Functional Groups
... alcohol carbon. Example—1-propanol Secondary alcohols have 2 carbons bonded to the alcohol carbon. Example—2-propanol Tertiary alcohols have 3 carbons bonded to the alcohol carbon. Example—2-methyl-2-butanol ...
... alcohol carbon. Example—1-propanol Secondary alcohols have 2 carbons bonded to the alcohol carbon. Example—2-propanol Tertiary alcohols have 3 carbons bonded to the alcohol carbon. Example—2-methyl-2-butanol ...
Hein and Arena
... of reactions involved in making compounds that can be used in a separate process to manufacture an energy-rich compound called ATP. A reaction early in the citric acid cycle involves the oxidation of an alcohol. Of the two reactants shown below (each is a reactant somewhere in the cycle), which can ...
... of reactions involved in making compounds that can be used in a separate process to manufacture an energy-rich compound called ATP. A reaction early in the citric acid cycle involves the oxidation of an alcohol. Of the two reactants shown below (each is a reactant somewhere in the cycle), which can ...
Chem 400 Review Chem 350 JJ.S17
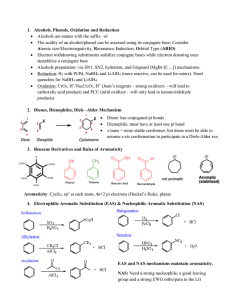
... 1. Alcohols, Phenols, Oxidation and Reduction Alcohols are names with the suffix –ol The acidity of an alcohol/phenol can be assessed using its conjugate base: Consider Atomic size/Electronegativity, Resonance, Induction, Orbital Type (ARIO) Electron withdrawing substituents stabilize conjugat ...
... 1. Alcohols, Phenols, Oxidation and Reduction Alcohols are names with the suffix –ol The acidity of an alcohol/phenol can be assessed using its conjugate base: Consider Atomic size/Electronegativity, Resonance, Induction, Orbital Type (ARIO) Electron withdrawing substituents stabilize conjugat ...
Click on image to content
... functional group in ethene is , and in ethyne, it is – C ≡ C – . Thus, we see that the properties of a compound depend on the functional group. ...
... functional group in ethene is , and in ethyne, it is – C ≡ C – . Thus, we see that the properties of a compound depend on the functional group. ...
Functional Groups
... Atoms other than hydrogen or carbon covalently bonded to a carbon atom in an organic molecule. Most commonly oxygen, nitrogen, or the halogens. The presence of a functional group drastically changes the chemical properties of a molecule. ...
... Atoms other than hydrogen or carbon covalently bonded to a carbon atom in an organic molecule. Most commonly oxygen, nitrogen, or the halogens. The presence of a functional group drastically changes the chemical properties of a molecule. ...
Notes, Part II
... The –OH group in alcohols makes them reasonable polar in small molecules (up to 4 carbons), and so they dissolve well in water. (Why not longer chained alcohols?) NAMING alcohols – we’ll stick to the simple ones. Drop the “e” from the end of the hydrocarbon chain and add “-ol” If necessary, ...
... The –OH group in alcohols makes them reasonable polar in small molecules (up to 4 carbons), and so they dissolve well in water. (Why not longer chained alcohols?) NAMING alcohols – we’ll stick to the simple ones. Drop the “e” from the end of the hydrocarbon chain and add “-ol” If necessary, ...
Chem 3.5 Answers #3
... The presence of the OH group on propanol allows hydrogen bonding to occur between propanol molecules. The attractions between propane molecules are weak Van der Waals forces and so the energy needed to separate its molecules from each other is much less giving a lower B. Pt. The OH bond allows the a ...
... The presence of the OH group on propanol allows hydrogen bonding to occur between propanol molecules. The attractions between propane molecules are weak Van der Waals forces and so the energy needed to separate its molecules from each other is much less giving a lower B. Pt. The OH bond allows the a ...
Reactions of Alkenes Organic Chemistry
... ** catalyst a reactant that speeds up the reaction but it is not used up ** Markovnikov’s Rule states that if the alkene is unsymmetrical, the Hydrogen atoms will be attached to the carbon atom with most hydrogen atoms. ...
... ** catalyst a reactant that speeds up the reaction but it is not used up ** Markovnikov’s Rule states that if the alkene is unsymmetrical, the Hydrogen atoms will be attached to the carbon atom with most hydrogen atoms. ...
