98 pts
... • (T) All E1 reactions involve formation of carbocations; • (T) More stable carbocations are generated faster; • (T) Carbocations are electrophiles; • (T) Carbocations are electron deficient; • (T) Free radicals are electron deficient; • (T) Alcohols are Brønsted bases; • (F) The rate-determining st ...
... • (T) All E1 reactions involve formation of carbocations; • (T) More stable carbocations are generated faster; • (T) Carbocations are electrophiles; • (T) Carbocations are electron deficient; • (T) Free radicals are electron deficient; • (T) Alcohols are Brønsted bases; • (F) The rate-determining st ...
ch13[1].
... • Addition of carbon nucleophiles is one of the most important types of nucleophilic additions to a C=O group. • A new carbon-carbon bond is formed in the process. • We study addition of carbon nucleophiles called Grignard reagents. • Victor Grignard was awarded the Nobel Prize for chemistry in 1912 ...
... • Addition of carbon nucleophiles is one of the most important types of nucleophilic additions to a C=O group. • A new carbon-carbon bond is formed in the process. • We study addition of carbon nucleophiles called Grignard reagents. • Victor Grignard was awarded the Nobel Prize for chemistry in 1912 ...
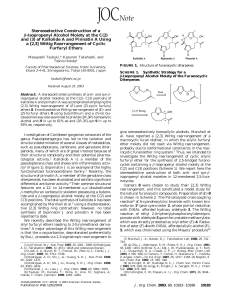
Stereoselective Construction of a β
... did not proceed in Et2O14 (entry 5). The rearrangement of (Z)-8 proceeded with relatively high diastereoselectivity (84-92%de) compared with that of (E)-8 (entries 8-10). Assignment of the relative stereochemistry of both anti- and syn-9 was based on 2D-NOE experiments15 and comparison of the 1H NMR ...
... did not proceed in Et2O14 (entry 5). The rearrangement of (Z)-8 proceeded with relatively high diastereoselectivity (84-92%de) compared with that of (E)-8 (entries 8-10). Assignment of the relative stereochemistry of both anti- and syn-9 was based on 2D-NOE experiments15 and comparison of the 1H NMR ...
Alcohols, phenols, thiols and ethers notes
... • Alkyl groups don’t always bond to the oxygen at the end carbon. • In these cases, name the ether using the largest alkyl group as the parent chain and the “alkoxy group” as a branch, using a number to identify which carbon is bonded to the oxygen ...
... • Alkyl groups don’t always bond to the oxygen at the end carbon. • In these cases, name the ether using the largest alkyl group as the parent chain and the “alkoxy group” as a branch, using a number to identify which carbon is bonded to the oxygen ...
Imine formation
... 6. Predict the products of these imine formations and aldol sdditions. How are they similar to each other? (Hint: Use the example strategy of identifying the nucleophile and electrophile and drawing the condensed product.) ...
... 6. Predict the products of these imine formations and aldol sdditions. How are they similar to each other? (Hint: Use the example strategy of identifying the nucleophile and electrophile and drawing the condensed product.) ...
A-level Chemistry Question paper Unit 04 - Kinetics, Equilibria
... – organise information clearly – use scientific terminology accurately. Advice l You are advised to spend about 75 minutes on Section A and about 30 minutes on Section B. ...
... – organise information clearly – use scientific terminology accurately. Advice l You are advised to spend about 75 minutes on Section A and about 30 minutes on Section B. ...
Grignard Reaction - OpenBU
... until your volume is approximately 6 mL. DO NOT LET YOUR REACTION GO DRY. After letting the reaction mixture stir for 30 minutes, nearly all of the magnesium should have disappeared, at which point you should cool the mixture to room temperature and proceed to the next step. Synthesis of a benzoic a ...
... until your volume is approximately 6 mL. DO NOT LET YOUR REACTION GO DRY. After letting the reaction mixture stir for 30 minutes, nearly all of the magnesium should have disappeared, at which point you should cool the mixture to room temperature and proceed to the next step. Synthesis of a benzoic a ...
Grignard Reaction - OpenBU
... until your volume is approximately 6 mL. DO NOT LET YOUR REACTION GO DRY. After letting the reaction mixture stir for 30 minutes, nearly all of the magnesium should have disappeared, at which point you should cool the mixture to room temperature and proceed to the next step. Synthesis of a benzoic a ...
... until your volume is approximately 6 mL. DO NOT LET YOUR REACTION GO DRY. After letting the reaction mixture stir for 30 minutes, nearly all of the magnesium should have disappeared, at which point you should cool the mixture to room temperature and proceed to the next step. Synthesis of a benzoic a ...
