10.3 PREPARATION OF ETHERS
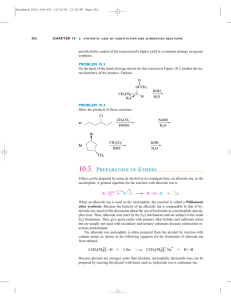
... ether synthesis. Because the basicity of an alkoxide ion is comparable to that of hydroxide ion, much of the discussion about the use of hydroxide as a nucleophile also applies here. Thus, alkoxide ions react by the SN2 mechanism and are subject to the usual SN2 limitations. They give good yields wi ...
... ether synthesis. Because the basicity of an alkoxide ion is comparable to that of hydroxide ion, much of the discussion about the use of hydroxide as a nucleophile also applies here. Thus, alkoxide ions react by the SN2 mechanism and are subject to the usual SN2 limitations. They give good yields wi ...
m4 phenol and diazo salts
... it dissolves very slightly in water to form a weak acidic solution it is a stronger acid than aliphatic alcohols the ring helps weaken the O-H bond and stabilises the resulting anion C6H5OH(aq) ...
... it dissolves very slightly in water to form a weak acidic solution it is a stronger acid than aliphatic alcohols the ring helps weaken the O-H bond and stabilises the resulting anion C6H5OH(aq) ...
Ultrasound Assisted Synthesis of 5,9
... pheromones [1]. 5,9-Dimethylpentadecane (1) and 5,9-dimethylhexadecane (2) are known as the major and minor constituents, respectively, of the sex pheromone of Leucoptera coffeella, a pest of coffee trees [2]. Several ways of synthesizing 1 have been described. Stereoisomers of 1 were synthesized st ...
... pheromones [1]. 5,9-Dimethylpentadecane (1) and 5,9-dimethylhexadecane (2) are known as the major and minor constituents, respectively, of the sex pheromone of Leucoptera coffeella, a pest of coffee trees [2]. Several ways of synthesizing 1 have been described. Stereoisomers of 1 were synthesized st ...
Nucleophilic substitution at saturated carbon
... polarizability of the atom. Because the electrons are farther away in the larger atom, they are not held as tightly and can, therefore, move more freely toward a positive charge. As a result, the electrons are able to overlap from farther away with the orbital of carbon, as shown in Figure 10.5. Thi ...
... polarizability of the atom. Because the electrons are farther away in the larger atom, they are not held as tightly and can, therefore, move more freely toward a positive charge. As a result, the electrons are able to overlap from farther away with the orbital of carbon, as shown in Figure 10.5. Thi ...
Question paper - Unit F322 - Chains, energy and resources
... (b) The ‘curly arrows’ model is used in reaction mechanisms to show the movement of electron pairs during chemical reactions. Choose a reaction mechanism that you have studied involving the curly arrow model. Name and describe your chosen reaction mechanism. In your answer, include: ...
... (b) The ‘curly arrows’ model is used in reaction mechanisms to show the movement of electron pairs during chemical reactions. Choose a reaction mechanism that you have studied involving the curly arrow model. Name and describe your chosen reaction mechanism. In your answer, include: ...
CHM 331 : General Organic Chemistry
... Example problems: give the major organic products of the following reactions ...
... Example problems: give the major organic products of the following reactions ...
Document
... Ozonolysis of Alkenes - oxidative cleavage of an alkene to carbonyl compounds (aldehydes and ketones). The and -bonds of the alkene are broken and replaced with C=O double bonds. C=C of aryl rings, CN and C=O do not react with ozone, CC react very slowly with ozone ...
... Ozonolysis of Alkenes - oxidative cleavage of an alkene to carbonyl compounds (aldehydes and ketones). The and -bonds of the alkene are broken and replaced with C=O double bonds. C=C of aryl rings, CN and C=O do not react with ozone, CC react very slowly with ozone ...
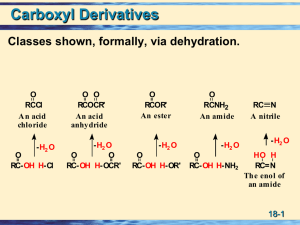
Chapter 3 Carboxylic Acids
... Carboxyl group is usually written -COOH. Aliphatic acids have an alkyl group bonded to COOH. Aromatic acids have an aryl group. Fatty acids are long-chain aliphatic acids. ...
... Carboxyl group is usually written -COOH. Aliphatic acids have an alkyl group bonded to COOH. Aromatic acids have an aryl group. Fatty acids are long-chain aliphatic acids. ...
STUDY GUIDE
... Addition polymers form when monomers link during addition reactions. Condensation polymers are polymers formed when monomers join during condensation reactions. The properties of addition polymers can be varied by selecting monomers with certain substituent atoms or groups. Polyesters are formed by ...
... Addition polymers form when monomers link during addition reactions. Condensation polymers are polymers formed when monomers join during condensation reactions. The properties of addition polymers can be varied by selecting monomers with certain substituent atoms or groups. Polyesters are formed by ...
Microsoft Word
... acidity still restricts its use with acid sensitive substrates. However, these methods are described only for ring opening reactions of epoxide with primary alcohols. Furthermore, many of these reagents are corrosive, moisture sensitive and are required in stoichiometric amounts. Therefore, the deve ...
... acidity still restricts its use with acid sensitive substrates. However, these methods are described only for ring opening reactions of epoxide with primary alcohols. Furthermore, many of these reagents are corrosive, moisture sensitive and are required in stoichiometric amounts. Therefore, the deve ...
Derivatization of polar compounds for GC - Sigma
... with your GC column? For example silyl derivatives should not be analyzed on a polyethylene glycol (PEG) based phase such as SUPELCOWAX or Carbowax ...
... with your GC column? For example silyl derivatives should not be analyzed on a polyethylene glycol (PEG) based phase such as SUPELCOWAX or Carbowax ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.