
Welcome to Class 7
... keto groups and hydroxyl groups. In aqueous solutions, most monosaccharides occur as cyclic structures. They result from hemiacetal or hemiketal formation between aldehyde or keto groups and hydroxyl groups on the same molecule. The reaction is freely reversible. ...
... keto groups and hydroxyl groups. In aqueous solutions, most monosaccharides occur as cyclic structures. They result from hemiacetal or hemiketal formation between aldehyde or keto groups and hydroxyl groups on the same molecule. The reaction is freely reversible. ...
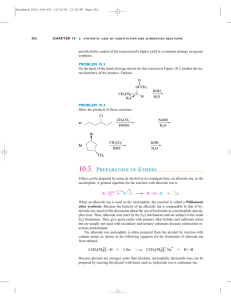
10.3 PREPARATION OF ETHERS
... alkyl sulfonate ester, by an SN2 mechanism, produces a substituted phthalimide with an alkyl group bonded to the nitrogen. The electrons on the nitrogen of this alkylated phthalimide are not nucleophilic, so there is no danger of multiple alkylation. The carbonyl groups are then removed to give the ...
... alkyl sulfonate ester, by an SN2 mechanism, produces a substituted phthalimide with an alkyl group bonded to the nitrogen. The electrons on the nitrogen of this alkylated phthalimide are not nucleophilic, so there is no danger of multiple alkylation. The carbonyl groups are then removed to give the ...
Ch 10- Alcohols and Ethers
... • Ethers have BP that are roughly comparable with alkanes of similar molecular weight • Alcohols on the other hand have much higher BP’s due to hydrogen bonding • Ethers can hydrogen bond with water, just not ...
... • Ethers have BP that are roughly comparable with alkanes of similar molecular weight • Alcohols on the other hand have much higher BP’s due to hydrogen bonding • Ethers can hydrogen bond with water, just not ...
base hydrolysis of cobalt(iii)
... observed experimentally. Finally, reference is made to Fig. 3 and the indication that the strongly nucelophilic reagents N 3 and NO2react with [Coen2Cl2 ]+ by an S N 2 mechanism. We repeated these studies in methanol solution and also added the reagent acetate ion. Our results(13) in buffered soluti ...
... observed experimentally. Finally, reference is made to Fig. 3 and the indication that the strongly nucelophilic reagents N 3 and NO2react with [Coen2Cl2 ]+ by an S N 2 mechanism. We repeated these studies in methanol solution and also added the reagent acetate ion. Our results(13) in buffered soluti ...
NaBH4 Reduction of Vanillin
... without consequence. It should also be noted that when using water as solvent, NaBH4 is relatively stable at pH 10 or higher. However, if a weakly acidic proton is present (i.e. a carboxylic acid or even a phenol), NaBH4 will react with the acid, which would thus destroy your reagent. The reducti ...
... without consequence. It should also be noted that when using water as solvent, NaBH4 is relatively stable at pH 10 or higher. However, if a weakly acidic proton is present (i.e. a carboxylic acid or even a phenol), NaBH4 will react with the acid, which would thus destroy your reagent. The reducti ...
Benzyne Mechanism
... Benzylic position is the most reactive. Chlorination is not as selective as bromination, results in mixtures. Br2 reacts only at the benzylic position. ...
... Benzylic position is the most reactive. Chlorination is not as selective as bromination, results in mixtures. Br2 reacts only at the benzylic position. ...
(a) Draw a primary, a secondary, and a tertiary alcohol for the
... When propan-1-ol reacts with HCl, a substitution reaction occurs; in this reaction the Cl from HCl replaces the –OH group from propan-1-ol, forming a haloalkane. The reaction between conc. H2SO4 / heat, and propan-1-ol is an elimination reaction because an –OH group attached to C1, and a hydrogen at ...
... When propan-1-ol reacts with HCl, a substitution reaction occurs; in this reaction the Cl from HCl replaces the –OH group from propan-1-ol, forming a haloalkane. The reaction between conc. H2SO4 / heat, and propan-1-ol is an elimination reaction because an –OH group attached to C1, and a hydrogen at ...
[1] Ans1.Dows-proc - Sacred Heart School Moga,Best ICSE School
... In contrast silver nitrate (AgNO2) is a covalent compound and hence do not have a –ve charge on the O atom. Instead both the O atoms and the N atoms carry lone pair of electrons. Since N is less electronegative than oxygen, therefore lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom is more easily availab ...