Grignard Reaction - Synthesis of Substituted Benzoic Acids
... until your volume is approximately 6 mL. DO NOT LET YOUR REACTION GO DRY. After letting the reaction mixture stir for 30 minutes, nearly all of the magnesium should have disappeared, at which point you should cool the mixture to room temperature and proceed to the next step. Synthesis of a benzoic a ...
... until your volume is approximately 6 mL. DO NOT LET YOUR REACTION GO DRY. After letting the reaction mixture stir for 30 minutes, nearly all of the magnesium should have disappeared, at which point you should cool the mixture to room temperature and proceed to the next step. Synthesis of a benzoic a ...
Reaction with hydrogen halides
... needed to increase the motion of the molecules and cause the alkane to melt or boil; the greater the viscosity and the greater the density. However, the effect of chain length decreases as the chains get longer. This is the case because in smaller molecules an additional carbon and its hydrogen caus ...
... needed to increase the motion of the molecules and cause the alkane to melt or boil; the greater the viscosity and the greater the density. However, the effect of chain length decreases as the chains get longer. This is the case because in smaller molecules an additional carbon and its hydrogen caus ...
Practice Exam 2
... a) there are no oxygen atoms to remove from the alcohol carbon. b) there are no hydrogen atoms attached to the alcohol carbon. c) the alcohol carbon is bonded to four groups so no oxygen can be added to it. d) the alcohol carbon is bonded to four groups so no hydrogen can be added to it. e) the alco ...
... a) there are no oxygen atoms to remove from the alcohol carbon. b) there are no hydrogen atoms attached to the alcohol carbon. c) the alcohol carbon is bonded to four groups so no oxygen can be added to it. d) the alcohol carbon is bonded to four groups so no hydrogen can be added to it. e) the alco ...
04_01_03.html
... Overview of Chapter This chapter introduces chemical reactions and their mechanisms by focusing on two reactions that yield alkyl halides. (1) alcohol + hydrogen halide ROH + HX RX + H2O (2) alkane + halogen RH + X2 RX + HX Both are substitution reactions ...
... Overview of Chapter This chapter introduces chemical reactions and their mechanisms by focusing on two reactions that yield alkyl halides. (1) alcohol + hydrogen halide ROH + HX RX + H2O (2) alkane + halogen RH + X2 RX + HX Both are substitution reactions ...
Reaction of Organometallic Reagents with Aldehydes and Ketones.
... • Nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic acyl substitution involve the same first step—nucleophilic attack on the electrophilic carbonyl carbon to form a tetrahedral intermediate. • The difference between the two reactions is what then happens to the intermediate. • Aldehydes and ketones cannot unde ...
... • Nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic acyl substitution involve the same first step—nucleophilic attack on the electrophilic carbonyl carbon to form a tetrahedral intermediate. • The difference between the two reactions is what then happens to the intermediate. • Aldehydes and ketones cannot unde ...
File
... Explain why tertiary alcohols cannot be oxidised in this way. Tertiary alcohols can not be oxidised because there are no hydrogens to be removed from the carbon that is bonded to the alcohol group. For oxidation to occur there must be hydrogen available to be removed from the carbon atom that is bon ...
... Explain why tertiary alcohols cannot be oxidised in this way. Tertiary alcohols can not be oxidised because there are no hydrogens to be removed from the carbon that is bonded to the alcohol group. For oxidation to occur there must be hydrogen available to be removed from the carbon atom that is bon ...
Porphyrin Complex - Center for Biomimetic Systems
... (7) 2 decayed back to an iron(III) porphyrin complex at a fast rate in the absence of H2O, but the decay of 2 became slower with the increase of H2O concentration in the reaction solutions. (8) The formation of an iron(III) porphyrin complex may be the result of a facile oxidation of an iron(II) por ...
... (7) 2 decayed back to an iron(III) porphyrin complex at a fast rate in the absence of H2O, but the decay of 2 became slower with the increase of H2O concentration in the reaction solutions. (8) The formation of an iron(III) porphyrin complex may be the result of a facile oxidation of an iron(II) por ...
Addition Reactions of Carbonyls Part 1
... conditions), there is a very important exception to this rule. Sugars are polyhydroxyketones or polyhydroxyaldehydes but the carbonyl group isn’t immediately obvious because an electrophilic addition reaction occurs in the presence of aqueous acid, forming a stable 5- or 6-atom ring. e.g. The polyhy ...
