Carboxylic Acid Structure and Chemistry
... conditions" nucleophiles can attack the acids carbonyl and displace the acid OH as water, or another good leaving group. Such is the case in esterification reactions performed under acidic conditions. In these reactions an acid is treated with an alcohol which serves as the nucleophile, and an acid ...
... conditions" nucleophiles can attack the acids carbonyl and displace the acid OH as water, or another good leaving group. Such is the case in esterification reactions performed under acidic conditions. In these reactions an acid is treated with an alcohol which serves as the nucleophile, and an acid ...
applied sciences Chiral β-Amino Alcohols as Ligands for the N
... hydroxides gave almost the same ee’s as potassium hydroxide, the yield being higher with the latter (compare entries 2, 6 and 7 in Table 1). We tried to reduce the amount of the Ru-dimer to 3 mol%, but this considerably slowed down the transfer hydrogenation process and resulted in a lower yield of ...
... hydroxides gave almost the same ee’s as potassium hydroxide, the yield being higher with the latter (compare entries 2, 6 and 7 in Table 1). We tried to reduce the amount of the Ru-dimer to 3 mol%, but this considerably slowed down the transfer hydrogenation process and resulted in a lower yield of ...
amine
... • Quinine – used to treat malaria • Opium – used to make codeine (in cough medicines), morphine (pain killer), and heroin ...
... • Quinine – used to treat malaria • Opium – used to make codeine (in cough medicines), morphine (pain killer), and heroin ...
Reaction of Organometallic Reagents with Aldehydes and Ketones.
... • The difference between the two reactions is what then happens to the intermediate. • Aldehydes and ketones cannot undergo substitution because they do not have a good leaving group bonded to the newly formed sp3 hybridized carbon. ...
... • The difference between the two reactions is what then happens to the intermediate. • Aldehydes and ketones cannot undergo substitution because they do not have a good leaving group bonded to the newly formed sp3 hybridized carbon. ...
Organic Chemistry ruba
... Can be formed from the dehydration of secondary alcohols with a catalyst. Propanone is formed from the oxidation of 2propanol using KMnO4 or PCC catalyst.* (c) 2006, Mark Rosengarten ...
... Can be formed from the dehydration of secondary alcohols with a catalyst. Propanone is formed from the oxidation of 2propanol using KMnO4 or PCC catalyst.* (c) 2006, Mark Rosengarten ...
alcohol
... 3. Explain the effects of alcohol and specific drugs and poisons on the body. 4. Discuss chemical agents that may be used for ...
... 3. Explain the effects of alcohol and specific drugs and poisons on the body. 4. Discuss chemical agents that may be used for ...
Homogeneously catalysed hydrogenation of unsaturated fatty acids
... y = x + - a+bx This equation, which represents a hyperbola, allows a simple representation of a complicated chemical reaction and is of practical importance for a systematic study of catalytic processes. It was found that the course of the hydrogenation of unsaturated acids under influence of Cu- an ...
... y = x + - a+bx This equation, which represents a hyperbola, allows a simple representation of a complicated chemical reaction and is of practical importance for a systematic study of catalytic processes. It was found that the course of the hydrogenation of unsaturated acids under influence of Cu- an ...
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons I : Alkenes
... Alkenes that contain two double bonds are called Dienes: If the double bonds are separated by only one single bond, the diene is said to be conjugated. If the double bonds are separated by more than one single bond, the diene is called non conjugated diene. Dienes are named by the IUPAC system ...
... Alkenes that contain two double bonds are called Dienes: If the double bonds are separated by only one single bond, the diene is said to be conjugated. If the double bonds are separated by more than one single bond, the diene is called non conjugated diene. Dienes are named by the IUPAC system ...
Handout: Naming Organic Compounds Substituents Longest carbon
... 3. Name prefix: substituent position #s and names (group repeated substituents together using di-, tri-, etc). 4. Write full name, listing substituents in alphabetical order (ignore di-, tetra- in alphabetizing). ...
... 3. Name prefix: substituent position #s and names (group repeated substituents together using di-, tri-, etc). 4. Write full name, listing substituents in alphabetical order (ignore di-, tetra- in alphabetizing). ...