... In contrast silver nitrate (AgNO2) is a covalent compound and hence do not have a –ve charge on the O atom. Instead both the O atoms and the N atoms carry lone pair of electrons. Since N is less electronegative than oxygen, therefore lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom is more easily availab ...
Alcohols
... Aldehydes and ketones are polar molecules because of the polar carbon-oxygen double bond. Their boiling points are lower than alcohols of similar sizes because the do not form hydrogen bonds. They are more soluble in water then hydrocarbons. These compounds are soluble in both polar and nonp ...
... Aldehydes and ketones are polar molecules because of the polar carbon-oxygen double bond. Their boiling points are lower than alcohols of similar sizes because the do not form hydrogen bonds. They are more soluble in water then hydrocarbons. These compounds are soluble in both polar and nonp ...
Bk3BP08EE
... CH3CH2• radical which attacks a chlorine molecule to form chloroethane. The chloroethane formed may be attacked by another chlorine radical to form CH3CHCl• radical. The CH3CHCl• radical may further attack a chlorine molecule to form dichloroethane. The chain reaction continues to occur until hexach ...
... CH3CH2• radical which attacks a chlorine molecule to form chloroethane. The chloroethane formed may be attacked by another chlorine radical to form CH3CHCl• radical. The CH3CHCl• radical may further attack a chlorine molecule to form dichloroethane. The chain reaction continues to occur until hexach ...
Chapter 17: Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition to the
... • There will be two possible Wittig routes to an alkene. • Analyze the structure retrosynthetically, i.e., work the synthesis out backwards. • Disconnect (break the bond of the target that can be formed by a known reaction) the doubly bonded carbons. One becomes the aldehyde or ketone, the other th ...
... • There will be two possible Wittig routes to an alkene. • Analyze the structure retrosynthetically, i.e., work the synthesis out backwards. • Disconnect (break the bond of the target that can be formed by a known reaction) the doubly bonded carbons. One becomes the aldehyde or ketone, the other th ...
carbonyl group
... Hydrogen cyanide has no unshared electron pair on its carbon, so it cannot function as a carbon nucleophile. The base converts some of the hydrogen cyanide to cyanide ion (NC-), however, which then acts as a carbon nucleophile. ...
... Hydrogen cyanide has no unshared electron pair on its carbon, so it cannot function as a carbon nucleophile. The base converts some of the hydrogen cyanide to cyanide ion (NC-), however, which then acts as a carbon nucleophile. ...
Ch04-04-alkenes-2
... Exergonic reaction: early transition state resembles reactants (I). Endergonic reaction: late transition state resembles products (II). ...
... Exergonic reaction: early transition state resembles reactants (I). Endergonic reaction: late transition state resembles products (II). ...
Aldehydes and ketones
... • These names are taken from Latin roots as are the first 5 carboxylic acids • Greek letters are used to indicate the position of substituents with the carbon atom adjacent or bonded to the carbonyl carbon being the a carbon ...
... • These names are taken from Latin roots as are the first 5 carboxylic acids • Greek letters are used to indicate the position of substituents with the carbon atom adjacent or bonded to the carbonyl carbon being the a carbon ...
A Model for Catalytically Active Zinc(I1) Ion in Liver
... CloH24N4Zn(CF3S03)2: C, 25.56; H, 4.29; N, 9.94. Found: C, 25.53; H, 4.34; N , 9.97. Reactions of p -Nitrobenzaldehyde (9) with Alcohols Catalyzed by Various Zn" Species. p-Nitrobenzaldehyde (9,0.125 mmol) was added in one portion to a 1.0 mL alcohol solution of a Zn" catalyst (total [Zn"] = 1 mM). ...
... CloH24N4Zn(CF3S03)2: C, 25.56; H, 4.29; N, 9.94. Found: C, 25.53; H, 4.34; N , 9.97. Reactions of p -Nitrobenzaldehyde (9) with Alcohols Catalyzed by Various Zn" Species. p-Nitrobenzaldehyde (9,0.125 mmol) was added in one portion to a 1.0 mL alcohol solution of a Zn" catalyst (total [Zn"] = 1 mM). ...