... conditions), there is a very important exception to this rule. Sugars are polyhydroxyketones or polyhydroxyaldehydes but the carbonyl group isn’t immediately obvious because an electrophilic addition reaction occurs in the presence of aqueous acid, forming a stable 5- or 6-atom ring. e.g. The polyhy ...
Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
... water. The reaction with R’ COCI is carried out in the presence of pyridine so as to neutralise HCI which is formed during the reaction. The introduction of acetyl (CH3CO-) group in phenols is known as acetylation. Acetylation of salicylic acid produces aspirin. ...
... water. The reaction with R’ COCI is carried out in the presence of pyridine so as to neutralise HCI which is formed during the reaction. The introduction of acetyl (CH3CO-) group in phenols is known as acetylation. Acetylation of salicylic acid produces aspirin. ...
Chapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions
... As in carbocations, more alkyl groups stabilize + character Ketone has more alkyl groups, stabilizing the C=O carbon ...
... As in carbocations, more alkyl groups stabilize + character Ketone has more alkyl groups, stabilizing the C=O carbon ...
Organic Chemistry Boardwork
... Further substitution in chain reactions Some chloromethane molecules formed during free radical substitution between methane and chlorine will undergo further substitution to form dichloromethane. Further substitution can occur until all hydrogens are substituted. ...
... Further substitution in chain reactions Some chloromethane molecules formed during free radical substitution between methane and chlorine will undergo further substitution to form dichloromethane. Further substitution can occur until all hydrogens are substituted. ...
10. Alkyl Halides
... alkenes to give Markovnikov product (see Alkenes chapter) Alkyl dihalide from anti addition of bromine or chlorine ...
... alkenes to give Markovnikov product (see Alkenes chapter) Alkyl dihalide from anti addition of bromine or chlorine ...
Organic chemistry and analysis
... As the electron pair moves around the ring, the negative charge only ever appears at the 2, 4 and 6 positions. This means that electrophiles are directed towards the 2, 4 and 6 positions. ...
... As the electron pair moves around the ring, the negative charge only ever appears at the 2, 4 and 6 positions. This means that electrophiles are directed towards the 2, 4 and 6 positions. ...
Links - American Chemical Society
... not altered by drying the esters with activity I alumina immediately prior to use. These observations combine to make an extremely simple and attractive protocol for ester reduction: simply mixing the reagents and monitoring the reaction by TLC, followed by hydrolysis and extraction, provides the de ...
... not altered by drying the esters with activity I alumina immediately prior to use. These observations combine to make an extremely simple and attractive protocol for ester reduction: simply mixing the reagents and monitoring the reaction by TLC, followed by hydrolysis and extraction, provides the de ...
An Oxidation-Reduction Scheme: Borneol, Camphor, Isoborneol1
... sodium borohydride NaBH4, are widely used in reducing carbonyl groups. Lithium aluminum hydride, for example, reduces many compounds containing carbonyl groups, such as aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, or amides, whereas sodium borohydride reduces only aldehydes and ketones. The reduced ...
... sodium borohydride NaBH4, are widely used in reducing carbonyl groups. Lithium aluminum hydride, for example, reduces many compounds containing carbonyl groups, such as aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, or amides, whereas sodium borohydride reduces only aldehydes and ketones. The reduced ...
Carbenes and Nitrenes: Structure, generaNon and reacNvity
... Then, N-‐heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs) already seen. The first applica4ons of thiazolydenes in umpolung organocatalysis were reported as early as 1943 (J. Pharm. Soc. Jpn. 1943, 63, 296) and metal complexes of NHC ...
... Then, N-‐heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs) already seen. The first applica4ons of thiazolydenes in umpolung organocatalysis were reported as early as 1943 (J. Pharm. Soc. Jpn. 1943, 63, 296) and metal complexes of NHC ...
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement

The Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement (TDR) is the chemical reaction of a 1-aminomethyl-cycloalkanol with nitrous acid to form an enlarged cycloketone.The Tiffeneau–Demjanov ring expansion, Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement, or TDR, provides an easy way to increase amino-substituted cycloalkanes and cycloalkanols in size by one carbon. Ring sizes from cyclopropane through cyclooctane are able to undergo Tiffeneau–Demjanov ring expansion with some degree of success. Yields decrease as initial ring size increases, and the ideal use of TDR is for synthesis of five, six, and seven membered rings. A principal synthetic application of Tiffeneau–Demjanov ring expansion is to bicyclic or polycyclic systems. Several reviews on this reaction have been published.
![ch13[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008194698_1-d188c504eac7b7806e762a2340484910-300x300.png)