Organic Chemistry – Summary of Reactions and Conditions
... contain copper (II) complexes. These complexes enable Cu (II) to remain in solution in the presence of alkali. Ketones are resistant to oxidation and do not react with Benedict's solution. Tollen's reagent (ammoniacal silver nitrate) (not a preparative method) Prepared by adding excess ammonia solut ...
... contain copper (II) complexes. These complexes enable Cu (II) to remain in solution in the presence of alkali. Ketones are resistant to oxidation and do not react with Benedict's solution. Tollen's reagent (ammoniacal silver nitrate) (not a preparative method) Prepared by adding excess ammonia solut ...
Slide 1
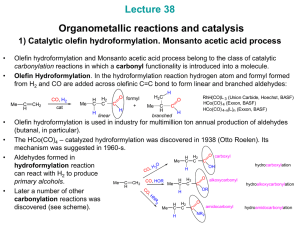
... Olefin hydroformylation and Monsanto acetic acid process belong to the class of catalytic carbonylation reactions in which a carbonyl functionality is introduced into a molecule. Olefin Hydroformylation. In the hydroformylation reaction hydrogen atom and formyl formed from H2 and CO are added across ...
... Olefin hydroformylation and Monsanto acetic acid process belong to the class of catalytic carbonylation reactions in which a carbonyl functionality is introduced into a molecule. Olefin Hydroformylation. In the hydroformylation reaction hydrogen atom and formyl formed from H2 and CO are added across ...
PPT
... • Number the other substituents on the carbon chain. • An italic “N” is used as a prefix for a substituent on nitrogen. Examples: ...
... • Number the other substituents on the carbon chain. • An italic “N” is used as a prefix for a substituent on nitrogen. Examples: ...
INTRODUCING ACYL CHLORIDES (acid
... Substitution of the chlorine atom by other groups Acyl chlorides are extremely reactive, and in their reactions the chlorine atom is replaced by other things. In each case, in the first instance, hydrogen chloride gas is produced as steamy acidic fumes. However, in some cases the hydrogen chloride g ...
... Substitution of the chlorine atom by other groups Acyl chlorides are extremely reactive, and in their reactions the chlorine atom is replaced by other things. In each case, in the first instance, hydrogen chloride gas is produced as steamy acidic fumes. However, in some cases the hydrogen chloride g ...
Alcools
... The OH group has a higher priority than a multiple CC bond, a halogen, and an alkyl group in determining the carbon chain numbering. ...
... The OH group has a higher priority than a multiple CC bond, a halogen, and an alkyl group in determining the carbon chain numbering. ...
chapt13
... SN2 substitution (Substitution, nucleophilic bimolecular) A nucleophile attacks a carbon from the opposite side of the leaving group. An intermediate is theorized in which the nucleophile is partially bonded to the molecule, while the leaving group is partially dissociated. The nucleophile donates ...
... SN2 substitution (Substitution, nucleophilic bimolecular) A nucleophile attacks a carbon from the opposite side of the leaving group. An intermediate is theorized in which the nucleophile is partially bonded to the molecule, while the leaving group is partially dissociated. The nucleophile donates ...
Recognize the functional group and give a characteristic of this
... aura of respectability to descriptions of events or actions which would be offensive when expressed in plain English. The following is a list of Euphemisms in Science and their translations into plain English. ...
... aura of respectability to descriptions of events or actions which would be offensive when expressed in plain English. The following is a list of Euphemisms in Science and their translations into plain English. ...
Organic Chemistry: An Indian Journal
... Carbon-oxygen bond formation is a valuable reaction in organic synthesis and has generated considerable interest in recent years. Ethers are significant solvents and synthetic important supplements for the production of fragrances, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and dyestuffs [1,2]. The Williamson reac ...
... Carbon-oxygen bond formation is a valuable reaction in organic synthesis and has generated considerable interest in recent years. Ethers are significant solvents and synthetic important supplements for the production of fragrances, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and dyestuffs [1,2]. The Williamson reac ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.