogenoalkanes and
... nucleophile, electrophile or free radical. (3 marks) species ...
... nucleophile, electrophile or free radical. (3 marks) species ...
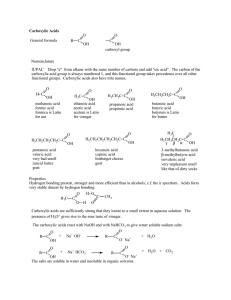
Naming the Carboxylic Acids
... polarized molecules such as water, alcohols and other carboxylic acids. Carboxylic acids up to butanoic acid are completely soluble in water. As neat liquids, and even in fairly dilute solutions, carboxylic acids form hydrogenbonded dimers (6–8 kcal mol-1). ...
... polarized molecules such as water, alcohols and other carboxylic acids. Carboxylic acids up to butanoic acid are completely soluble in water. As neat liquids, and even in fairly dilute solutions, carboxylic acids form hydrogenbonded dimers (6–8 kcal mol-1). ...
Study Guide for Exam 4 Chapter 17
... intermolecular forces determine their relative boiling points compared to other types of organic molecules, and their solubility in water. Complete chemical equations by writing structural formulas for products or reagents of reactions, or fill in the blanks where reagents or catalysts are needed ...
... intermolecular forces determine their relative boiling points compared to other types of organic molecules, and their solubility in water. Complete chemical equations by writing structural formulas for products or reagents of reactions, or fill in the blanks where reagents or catalysts are needed ...
Organic Reactions
... – Alcohol + oxidizing agent COOH (1, complete) /Aldehyde (1, partial)/Ketone (2) – Obviously an Oxidation reaction – Reaction condition: aqueous, acidic solution. The carboxylic acid and the aldehyde can be obtained through different experimental set-ups • Distill to get aldehyde • Heat under r ...
... – Alcohol + oxidizing agent COOH (1, complete) /Aldehyde (1, partial)/Ketone (2) – Obviously an Oxidation reaction – Reaction condition: aqueous, acidic solution. The carboxylic acid and the aldehyde can be obtained through different experimental set-ups • Distill to get aldehyde • Heat under r ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... ________ 21. Double-replacement reactions are generally driven by the formation of: a. a precipitate. c. water. b. a gaseous product. d. all of the above ________ 22. If butane (C4H10) undergoes complete combustion: a. 8 CO2 is one product. c. 9 O2 is one reactant. b. 8 CO is one product. d. 10 O2 i ...
... ________ 21. Double-replacement reactions are generally driven by the formation of: a. a precipitate. c. water. b. a gaseous product. d. all of the above ________ 22. If butane (C4H10) undergoes complete combustion: a. 8 CO2 is one product. c. 9 O2 is one reactant. b. 8 CO is one product. d. 10 O2 i ...
Organic Tutorial 1st Year MT03
... Peter Sykes,“A Guidebook to Mechanism in Organic Chemistry”, and Eames & Peach “Stereochemistry at a Glance”. Notes and Questions a) Summary on not more than 6 sides. This should outline the possible mechanisms and the evidence on which they are based, in particular the evidence for inversion during ...
... Peter Sykes,“A Guidebook to Mechanism in Organic Chemistry”, and Eames & Peach “Stereochemistry at a Glance”. Notes and Questions a) Summary on not more than 6 sides. This should outline the possible mechanisms and the evidence on which they are based, in particular the evidence for inversion during ...
Investigating Esters
... The reaction is reversible and the reaction proceeds very slowly towards an equilibrium. It is difficult to achieve 100% conversion and the yield of the ester will not be high. It may possible to improve the yield by changing the reaction conditions. The methods of changing the position of the equil ...
... The reaction is reversible and the reaction proceeds very slowly towards an equilibrium. It is difficult to achieve 100% conversion and the yield of the ester will not be high. It may possible to improve the yield by changing the reaction conditions. The methods of changing the position of the equil ...
Investigating Esters
... The reaction is reversible and the reaction proceeds very slowly towards an equilibrium. It is difficult to achieve 100% conversion and the yield of the ester will not be high. It may possible to improve the yield by changing the reaction conditions. The methods of changing the position of the equil ...
... The reaction is reversible and the reaction proceeds very slowly towards an equilibrium. It is difficult to achieve 100% conversion and the yield of the ester will not be high. It may possible to improve the yield by changing the reaction conditions. The methods of changing the position of the equil ...
