Notes
... each functional group. These molecules contain more than one functional group. 1. Vanillin (a food flavouring) ...
... each functional group. These molecules contain more than one functional group. 1. Vanillin (a food flavouring) ...
chap 4 org chem
... Functional Groups Many organic molecules share similar properties because they have similar clusters of atoms: functional groups. Functional groups are added to a hydrocarbon chain Functional groups give the molecule a particular property, such as acidity or polarity. ...
... Functional Groups Many organic molecules share similar properties because they have similar clusters of atoms: functional groups. Functional groups are added to a hydrocarbon chain Functional groups give the molecule a particular property, such as acidity or polarity. ...
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Amides
... Fatty acids are derived from the coupling of acetic acid. Acetic acid is the primary building block for the biosynthesis of more naturally occurring compounds than any other single precursor substance. The substance 3-methyl-3-butenyl pyrophosphate is the crucial intermediate in the synthesis of ter ...
... Fatty acids are derived from the coupling of acetic acid. Acetic acid is the primary building block for the biosynthesis of more naturally occurring compounds than any other single precursor substance. The substance 3-methyl-3-butenyl pyrophosphate is the crucial intermediate in the synthesis of ter ...
Biochemistry Carbon Compounds
... Polar molecules are ______________, (“water-loving“) and are soluble in water. When found on a simple carbon-based molecule, a hydroxyl group makes that molecule into an “alcohol.” There are many kinds of alcohols. One common alcohol is called ethanol, and this is the molecule found in alcoholic bev ...
... Polar molecules are ______________, (“water-loving“) and are soluble in water. When found on a simple carbon-based molecule, a hydroxyl group makes that molecule into an “alcohol.” There are many kinds of alcohols. One common alcohol is called ethanol, and this is the molecule found in alcoholic bev ...
Polymerization
... i. In other words, molecules with 2 functional groups can grow from both ends instead of just one end as in polyethylene. c. Formation of nylon – i. Hexanedioic acid (2 carboxylic acid groups) and 1,6 diaminohexane (2 amine groups) O HO OH ...
... i. In other words, molecules with 2 functional groups can grow from both ends instead of just one end as in polyethylene. c. Formation of nylon – i. Hexanedioic acid (2 carboxylic acid groups) and 1,6 diaminohexane (2 amine groups) O HO OH ...
How to study organic chemistry?
... Effect of H-Bond on acidity,basicity,B.P. Order,H-Bonding during tautomerism. ...
... Effect of H-Bond on acidity,basicity,B.P. Order,H-Bonding during tautomerism. ...
Acetaldehyde - Special Hoperations
... An organic compound. An aldehyde. Many fragrances are aldehydes and acetaldehyde is manufactured for the production of perfumes as well as being a precursor to acetic acid (vinegar). It is found widely in nature in breads, fruits, coffee and a part of normal plant metabolism. Fermentation by brewer’ ...
... An organic compound. An aldehyde. Many fragrances are aldehydes and acetaldehyde is manufactured for the production of perfumes as well as being a precursor to acetic acid (vinegar). It is found widely in nature in breads, fruits, coffee and a part of normal plant metabolism. Fermentation by brewer’ ...
carboxylic acids esters amides (R
... Cyclic anhydrides have use in organic chemistry; e.g. in Diels-Alder reactions. Again, the most commonly used anhydride is acetic anhydride. This reagent can be used to acetylate functional groups such as alcohols and amines. Acetylation can modify both the chemistry and biological activity of a com ...
... Cyclic anhydrides have use in organic chemistry; e.g. in Diels-Alder reactions. Again, the most commonly used anhydride is acetic anhydride. This reagent can be used to acetylate functional groups such as alcohols and amines. Acetylation can modify both the chemistry and biological activity of a com ...
Slide 1
... • Phenols are weak acids and react with NaOH and other strong bases to form water-soluble salts. OH + NaOH Phenol ...
... • Phenols are weak acids and react with NaOH and other strong bases to form water-soluble salts. OH + NaOH Phenol ...
Ethers and Epoxides
... Aldehydes and Ketones • Aldehydes and ketones are characterized by the the carbonyl functional group (C=O) • The compounds occur widely in nature as intermediates in metabolism and biosynthesis • They are also common as chemicals, as solvents, monomers, adhesives, agrichemicals and ...