CHAPTER 11 BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE:
... • Polymers are formed from combinations of monomers. • They can be classified many ways. –Thermoplastics can be heated and reformed again and again. –Thermosetting plastics are heated and formed, but cannot be heated and reformed because of their high degree of cross-linking. ...
... • Polymers are formed from combinations of monomers. • They can be classified many ways. –Thermoplastics can be heated and reformed again and again. –Thermosetting plastics are heated and formed, but cannot be heated and reformed because of their high degree of cross-linking. ...
2287 Summary
... Brominated Ketones.-The procedure for the preparation was that of Schmidt,6 according to which the ketone is brominated in glacial acetic acid. a-Bromo-n-va1erophenone.-As this substance has not previously been described in the literature, it may be mentioned that it is a straw-colored liquid boilin ...
... Brominated Ketones.-The procedure for the preparation was that of Schmidt,6 according to which the ketone is brominated in glacial acetic acid. a-Bromo-n-va1erophenone.-As this substance has not previously been described in the literature, it may be mentioned that it is a straw-colored liquid boilin ...
Organometallic Compounds - Savita Pall and Chemistry
... Since Mg lies to the left of carbon in the Periodic Table, carbon is the more significant electronegative atom. Thus, the Mg—C bond is largely covalent with a highly polar character, thus we get a dipole where the carbon (of the alkyl, R) has a slightly negative charge, whilst magnesium being the mo ...
... Since Mg lies to the left of carbon in the Periodic Table, carbon is the more significant electronegative atom. Thus, the Mg—C bond is largely covalent with a highly polar character, thus we get a dipole where the carbon (of the alkyl, R) has a slightly negative charge, whilst magnesium being the mo ...
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 13 – Alcohols (II)
... • Carbocations can undergo three types or reactions, as we have seen: o They can rearrange – if the structure allows it, secondary carbocations can undergo hydride shifts or methyl shifts to become more stable tertiary carbocations. These carbocations then undergo further reaction. o They can react ...
... • Carbocations can undergo three types or reactions, as we have seen: o They can rearrange – if the structure allows it, secondary carbocations can undergo hydride shifts or methyl shifts to become more stable tertiary carbocations. These carbocations then undergo further reaction. o They can react ...
Chapter 1 - chemistry
... Iron compounds are often used as catalysts for aromatic substitution reactions. ...
... Iron compounds are often used as catalysts for aromatic substitution reactions. ...
Alcohols
... • Ethanol reacts with sodium metal to form sodium ethoxide (NaOCH2CH3), a strong base commonly used for elimination reactions. • More hindered alcohols like 2-propanol or tert-butanol react faster with potassium than with sodium. ...
... • Ethanol reacts with sodium metal to form sodium ethoxide (NaOCH2CH3), a strong base commonly used for elimination reactions. • More hindered alcohols like 2-propanol or tert-butanol react faster with potassium than with sodium. ...
Aromatic electrophilic substitution
... positively charged carbon electrophile called an acylium ion, which is resonance stabilized. • The positively charged carbon atom of the acylium ion then goes on to react with benzene in the two step mechanism of electrophilic aromatic substitution. ...
... positively charged carbon electrophile called an acylium ion, which is resonance stabilized. • The positively charged carbon atom of the acylium ion then goes on to react with benzene in the two step mechanism of electrophilic aromatic substitution. ...
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement

The Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement (TDR) is the chemical reaction of a 1-aminomethyl-cycloalkanol with nitrous acid to form an enlarged cycloketone.The Tiffeneau–Demjanov ring expansion, Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement, or TDR, provides an easy way to increase amino-substituted cycloalkanes and cycloalkanols in size by one carbon. Ring sizes from cyclopropane through cyclooctane are able to undergo Tiffeneau–Demjanov ring expansion with some degree of success. Yields decrease as initial ring size increases, and the ideal use of TDR is for synthesis of five, six, and seven membered rings. A principal synthetic application of Tiffeneau–Demjanov ring expansion is to bicyclic or polycyclic systems. Several reviews on this reaction have been published.






![[1] Ans1.Dows-proc - Sacred Heart School Moga,Best ICSE School](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015878975_1-55791b331e05591620375059b6f74bac-300x300.png)















