Lecture 10 Carbon-Nitrogen Bonds Formation I
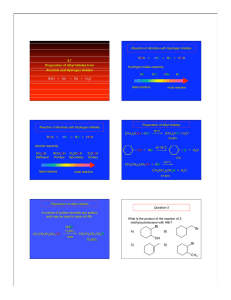
... Lecture 11 Carbon-Nitrogen Bonds Formation II 4.3.1.3 Robinson-Schopf Reaction Compounds that are enolic or potentially enolic react with a mixture of aldehydes and primary or secondary amine in the presence of an acid to afford amine salt which, after basification, gives an aminomethyl derivative. ...
... Lecture 11 Carbon-Nitrogen Bonds Formation II 4.3.1.3 Robinson-Schopf Reaction Compounds that are enolic or potentially enolic react with a mixture of aldehydes and primary or secondary amine in the presence of an acid to afford amine salt which, after basification, gives an aminomethyl derivative. ...
Ethers and Epoxides - faculty at Chemeketa
... with a base Thiolates react with primary or secondary alkyl halide to give sulfides (RSR’) Thiolates are excellent nucleophiles and react with ...
... with a base Thiolates react with primary or secondary alkyl halide to give sulfides (RSR’) Thiolates are excellent nucleophiles and react with ...
Chapter 18: Ethers and Epoxides
... with a base Thiolates react with primary or secondary alkyl halide to give sulfides (RSR’) Thiolates are excellent nucleophiles and react with ...
... with a base Thiolates react with primary or secondary alkyl halide to give sulfides (RSR’) Thiolates are excellent nucleophiles and react with ...
Ethers and Epoxides
... with a base Thiolates react with primary or secondary alkyl halide to give sulfides (RSR’) Thiolates are excellent nucleophiles and react with ...
... with a base Thiolates react with primary or secondary alkyl halide to give sulfides (RSR’) Thiolates are excellent nucleophiles and react with ...
101. Alcohols as alkylating agents in heteroarene C H functionalization
... well-understood biochemical process, it is underused by the synthetic organic chemistry community. We wondered whether it would be possible to take advantage of this naturally occurring process to accomplish mild, non-traditional alkylation reactions using alcohols as radical precursors. Because con ...
... well-understood biochemical process, it is underused by the synthetic organic chemistry community. We wondered whether it would be possible to take advantage of this naturally occurring process to accomplish mild, non-traditional alkylation reactions using alcohols as radical precursors. Because con ...
Catalytic asymmetric carbonyl addition reactions catalysed by group
... alkynes with aldehydes can be accomplished in the presence of a catalytic amount of the commercially available (+)-(neomenthyl)-diphenylphosphine 18 (NMDPP) to give trisubstituted allylic alcohols with excellent regioselectivity and in up to 96% ee. Variation of the alkyne substituents are tolerated ...
... alkynes with aldehydes can be accomplished in the presence of a catalytic amount of the commercially available (+)-(neomenthyl)-diphenylphosphine 18 (NMDPP) to give trisubstituted allylic alcohols with excellent regioselectivity and in up to 96% ee. Variation of the alkyne substituents are tolerated ...
Alkene-Addn-PartB-2012-ques
... character; more stable transition state (left) has positive charge on more highly substituted carbon ...
... character; more stable transition state (left) has positive charge on more highly substituted carbon ...
4.7 Preparation of Alkyl Halides from Alcohols and Hydrogen
... The product of this step is a carbocation. It is an intermediate in the overall process. ...
... The product of this step is a carbocation. It is an intermediate in the overall process. ...
Titania-catalysed oxidative dehydrogenation of ethyl lactate
... CeO2 and ZnO) as catalysts. The performance of all the catalysts were tested in a batch reactor, monitoring the consumption of ethyl lactate 1 and the production of ethyl pyruvate 2 (eqn (1)). In all cases no solvent was used and the catalyst : substrate ratio was kept constant at 100 : 1 w/w. Four ...
... CeO2 and ZnO) as catalysts. The performance of all the catalysts were tested in a batch reactor, monitoring the consumption of ethyl lactate 1 and the production of ethyl pyruvate 2 (eqn (1)). In all cases no solvent was used and the catalyst : substrate ratio was kept constant at 100 : 1 w/w. Four ...
