CH402 Asymmetric catalytic reactions Prof M. Wills
... Asymmetric catalysis – Enolate alkylation The reaction proceeds via a complex in which the catalyst and the enolate are bound by a hydrogen bond (at least, that's the theory): Cl ...
... Asymmetric catalysis – Enolate alkylation The reaction proceeds via a complex in which the catalyst and the enolate are bound by a hydrogen bond (at least, that's the theory): Cl ...
Knowing that lipids
... Water is polar and oil is non-polar and hydrophobic. Thus, water cannot form intermolecular bonds with the oil but it forms hydrogen bonds with itself forming a separation. Two oils mixed together don’t form any bonds so they don’t need to separate. Like dissolves like. ...
... Water is polar and oil is non-polar and hydrophobic. Thus, water cannot form intermolecular bonds with the oil but it forms hydrogen bonds with itself forming a separation. Two oils mixed together don’t form any bonds so they don’t need to separate. Like dissolves like. ...
carboxylic acid
... Recall and explain the physical properties of carboxylic acids Recall the structures of carboxylic acids, esters and acyl chlorides Recall the acidic properties of carboxylic acids Recall and explain the esterification of carboxylic acids Write balanced equations representing any reactions in the se ...
... Recall and explain the physical properties of carboxylic acids Recall the structures of carboxylic acids, esters and acyl chlorides Recall the acidic properties of carboxylic acids Recall and explain the esterification of carboxylic acids Write balanced equations representing any reactions in the se ...
Chemistry 1 - Edexcel
... (ii) Carbon dioxide is used in some fire extinguishers. Explain why carbon dioxide is effective at extinguishing fires. ...
... (ii) Carbon dioxide is used in some fire extinguishers. Explain why carbon dioxide is effective at extinguishing fires. ...
Pop-Quiz Sit down quietly and draw the following structures.
... • Recall that structural isomers are molecules that share the same formula but differ in their atom-to-atom connectivities. • Carboxylic acids and esters that have a given number of carbon atoms form another example of functional group isomers: ...
... • Recall that structural isomers are molecules that share the same formula but differ in their atom-to-atom connectivities. • Carboxylic acids and esters that have a given number of carbon atoms form another example of functional group isomers: ...
2002
... As explained in the programme guide for B.Sc. Programme, you have to do 2 Assignments for this elective courses in Organic Chemistry. Both of these Assignments are Tutor Marked (TMAs). The blockwise distribution of assignments is as follows: ...
... As explained in the programme guide for B.Sc. Programme, you have to do 2 Assignments for this elective courses in Organic Chemistry. Both of these Assignments are Tutor Marked (TMAs). The blockwise distribution of assignments is as follows: ...
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
... layer is allowed to flow back into the reaction, while the lower layer of the distillate is removed via a stopcock. ...
... layer is allowed to flow back into the reaction, while the lower layer of the distillate is removed via a stopcock. ...
Study Guide Exam 2 and 3 Sp2011
... If you are trying to determine if an amine is a primary, secondary or tertiary, you now replace the C with the N and the OH with lone pair of electrons on the picture for alcohols. Depending on how many other carbon atoms are bound to the nitrogen determines if it is primary, secondary or tertiary. ...
... If you are trying to determine if an amine is a primary, secondary or tertiary, you now replace the C with the N and the OH with lone pair of electrons on the picture for alcohols. Depending on how many other carbon atoms are bound to the nitrogen determines if it is primary, secondary or tertiary. ...
Phenols Like alcohols, phenols are starting materials for a wide
... Like alcohols, phenols are starting materials for a wide range of compounds. The functional group is again OH but unlike alcohols, it is attached directly to a benzene ring and this affects its reactivity. Parent compound: OH phenol ...
... Like alcohols, phenols are starting materials for a wide range of compounds. The functional group is again OH but unlike alcohols, it is attached directly to a benzene ring and this affects its reactivity. Parent compound: OH phenol ...
reactions of functional groups of organic compounds with
... to gives so called Schiff’s bases (aldimine; exercise 1.2) The aldehyde group is present in the entire spectrum of biologically significant organic molecules (carbohydrates). To functional detection is used usually the Fehling test. Cupric tartrate in an alkaline solution reacts with the aldehyde to ...
... to gives so called Schiff’s bases (aldimine; exercise 1.2) The aldehyde group is present in the entire spectrum of biologically significant organic molecules (carbohydrates). To functional detection is used usually the Fehling test. Cupric tartrate in an alkaline solution reacts with the aldehyde to ...
Learning Check
... in the presence of water and heat. What will be the products of this reaction? To write the hydrolysis products, separate the compound at the ester bond. Complete the formula of the carboxylic acid by adding –OH (from water) to the carbonyl group and –H (from water) to the alcohol. ...