1-14 Amines Amides
... IUPAC Names for Secondary and Tertiary Amines It is also possible to name secondary and tertiary amines (like those shown above) using the IUPAC method. To do that, you need to know one additional aspect of the IUPAC methodology. That is using the letter N to show the location of an alkyl group tha ...
... IUPAC Names for Secondary and Tertiary Amines It is also possible to name secondary and tertiary amines (like those shown above) using the IUPAC method. To do that, you need to know one additional aspect of the IUPAC methodology. That is using the letter N to show the location of an alkyl group tha ...
Preparation of alkyl halides There are lots of ways to make alkyl
... group. There are two main types of substitution reactions, called SN1 and SN2 reactions. We will discuss the mechanisms of those reactions in detail next class. The overall substitution reaction is shown below: ...
... group. There are two main types of substitution reactions, called SN1 and SN2 reactions. We will discuss the mechanisms of those reactions in detail next class. The overall substitution reaction is shown below: ...
Exam 2 - Wake Forest University
... Do not open or begin this exam until instructed. This exam consists of 5 pages plus the cover page. Before starting the exam, check to make sure that you have all of the pages. The exam has a total of 100 points and includes 13 questions. Only legible answers written on the exam will be considered f ...
... Do not open or begin this exam until instructed. This exam consists of 5 pages plus the cover page. Before starting the exam, check to make sure that you have all of the pages. The exam has a total of 100 points and includes 13 questions. Only legible answers written on the exam will be considered f ...
Theory
... carboxylic acid with long aliphatic chain, polarity of O-H bond in carboxylic group is lowered (electrons are moved from this chain towards COOH – positive inductive effect) and proton is not so “keen” to be dissociated – the acid is weak. Formic acid is thus the strongest unsubstituted monocarboxyl ...
... carboxylic acid with long aliphatic chain, polarity of O-H bond in carboxylic group is lowered (electrons are moved from this chain towards COOH – positive inductive effect) and proton is not so “keen” to be dissociated – the acid is weak. Formic acid is thus the strongest unsubstituted monocarboxyl ...
Properties of amines
... Amines are compounds based on an ammonia molecule (NH3), where one or more of the hydrogen atoms is replaced by a carbon chain. Thus R—NH2 is a primary amine, while R—NH—R’ is a secondary amine, and R—N(R’)—R’’ is a tertiary amine. You will only be asked to name primary amines. Note that 2-aminopro ...
... Amines are compounds based on an ammonia molecule (NH3), where one or more of the hydrogen atoms is replaced by a carbon chain. Thus R—NH2 is a primary amine, while R—NH—R’ is a secondary amine, and R—N(R’)—R’’ is a tertiary amine. You will only be asked to name primary amines. Note that 2-aminopro ...
Origins of Life - Yale University
... sediments on the floor of the world’s oceans. How these deposits were formed is a mystery. But what is important is their size. It is estimated that the global methane hydrate deposits contain approximately 1013 tons of carbon, or about twice the combined amount in all reserves of coal, oil, and con ...
... sediments on the floor of the world’s oceans. How these deposits were formed is a mystery. But what is important is their size. It is estimated that the global methane hydrate deposits contain approximately 1013 tons of carbon, or about twice the combined amount in all reserves of coal, oil, and con ...
l - CMatthews
... b) According to these results, what would be the initial rate (in mol/(L·s)) if all three concentrations are: [BrO3-]=[Br-]=[H+]=0.20 mol/L? c) State the overall order of the reaction 8. Sketch a potential energy diagram for a system in which Ea = + 50kJ, and H= 20 kJ. Label the axes, reactants, pr ...
... b) According to these results, what would be the initial rate (in mol/(L·s)) if all three concentrations are: [BrO3-]=[Br-]=[H+]=0.20 mol/L? c) State the overall order of the reaction 8. Sketch a potential energy diagram for a system in which Ea = + 50kJ, and H= 20 kJ. Label the axes, reactants, pr ...
Semester 2 Review
... UNIT 11 – REACTION RATES 49. List the factors that affect the RATE of a chemical reaction. Tell HOW they affect the rate. ...
... UNIT 11 – REACTION RATES 49. List the factors that affect the RATE of a chemical reaction. Tell HOW they affect the rate. ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.