View/Open
... product on hydrogenation. The results of such an experiment involving platinumcatalyzed hydrogenation of three butene isomers are shown in Fig. 7.2. All three isomers yield the same product—butane—but the heat of reaction is different in each case. On conversion to butane, 1-butene liberates the mos ...
... product on hydrogenation. The results of such an experiment involving platinumcatalyzed hydrogenation of three butene isomers are shown in Fig. 7.2. All three isomers yield the same product—butane—but the heat of reaction is different in each case. On conversion to butane, 1-butene liberates the mos ...
Dr.Farshid Zand Department of chemistry Organic Chem 233 L San
... Suitable derivatives for the purpose of identification are stable solids which melt between 50 – 250 °C, and which are readily prepared in good yields from unknowns to be identified. For the purpose of this course, the directions given here are taken form Shriner, Fuson and Curtin and modified for u ...
... Suitable derivatives for the purpose of identification are stable solids which melt between 50 – 250 °C, and which are readily prepared in good yields from unknowns to be identified. For the purpose of this course, the directions given here are taken form Shriner, Fuson and Curtin and modified for u ...
Topic 8 notes - A
... If haloalkanes are boiled with an ethanolic solution of KOH instead of with an aqueous solution, they will undergo elimination of an HX molecule to give an alkene: R1R2CHR3R4CBr + OH- R1R2C=CR3R4 + Br- + H2O NaOH is not used since it is only sparingly soluble in ethanol. This reaction works best i ...
... If haloalkanes are boiled with an ethanolic solution of KOH instead of with an aqueous solution, they will undergo elimination of an HX molecule to give an alkene: R1R2CHR3R4CBr + OH- R1R2C=CR3R4 + Br- + H2O NaOH is not used since it is only sparingly soluble in ethanol. This reaction works best i ...
Rapid and Efficient Functionalized Ionic Liquid-Catalyzed
... electron-withdrawing chloride and bromide groups) were chosen as the substrates. The results are listed in Table 3. It can be seen that the benzaldehyde, 2-chrolobenzaldehyde and 3-bromobenzaldehyde can undergo an aldol condensation process effectively, giving the corresponding product α,β-unsaturat ...
... electron-withdrawing chloride and bromide groups) were chosen as the substrates. The results are listed in Table 3. It can be seen that the benzaldehyde, 2-chrolobenzaldehyde and 3-bromobenzaldehyde can undergo an aldol condensation process effectively, giving the corresponding product α,β-unsaturat ...
Redox Reactions of NO and O in Iron Enzymes Mattias Blomberg
... acceptor, has fascinated the scientific community for decades. This process is often referred to as respiration, and the electron acceptor can be either O2 in aerobic conditions or nitric oxides in an anaerobic environment. Many of the mechanisms in these processes are still not fully understood. In ...
... acceptor, has fascinated the scientific community for decades. This process is often referred to as respiration, and the electron acceptor can be either O2 in aerobic conditions or nitric oxides in an anaerobic environment. Many of the mechanisms in these processes are still not fully understood. In ...
98 pts
... • (T) All E1 reactions involve formation of carbocations; • (T) More stable carbocations are generated faster; • (T) Carbocations are electrophiles; • (T) Carbocations are electron deficient; • (T) Free radicals are electron deficient; • (T) Alcohols are Brønsted bases; • (F) The rate-determining st ...
... • (T) All E1 reactions involve formation of carbocations; • (T) More stable carbocations are generated faster; • (T) Carbocations are electrophiles; • (T) Carbocations are electron deficient; • (T) Free radicals are electron deficient; • (T) Alcohols are Brønsted bases; • (F) The rate-determining st ...
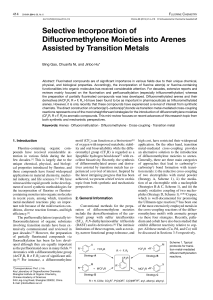
Selective Incorporation of Difluoromethylene
... double bond. In 2004, Sato et al. reinvestigated this reaction with bromodifluoroacetate [BrCF2CO2Et].[11b] For aryl iodide substrates, moderate yields were obtained after reaction in DMSO for hours at 55 oC. Hu and coworkers’ investigations on the copper-mediated reaction between aryl iodide and io ...