... in the presence of water and heat. What will be the products of this reaction? To write the hydrolysis products, separate the compound at the ester bond. Complete the formula of the carboxylic acid by adding –OH (from water) to the carbonyl group and –H (from water) to the alcohol. ...
Alcohols - Calderglen High School
... Peeled apples turn brown due to the reaction of compounds called phenols. The first two steps in the reaction of one phenol, A are; ...
... Peeled apples turn brown due to the reaction of compounds called phenols. The first two steps in the reaction of one phenol, A are; ...
Chapter 24 Organic Chemistry
... organic bases that react with water to produce ammonia. organic acids that react with water to produce ammonia. organic bases that react with acids to form ammonium salts. organic acids that react with bases to form ammonium salts. none of these. ...
... organic bases that react with water to produce ammonia. organic acids that react with water to produce ammonia. organic bases that react with acids to form ammonium salts. organic acids that react with bases to form ammonium salts. none of these. ...
ALDOL CONDENSATION
... In the first step of the mechanism, an α‐proton is removed by a strong base, resulting in the formation of an enolate anion, which is made relatively stable by the delocalization of electrons. ¾ Next, the carbonyl carbon of the (other) ester is nucleophilically attacked by the enolate anion. ...
... In the first step of the mechanism, an α‐proton is removed by a strong base, resulting in the formation of an enolate anion, which is made relatively stable by the delocalization of electrons. ¾ Next, the carbonyl carbon of the (other) ester is nucleophilically attacked by the enolate anion. ...
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
... NH3, primary (RNH2) and secondary amines (R2NH) • The reaction with tertiary amines (R3N) gives an unstable species that cannot be isolated • HCl is neutralized by the amine or an added base ...
... NH3, primary (RNH2) and secondary amines (R2NH) • The reaction with tertiary amines (R3N) gives an unstable species that cannot be isolated • HCl is neutralized by the amine or an added base ...
Exam 3 - Chemistry
... For SN2, stabilization of the transition state speeds the reaction. By the Hammond postulate the transition state ‘resembles’ the starting alkyl halide. Both of these are secondary. But since ...
... For SN2, stabilization of the transition state speeds the reaction. By the Hammond postulate the transition state ‘resembles’ the starting alkyl halide. Both of these are secondary. But since ...
22-2 Alcohols, Ethers, and Amines
... • Amines are of the form R-NH2. • Amines are considered primary, secondary, or tertiary depending on how many carbon chains have substituted for hydrogens in the NH3. • To Name amines, say the numbers of the –NH2 locations followed the root-word from the ...
... • Amines are of the form R-NH2. • Amines are considered primary, secondary, or tertiary depending on how many carbon chains have substituted for hydrogens in the NH3. • To Name amines, say the numbers of the –NH2 locations followed the root-word from the ...
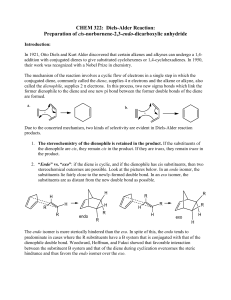
Diels-Alder Reaction:
... Even though s-trans conformation of dienes is more stable due to steric reasons, the s-cis conformation is needed to carry out the Diels-Alder reaction. The s-cis conformation of the diene would yield a six membered ring with a cis double bond whereas a diene in s-trans conformation would demand a t ...
... Even though s-trans conformation of dienes is more stable due to steric reasons, the s-cis conformation is needed to carry out the Diels-Alder reaction. The s-cis conformation of the diene would yield a six membered ring with a cis double bond whereas a diene in s-trans conformation would demand a t ...
CYSTEINE
... Has thiol group containing sulfur Molecular formula is C3H7NO2S Cysteine along with glycine and glutamic acid is found in all human tissues Can form into Cystine when exposed to air due to oxidation Stabilizes extracellular protein ...
... Has thiol group containing sulfur Molecular formula is C3H7NO2S Cysteine along with glycine and glutamic acid is found in all human tissues Can form into Cystine when exposed to air due to oxidation Stabilizes extracellular protein ...
Chapter 21: Carboxylic acid Derivatives I. Introduction
... The word anhydride literally means without water, and an acid anhydride is the combination of two molecules of carboxylic acid with the elimination of one molecule of water. ...
... The word anhydride literally means without water, and an acid anhydride is the combination of two molecules of carboxylic acid with the elimination of one molecule of water. ...
Amines By
... The Amines are the organic chemistry relatives of ammonia However in amines one or more of the hydrogen atoms on the ammonia molecule are replaced by alkyl chains Amines with one alkyl group are primary amines, with two they are secondary, and with three they are tertiary amines. Like ammoni ...
... The Amines are the organic chemistry relatives of ammonia However in amines one or more of the hydrogen atoms on the ammonia molecule are replaced by alkyl chains Amines with one alkyl group are primary amines, with two they are secondary, and with three they are tertiary amines. Like ammoni ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.