Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids
... The best reagent for converting carboxylic acids to acid chlorides are thionyl chloride (SOCl2) and oxalyl chloride (COCl2) because they form gaseous by-products that do not contaminate the product. Thionyl chloride reaction produces SO2 while the oxalyl chloride reaction produces HCl, CO, and CO2 ( ...
... The best reagent for converting carboxylic acids to acid chlorides are thionyl chloride (SOCl2) and oxalyl chloride (COCl2) because they form gaseous by-products that do not contaminate the product. Thionyl chloride reaction produces SO2 while the oxalyl chloride reaction produces HCl, CO, and CO2 ( ...
4. Reactions of Alcohols and Thiols
... Oxidation and Reduction In the oxidation of an organic compound, there is an increase in the number of C—O bonds there is a loss of H In the reduction of an organic compound, there is an decrease in the number of C—O ...
... Oxidation and Reduction In the oxidation of an organic compound, there is an increase in the number of C—O bonds there is a loss of H In the reduction of an organic compound, there is an decrease in the number of C—O ...
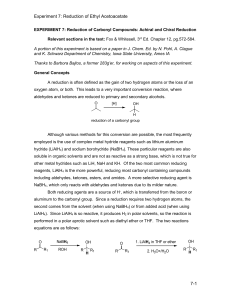
Experiment 7-Reduction
... A reduction is often defined as the gain of two hydrogen atoms or the loss of an oxygen atom, or both. This leads to a very important conversion reaction, where aldehydes and ketones are reduced to primary and secondary alcohols. O ...
... A reduction is often defined as the gain of two hydrogen atoms or the loss of an oxygen atom, or both. This leads to a very important conversion reaction, where aldehydes and ketones are reduced to primary and secondary alcohols. O ...
Reduction of Camphor to Borneol
... showing the expected stereochemistry of the products. Label the products as having been formed from exo approach or endo approach. 2. How might the geometry of the product change (OH in an endo or exo position?) if all the methyl groups of camphor were replaced with H? 3. The reduction mechanism is ...
... showing the expected stereochemistry of the products. Label the products as having been formed from exo approach or endo approach. 2. How might the geometry of the product change (OH in an endo or exo position?) if all the methyl groups of camphor were replaced with H? 3. The reduction mechanism is ...
Exercise 1
... issues; a plant like switchgrass, which is not used for food, may provide an alternate source of ethanol. Of course, one of the reasons switchgrass is not used for food is that its cellulose is made of arabinose units, rather than glucose units. The fermentation bacteria typically do not process ara ...
... issues; a plant like switchgrass, which is not used for food, may provide an alternate source of ethanol. Of course, one of the reasons switchgrass is not used for food is that its cellulose is made of arabinose units, rather than glucose units. The fermentation bacteria typically do not process ara ...
Organic chemistry
... The chemistry course comprises organic, inorganic and physical chemistry courses. The general courses provide an overview of the atomic structure, past and present. The electron configuration of the elements and their position in the periodic table are elaborated. The course sets major concepts in c ...
... The chemistry course comprises organic, inorganic and physical chemistry courses. The general courses provide an overview of the atomic structure, past and present. The electron configuration of the elements and their position in the periodic table are elaborated. The course sets major concepts in c ...
Organic Chemistry - Rutgers University, Newark
... to (R)-2-octyl acetate Step 1: formation of a p-toluenesulfonate (Ts) ester OTs ...
... to (R)-2-octyl acetate Step 1: formation of a p-toluenesulfonate (Ts) ester OTs ...
20.4 Acid-Base Properties of Carboxylic Acids
... 1) You have a mixture of naphthalene and benzoic acid that you wish to separate. How might you take advantage of the acidity of one component in the mixture to accomplish the ...
... 1) You have a mixture of naphthalene and benzoic acid that you wish to separate. How might you take advantage of the acidity of one component in the mixture to accomplish the ...
Chapter #2 - FIU Faculty Websites
... With two or more carbons, multiple bonds are possible z Alkenes contain one or more carbon-carbon double bonds z Alkynes contain one or more carbon-carbon triple bonds z Aromatic hydrocarbons contain benzene-like stable structures ...
... With two or more carbons, multiple bonds are possible z Alkenes contain one or more carbon-carbon double bonds z Alkynes contain one or more carbon-carbon triple bonds z Aromatic hydrocarbons contain benzene-like stable structures ...
Amines - Chemistry Geek
... with one or more of the hydrogens replaced with a substituent such as an alkyl group. ...
... with one or more of the hydrogens replaced with a substituent such as an alkyl group. ...
File
... called a ketohexose. How do I know what the reduction product is. Reduction of glucose gives us sorbitol. Fructose is attached to only 3 atoms therefore it is achiral and when it is reduced the OH group will come to the top or bottom and on either way it forms alcohol. Therefore it gives us sorbitol ...
... called a ketohexose. How do I know what the reduction product is. Reduction of glucose gives us sorbitol. Fructose is attached to only 3 atoms therefore it is achiral and when it is reduced the OH group will come to the top or bottom and on either way it forms alcohol. Therefore it gives us sorbitol ...
tests for FLAVONOIDS
... Primary and secondary alcohols and aldehydes react with chromic acid or Jone’s reagent and give a blue-green precipitate in this test. Aldehydes are oxidized to carboxylic acids, secondary alcohols are oxidized to ketones and primary alcohols are oxidized first to aldehydes and then to carboxylic ac ...