... double bond. In 2004, Sato et al. reinvestigated this reaction with bromodifluoroacetate [BrCF2CO2Et].[11b] For aryl iodide substrates, moderate yields were obtained after reaction in DMSO for hours at 55 oC. Hu and coworkers’ investigations on the copper-mediated reaction between aryl iodide and io ...
english,
... In incubation with cellobiose and glycosyl acceptors, almond b-glucosidase gave glucosides of primary and secondary alcohols with yields of 14.4–45.0 %, Table I. The obtained yields for monoterpene b-glucosides of geraniol and nerol were higher than previously reported.23,24 The reaction was carried ...
... In incubation with cellobiose and glycosyl acceptors, almond b-glucosidase gave glucosides of primary and secondary alcohols with yields of 14.4–45.0 %, Table I. The obtained yields for monoterpene b-glucosides of geraniol and nerol were higher than previously reported.23,24 The reaction was carried ...
Studies toward the Stereoselective Synthesis of the
... plays a pivotal role in this synthetic route as all 4 stereogenic centres present in the 3,7dimethylundecane-1,5,6-triol target are generated by this methodology at three different stages of the proposed synthesis. The epoxy alcohol formed at each stage was subjected to regioselective ring opening f ...
... plays a pivotal role in this synthetic route as all 4 stereogenic centres present in the 3,7dimethylundecane-1,5,6-triol target are generated by this methodology at three different stages of the proposed synthesis. The epoxy alcohol formed at each stage was subjected to regioselective ring opening f ...
Example of Lab Notebook
... to the theoretical value of 113–115oC. Although reasonably pure, the wider range and depressed values indicate the presence of impurities. Improper drying and removal of water could account for this result. In addition, incomplete washing the product during the filtration process could have allowed ...
... to the theoretical value of 113–115oC. Although reasonably pure, the wider range and depressed values indicate the presence of impurities. Improper drying and removal of water could account for this result. In addition, incomplete washing the product during the filtration process could have allowed ...
Organic Chemistry/Fourth Edition: e-Text
... Here we see an example of the Wittig reaction applied to diene synthesis by use of an ylide containing a carbon–carbon double bond. ...
... Here we see an example of the Wittig reaction applied to diene synthesis by use of an ylide containing a carbon–carbon double bond. ...
Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA 2006
... ne of the most fascinating catalytic reactions in biology is the reduction of dinitrogen to ammonia by various nitrogenases, the first and most studied being one whose core contains seven irons and one molybdenum (1–4). ‘‘Alternative’’ nitrogenases are now known, one that contains vanadium instead o ...
... ne of the most fascinating catalytic reactions in biology is the reduction of dinitrogen to ammonia by various nitrogenases, the first and most studied being one whose core contains seven irons and one molybdenum (1–4). ‘‘Alternative’’ nitrogenases are now known, one that contains vanadium instead o ...
Tunge - IARC Research
... enantioselectivity of the rearrangement of 1n with that of a standard asymmetric allylic alkylation using the palladium complex of Trost’s ligand 10 in both cases (Scheme 15). Since the allyl fragment is symmetrical, the same π-allyl complex is expected to form from either substrate. Stabilized nucl ...
... enantioselectivity of the rearrangement of 1n with that of a standard asymmetric allylic alkylation using the palladium complex of Trost’s ligand 10 in both cases (Scheme 15). Since the allyl fragment is symmetrical, the same π-allyl complex is expected to form from either substrate. Stabilized nucl ...
Wolff–Kishner reduction

The Wolff–Kishner reduction is a reaction used in organic chemistry to convert carbonyl functionalities into methylene groups. In the context of complex molecule synthesis, it is most frequently employed to remove a carbonyl group after it has served its synthetic purpose of activating an intermediate in a preceding step. As such, there is no obvious retron for this reaction. Originally reported by Nikolai Kischner in 1911 and Ludwig Wolff in 1912, it has been applied to the total synthesis of scopadulcic acid B, aspidospermidine and dysidiolide.In general, the reaction mechanism first involves the in situ generation of a hydrazone by condensation of hydrazine with the ketone or aldehyde substrate. Sometimes it is however advantageous to use a pre-formed hydrazone as substrate (see modifications). The hydrazone is deprotonated by alkoxide base followed by a concerted, rate-determining step in which a diimide anion is formed. Collapse of this alkyldiimde with loss of N2 leads to formation of an alkylanion which can be protonated by solvent to give the desired product.Because the Wolff–Kishner reduction requires highly basic conditions, it is unsuitable for base-sensitive substrates. However, this method can be superior over the related Clemmensen reduction for acid-sensitive compounds such as pyrroles and for high-molecular weight compounds.