alcohol - What is Chemistry?
... Solubility of methanol in (i) cyclohexane – not very soluble methanol is polar cyclohexane is not (ii) water - completely soluble because it is polar. As alcohol molecule gets bigger the polar part becomes less significant so the alcohol becomes less soluble in water and more soluble in cycloh ...
... Solubility of methanol in (i) cyclohexane – not very soluble methanol is polar cyclohexane is not (ii) water - completely soluble because it is polar. As alcohol molecule gets bigger the polar part becomes less significant so the alcohol becomes less soluble in water and more soluble in cycloh ...
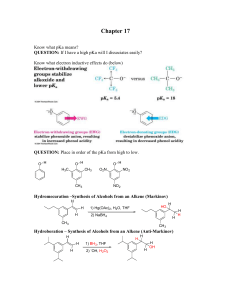
Chapter 17 - Ellis Benjamin
... Reduction of and Ketone or Aldehyde using Lithium Aluminum Hydride to form and Alcohol. O ...
... Reduction of and Ketone or Aldehyde using Lithium Aluminum Hydride to form and Alcohol. O ...
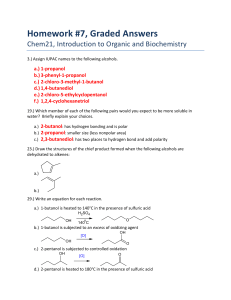
Discussion Sheet 11
... Skill 3: Reactions of alcohols are key C-C bond forming steps in multistep synthesis ...
... Skill 3: Reactions of alcohols are key C-C bond forming steps in multistep synthesis ...
12SN-23-10 OBJECTIVE: Identify how alcohols are classified and
... Identify how alcohols are classified and named. Predict how the solubility of an alcohol varies with the length of its carbon chain. Name the reactions of alkenes that may be used to introduce functional groups. Construct the general structure of an ether and describe how ethers are named. Identify ...
... Identify how alcohols are classified and named. Predict how the solubility of an alcohol varies with the length of its carbon chain. Name the reactions of alkenes that may be used to introduce functional groups. Construct the general structure of an ether and describe how ethers are named. Identify ...
ALCOHOLS - Chemistry Geek
... Step 6: The number can be placed before name or between the parent chain and –ol ...
... Step 6: The number can be placed before name or between the parent chain and –ol ...
chemistry 2 - waiukucollegescience
... Draw structural formulae for the following organic compounds. (a) 2-chloropropane ...
... Draw structural formulae for the following organic compounds. (a) 2-chloropropane ...
10.3 Alcohols
... Common Names of Alcohols • Many alcohols have common names based on naming the hydrocarbon chain as an alkyl group and adding the word alcohol. ...
... Common Names of Alcohols • Many alcohols have common names based on naming the hydrocarbon chain as an alkyl group and adding the word alcohol. ...
Test Review
... You should know how to name and draw the structures for the following classes of compounds: alcohols, ethers (both IUPAC and common ways), phenols (see ch. 12), and thiols. ...
... You should know how to name and draw the structures for the following classes of compounds: alcohols, ethers (both IUPAC and common ways), phenols (see ch. 12), and thiols. ...
Reactions of alcohols
... This photo shows ethanol, propan-1-ol and butan-1-ol in water. The first two are completely miscible in water, while butan-1-ol is not miscible in water. ...
... This photo shows ethanol, propan-1-ol and butan-1-ol in water. The first two are completely miscible in water, while butan-1-ol is not miscible in water. ...
Alcohols, Aldehydes and Ketones
... Alcohols, Aldehydes and Ketones Primary alcohols can be oxidised to form aldehydes which are further oxidised to carboxylic acids. Secondary alcohols can be oxidised to ketones but can then not be oxidised further. Tertiary alcohols can not be oxidised at all. Strong oxidising agents such as acidifi ...
... Alcohols, Aldehydes and Ketones Primary alcohols can be oxidised to form aldehydes which are further oxidised to carboxylic acids. Secondary alcohols can be oxidised to ketones but can then not be oxidised further. Tertiary alcohols can not be oxidised at all. Strong oxidising agents such as acidifi ...
June 6 – Alcohols - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... becomes more important than the polar –OH bonds. Therefore small alcohols are more polar than alcohols with large hydrocarbon portions • the capacity for alcohols for hydrogen bonding makes them extremely soluble in water. The solubility of an alcohol decreases as the number of carbon atoms increase ...
... becomes more important than the polar –OH bonds. Therefore small alcohols are more polar than alcohols with large hydrocarbon portions • the capacity for alcohols for hydrogen bonding makes them extremely soluble in water. The solubility of an alcohol decreases as the number of carbon atoms increase ...
File
... Alcohols (alkanols) (R-OH) Alcohols are derived from hydrocarbons and contain -OH groups. The names are derived from the hydrocarbon name with ol replacing the e at the end of the -ane suffix. Example: ethane becomes ethanol. Since the O-H bond is polar, alcohols are more water soluble than alkanes. ...
... Alcohols (alkanols) (R-OH) Alcohols are derived from hydrocarbons and contain -OH groups. The names are derived from the hydrocarbon name with ol replacing the e at the end of the -ane suffix. Example: ethane becomes ethanol. Since the O-H bond is polar, alcohols are more water soluble than alkanes. ...
File
... CH2OHCH2OH = 1,2-ethanediol or ethylene glycol 2) Alcohols which have 3 OH goups are called triols CH2OHCHOHCH2OH = 1,2, 3-propanetriol or glycerol or glycerin ...
... CH2OHCH2OH = 1,2-ethanediol or ethylene glycol 2) Alcohols which have 3 OH goups are called triols CH2OHCHOHCH2OH = 1,2, 3-propanetriol or glycerol or glycerin ...
C h e m g u i d e ... ALDEHYDES AND KETONES: REDUCTION
... (You could perfectly well condense these formulae as CH3COCH3 and CH3CH(OH)CH3, but as things get more complicated, it is easier to show the structures more fully.) (iii) CH3CCH2CH3 + 2[H] ...
... (You could perfectly well condense these formulae as CH3COCH3 and CH3CH(OH)CH3, but as things get more complicated, it is easier to show the structures more fully.) (iii) CH3CCH2CH3 + 2[H] ...
Abdul Majeed Seayad Project Synopsis (96 - ACE
... borrowing strategy: Alcohols as feedstock, for useful transformations without functional group readily available nontoxic feedstock would electrophiles in C-N and C-C bond interconversions is a challenge in organic and process chemistry. In a greatly impact the way in which APIs are forming reaction ...
... borrowing strategy: Alcohols as feedstock, for useful transformations without functional group readily available nontoxic feedstock would electrophiles in C-N and C-C bond interconversions is a challenge in organic and process chemistry. In a greatly impact the way in which APIs are forming reaction ...
Alcohols - ChemistryHSC
... Hydroxyl group covalently bonded to an alkyl chain or benzene ring (called phenols) Many naturally occurring in nature: glucose C6H12O6, glycerol C3H8O3 Most common alcohol is ethanol, which has been produced for thousands of years – Egyptian workers given beer rations! And governments have taxed al ...
... Hydroxyl group covalently bonded to an alkyl chain or benzene ring (called phenols) Many naturally occurring in nature: glucose C6H12O6, glycerol C3H8O3 Most common alcohol is ethanol, which has been produced for thousands of years – Egyptian workers given beer rations! And governments have taxed al ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.