... Aldehydes and Ketones • Aldehydes and ketones are characterized by the the carbonyl functional group (C=O) • The compounds occur widely in nature as intermediates in metabolism and biosynthesis • They are also common as chemicals, as solvents, monomers, adhesives, agrichemicals and ...
List of structures required at the exam of Medical Chemistry and
... coenzyme Q, biotin, FAD/FMN, THP, lipoic acid, TPP key functional groups and their reactions (e.g., reduction/oxidation, group transfer...) precursors and degradation products of complex citric acid cycle, glycolysis, pentose phosphate pathway (up to compounds (e.g. heme, nucleotides, ...), conversi ...
... coenzyme Q, biotin, FAD/FMN, THP, lipoic acid, TPP key functional groups and their reactions (e.g., reduction/oxidation, group transfer...) precursors and degradation products of complex citric acid cycle, glycolysis, pentose phosphate pathway (up to compounds (e.g. heme, nucleotides, ...), conversi ...
Chapter 14 – Organic Chemistry
... NOTE: When there are many carbon atoms, the nonpolar carbon atoms become more important and the molecule does not dissolve as well in water B. Hydrocarbons are nonpolar and do not dissolve in water ...
... NOTE: When there are many carbon atoms, the nonpolar carbon atoms become more important and the molecule does not dissolve as well in water B. Hydrocarbons are nonpolar and do not dissolve in water ...
The presence of an aromatic ring or other
... part of organic chemistry. Although it is often possible to establish the structure of a compound on the basis of spectra alone (IR, NMR, etc.), the spectra typically must be supplemented with other information about the compound: physical state and properties (melting point, boiling point, solubili ...
... part of organic chemistry. Although it is often possible to establish the structure of a compound on the basis of spectra alone (IR, NMR, etc.), the spectra typically must be supplemented with other information about the compound: physical state and properties (melting point, boiling point, solubili ...
Organic Chemistry: Functional Groups and Nutrients Objectives
... compounds; alkanes, alkenes and alkynes. We have mentioned that compounds that share similar features also share similar properties. There are many more. Many of these have substituted groups that produce these properties. These substituted groups are called functional groups. One of these functiona ...
... compounds; alkanes, alkenes and alkynes. We have mentioned that compounds that share similar features also share similar properties. There are many more. Many of these have substituted groups that produce these properties. These substituted groups are called functional groups. One of these functiona ...
EXPERIMENT 13
... 4. Set up your apparatus as shown on the left image. 8. Carefully separate the liquid in the flask after decanting it for 5 days. 5. Place the mixture in the Erlenmeyer flask. 9.Transfer the obtained liquid to a a new erlenmeyer flask and then add 2-3 6. Then place some lime water in a test tube. pi ...
... 4. Set up your apparatus as shown on the left image. 8. Carefully separate the liquid in the flask after decanting it for 5 days. 5. Place the mixture in the Erlenmeyer flask. 9.Transfer the obtained liquid to a a new erlenmeyer flask and then add 2-3 6. Then place some lime water in a test tube. pi ...
phenol
... tertiary (3'), depending on the number of carbon atoms bonded to the carbon atom that bears the hydroxyl group. А primary alcohol is an alcohol in which the hydroxyl-bearing carbon atom is attached to only one other carbon atom. А secondary alcohol is an alcohol in which the hydroxylbearing carbon a ...
... tertiary (3'), depending on the number of carbon atoms bonded to the carbon atom that bears the hydroxyl group. А primary alcohol is an alcohol in which the hydroxyl-bearing carbon atom is attached to only one other carbon atom. А secondary alcohol is an alcohol in which the hydroxylbearing carbon a ...
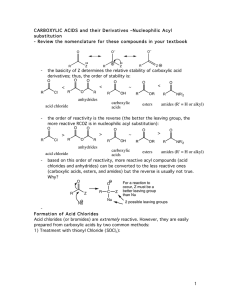
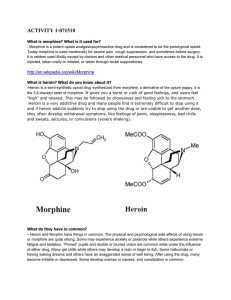
activity 1-071510 - ids
... heroin addiction are deadly diseases that require medical treatment. ...
... heroin addiction are deadly diseases that require medical treatment. ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.