... Primary and secondary alcohols and aldehydes react with chromic acid or Jone’s reagent and give a blue-green precipitate in this test. Aldehydes are oxidized to carboxylic acids, secondary alcohols are oxidized to ketones and primary alcohols are oxidized first to aldehydes and then to carboxylic ac ...
alcohol
... • In everyday speech, alcohol usually refers to the ethanol used in alcoholic beverages (beer, wine, or liquor.) • In chemistry, alcohols are a group of substances with a hydroxyl (–OH) group. ...
... • In everyday speech, alcohol usually refers to the ethanol used in alcoholic beverages (beer, wine, or liquor.) • In chemistry, alcohols are a group of substances with a hydroxyl (–OH) group. ...
Research Proposals
... 370 BCE – Theophrastus writings on use of oils to make fragrances longer lasting. 800 AD – Alembic distillation apparatus – Jabir ibn Hayyan 1200 AD – ...
... 370 BCE – Theophrastus writings on use of oils to make fragrances longer lasting. 800 AD – Alembic distillation apparatus – Jabir ibn Hayyan 1200 AD – ...
Nomenclature of Polyfunctional Organic Compounds
... methyl bromide and half under "B"for bromomethane. Furthermore, a CAS name must be strictly systematic so that it can be assigned and interpreted by computers; common names are not allowed. People,however,have different requirements than computers. For peoplewhich is to say chemists in their spoken ...
... methyl bromide and half under "B"for bromomethane. Furthermore, a CAS name must be strictly systematic so that it can be assigned and interpreted by computers; common names are not allowed. People,however,have different requirements than computers. For peoplewhich is to say chemists in their spoken ...
Chris Sprout”s
... synthesis has aided pharmaceutical companies in the discovery of better drugs. We believe that utilization of parallel combinatorial libraries is the best way to find better catalysts. By designing a novel class of ligands with easily diversified subunits the power of combinatorial chemistry can be ...
... synthesis has aided pharmaceutical companies in the discovery of better drugs. We believe that utilization of parallel combinatorial libraries is the best way to find better catalysts. By designing a novel class of ligands with easily diversified subunits the power of combinatorial chemistry can be ...
Week # 3 Homework doc
... charge on the oxygen. Because oxygen has two lone pairs, two different hydrogen bonds can be made to each oxygen. This is a very specific bond as indicated. Some combinations which are not hydrogen bonds include: hydrogen to another hydrogen or hydrogen to a carbon. Ques. 5: Draw an example of three ...
... charge on the oxygen. Because oxygen has two lone pairs, two different hydrogen bonds can be made to each oxygen. This is a very specific bond as indicated. Some combinations which are not hydrogen bonds include: hydrogen to another hydrogen or hydrogen to a carbon. Ques. 5: Draw an example of three ...
Lecture 18
... to be reasonable soluble in water so that it can be transported through the blood. Since amines are weak bases, they are often converted to salts with some acid and therefore may oral drugs have amine salts as part of their structure. One reason for their presence is that they confer some water solu ...
... to be reasonable soluble in water so that it can be transported through the blood. Since amines are weak bases, they are often converted to salts with some acid and therefore may oral drugs have amine salts as part of their structure. One reason for their presence is that they confer some water solu ...
Spring 2015 CH 421 Name ________________________________________ Section ___________ Post‐lab 3: The Grignard Reaction: Preparation of an Alcohol
... 4) Aldehydes undergo reaction with a Grignard reagent to provide an alcohol product. Many aldehydes are prone to air oxidation. For instance, a bottle of benzaldehyde will turn from a clear liquid to a white solid if left open over time. What is the oxidation produ ...
... 4) Aldehydes undergo reaction with a Grignard reagent to provide an alcohol product. Many aldehydes are prone to air oxidation. For instance, a bottle of benzaldehyde will turn from a clear liquid to a white solid if left open over time. What is the oxidation produ ...
Document
... • Fuels (e.g. the RM1.92 RM2.10 Ron95) are made up mostly of alkanes. In excess oxygen • CnH2n+2 + (1.5n+½)O2 nCO2 + (n+1)H2O ...
... • Fuels (e.g. the RM1.92 RM2.10 Ron95) are made up mostly of alkanes. In excess oxygen • CnH2n+2 + (1.5n+½)O2 nCO2 + (n+1)H2O ...
ALCOHOLS AND ETHERS
... On the more practical side, vast quantities of simple alcohols - methanol, ethanol, 2-propanol, 1-butan01 - and many ethers are made from petroleum-derived hydrocarbons. These alcohols are widely used as solvents and as intermediates for the synthesis of more complex substances. ...
... On the more practical side, vast quantities of simple alcohols - methanol, ethanol, 2-propanol, 1-butan01 - and many ethers are made from petroleum-derived hydrocarbons. These alcohols are widely used as solvents and as intermediates for the synthesis of more complex substances. ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.