Alcohols
... The reactivity of LiAlH4 is much greater than that of NaBH4 and is less selective in its reactions. LiAlH4 reacts vigorously with water and ethanol and must be used in an aprotic solvent such as diethyl ether. ...
... The reactivity of LiAlH4 is much greater than that of NaBH4 and is less selective in its reactions. LiAlH4 reacts vigorously with water and ethanol and must be used in an aprotic solvent such as diethyl ether. ...
Ester Lab / Adobe Acrobat Document
... 3. Refer to the observation table attached. To test tubes add 1.0mL (about 0.75cm) of the appropriate acid 4. Refer to the observation table attached. To each test tube add 10 drops of the appropriate alcohol 5. To each test tube add 2 drops of Concentrated Sulfuric Acid 6. Using test tube tongs, pu ...
... 3. Refer to the observation table attached. To test tubes add 1.0mL (about 0.75cm) of the appropriate acid 4. Refer to the observation table attached. To each test tube add 10 drops of the appropriate alcohol 5. To each test tube add 2 drops of Concentrated Sulfuric Acid 6. Using test tube tongs, pu ...
Spectroscopy WS 2
... There are four isomeric Alcohols with the molecular formula C 4H10O. They can be distinguished using a variety of analytical techniques. (a) ...
... There are four isomeric Alcohols with the molecular formula C 4H10O. They can be distinguished using a variety of analytical techniques. (a) ...
Biochemistry I (CHE 418 / 5418)
... replaces a leaving group (halides ,Cl, F, Br, are good leaving groups) • Leaving group an easily replaced atom or group of atoms that is held to a carbon by a realatively weak covalent bond. • See p.301 Fig. 9.5 and 9.6 ...
... replaces a leaving group (halides ,Cl, F, Br, are good leaving groups) • Leaving group an easily replaced atom or group of atoms that is held to a carbon by a realatively weak covalent bond. • See p.301 Fig. 9.5 and 9.6 ...
Analysing Alcohols
... Analysing Alcohols(12/03/2016) Aim: To outline an experiment to determine whether an unknown liquid is a primary secondary or tertiary alcohol. Equations Primary alcohol+excess oxygen CH3CH2OH+[O] ...
... Analysing Alcohols(12/03/2016) Aim: To outline an experiment to determine whether an unknown liquid is a primary secondary or tertiary alcohol. Equations Primary alcohol+excess oxygen CH3CH2OH+[O] ...
Oxidation of Alcohols
... 15.2: Preparation of Alcohols by Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones - add the equivalent of H2 across the -bond of the carbonyl to yield an alcohol O R ...
... 15.2: Preparation of Alcohols by Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones - add the equivalent of H2 across the -bond of the carbonyl to yield an alcohol O R ...
Alcohol Worksheet Key
... 3 has 4 carbons and therefore is most soluble in water. 1 and 2 have the same number of carbons, but 1 has 2 alcohol groups and is therefore more soluble. ...
... 3 has 4 carbons and therefore is most soluble in water. 1 and 2 have the same number of carbons, but 1 has 2 alcohol groups and is therefore more soluble. ...
Chapter Nine: Alcohols, Ethers and Epoxides
... Use knowledge about nucleophilic substitution reactions to predict products of reaction with ethers and their mechanism of formation. Predict the stereochemistry and optical activity of a product from an understanding of its mechanism of formation. Propose a reaction or sequence of reactions t ...
... Use knowledge about nucleophilic substitution reactions to predict products of reaction with ethers and their mechanism of formation. Predict the stereochemistry and optical activity of a product from an understanding of its mechanism of formation. Propose a reaction or sequence of reactions t ...
JSUNIL TUTORIAL, SAMASTIPUR,BIHAR Carbon and its compounds Answer the following questions:
... the alcohol and the acid from which it might be prepared. 13. A mixture of ethyne and oxygen is used for welding. Can you justify why a mixture of ethyne and air is not-used? 14. Write the reaction which is used as a test for ethanol and dehydration of ethanol. 15. What is reaction with ethanoic aci ...
... the alcohol and the acid from which it might be prepared. 13. A mixture of ethyne and oxygen is used for welding. Can you justify why a mixture of ethyne and air is not-used? 14. Write the reaction which is used as a test for ethanol and dehydration of ethanol. 15. What is reaction with ethanoic aci ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.