Acidity of Alcohols
... CO + 2H2 CH3OH (Pt catalyst, heat) CH3OH is an important solvent. CH3OH is toxic. (ingestion of 15 ml ...
... CO + 2H2 CH3OH (Pt catalyst, heat) CH3OH is an important solvent. CH3OH is toxic. (ingestion of 15 ml ...
Alcohols and Carbonyls - Deans Community High School
... C2H4 + H2O CH3CH2OH Cracking fractions from crude oil is a cheaper way to produce ethanol. (more expensive than making petrol) Reaction Conditions: 300oC , High Pressure 60 Atm. , phosphoric acid catalyst. ...
... C2H4 + H2O CH3CH2OH Cracking fractions from crude oil is a cheaper way to produce ethanol. (more expensive than making petrol) Reaction Conditions: 300oC , High Pressure 60 Atm. , phosphoric acid catalyst. ...
10.4 Alcohols - SCIS Teachers
... 10.4.3 Determine the products formed by the oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols. ...
... 10.4.3 Determine the products formed by the oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols. ...
Organic Chemistry: Introduction
... and halogenoalkanes (-F, -Cl, -Br, -I) • with reference to the carbon that is directly bonded to an alcohol group or a halogen: – Primary = carbon atom is only bonded to one other carbon – Secondary = carbon atom is bonded to two other carbons – Tertiary = carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon ...
... and halogenoalkanes (-F, -Cl, -Br, -I) • with reference to the carbon that is directly bonded to an alcohol group or a halogen: – Primary = carbon atom is only bonded to one other carbon – Secondary = carbon atom is bonded to two other carbons – Tertiary = carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon ...
Alcohols , Phenols and Ethers easy notes
... which have electron releasing inductive effect. In phenol, the hydroxyl group is directly attached to the sp2 hybridised carbon of benzene ring. Whereas in alcohols, the hydroxyl group is attached to the sp3 hybridised carbon of the alkyl group. The sp2 hybridised carbon has higher electronegativity ...
... which have electron releasing inductive effect. In phenol, the hydroxyl group is directly attached to the sp2 hybridised carbon of benzene ring. Whereas in alcohols, the hydroxyl group is attached to the sp3 hybridised carbon of the alkyl group. The sp2 hybridised carbon has higher electronegativity ...
Oxidation of alcohols and aldehydes
... Further oxidation of a primary alcohol • Using a process known as REFLUX, the reaction contents are continually heated at their boiling point temperature, so HOTTER and LONGER heating then alcohol conversion to an aldehyde • Still uses acidified potassium dichromate Primary + Oxidising Carboxylic ...
... Further oxidation of a primary alcohol • Using a process known as REFLUX, the reaction contents are continually heated at their boiling point temperature, so HOTTER and LONGER heating then alcohol conversion to an aldehyde • Still uses acidified potassium dichromate Primary + Oxidising Carboxylic ...
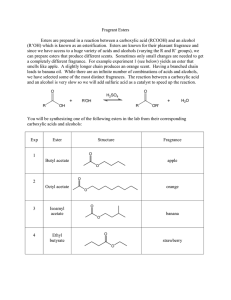
Fragrant Esters Esters are prepared in a reaction between a
... Esters are prepared in a reaction between a carboxylic acid (RCOOH) and an alcohol (R’OH) which is known as an esterification. Esters are known for their pleasant fragrance and since we have access to a huge variety of acids and alcohols (varying the R and R’ groups), we can prepare esters that prod ...
... Esters are prepared in a reaction between a carboxylic acid (RCOOH) and an alcohol (R’OH) which is known as an esterification. Esters are known for their pleasant fragrance and since we have access to a huge variety of acids and alcohols (varying the R and R’ groups), we can prepare esters that prod ...
The loss of water (dehydration) and the loss of hydrogen are two
... often called dehydrogenation rather than oxidation. Enzymes that catalyze such reactions are called dehydrogenases. Only primary and secondary alcohols can be oxidized by the loss of 2H atoms. Molecules of tertiary alcohols do not have an H atom on the carbon that holds the OH group, so 30 alcohols ...
... often called dehydrogenation rather than oxidation. Enzymes that catalyze such reactions are called dehydrogenases. Only primary and secondary alcohols can be oxidized by the loss of 2H atoms. Molecules of tertiary alcohols do not have an H atom on the carbon that holds the OH group, so 30 alcohols ...
A NEW APROACH TO N-SUBSTITUTED OXAZOLIDINE VIA NITRILIUM ION TRAPPING
... TRAPPING Mohammed Alhuniti, Deboprosad Mondal, and Salvatore D. Lepore* Abstract: We have recently demonstrated a direct conversion of secondary alcohols to amides with retention of configuration. This method involved the in situ formation of chlorosulfites followed by a reaction with nitrile comple ...
... TRAPPING Mohammed Alhuniti, Deboprosad Mondal, and Salvatore D. Lepore* Abstract: We have recently demonstrated a direct conversion of secondary alcohols to amides with retention of configuration. This method involved the in situ formation of chlorosulfites followed by a reaction with nitrile comple ...
Name the alcohol shown.
... Is the alcohol shown a primary, secondary or tertiary alcohol? 1. Primary. 2. Secondary. 3. Tertiary. ...
... Is the alcohol shown a primary, secondary or tertiary alcohol? 1. Primary. 2. Secondary. 3. Tertiary. ...
Formation of C-C Bonds via Catalytic Hydrogenation and Transfer
... laboratory reveals reductive C-C bond formation can be achieved under the conditions of catalytic hydrogenation. This concept is extended further via “C-C bond forming transfer hydrogenations”, wherein hydrogen exchange between alcohols and π-unsaturated reactants triggers generation of aldehyde-org ...
... laboratory reveals reductive C-C bond formation can be achieved under the conditions of catalytic hydrogenation. This concept is extended further via “C-C bond forming transfer hydrogenations”, wherein hydrogen exchange between alcohols and π-unsaturated reactants triggers generation of aldehyde-org ...
Organic 2 PPT
... are derivates of water; the -OH comes from water, and thus are somewhat soluble Alcohols of up to 4 carbons are soluble in water in all proportions; more than 4 carbons are usually less soluble, because the longer carbon chain is more nonpolar ...
... are derivates of water; the -OH comes from water, and thus are somewhat soluble Alcohols of up to 4 carbons are soluble in water in all proportions; more than 4 carbons are usually less soluble, because the longer carbon chain is more nonpolar ...
Organic Reactions Summary
... Elimination Removal of 2 atoms/groups to form a double bond Family Alcohols Alkyl halides ...
... Elimination Removal of 2 atoms/groups to form a double bond Family Alcohols Alkyl halides ...
Chapter 5
... The most common reaction of thiols in biological systems is their oxidation to disulfides, the functional group of which is a disulfide (-S-S-) bond. ◦ Thiols are readily oxidized to disulfides by O2. ◦ They are so susceptible to oxidation that they must be protected from contact with air during sto ...
... The most common reaction of thiols in biological systems is their oxidation to disulfides, the functional group of which is a disulfide (-S-S-) bond. ◦ Thiols are readily oxidized to disulfides by O2. ◦ They are so susceptible to oxidation that they must be protected from contact with air during sto ...
chemistry_23 - Bonar Law Memorial
... a class of chemical compounds called ethers. You will read about the chemical characteristics of ethers that make them good anesthetics. Alcohols How are alcohols classified and named? • An alcohol is an organic compound with an — OH group. • The —OH functional group in alcohols is called a hydroxyl ...
... a class of chemical compounds called ethers. You will read about the chemical characteristics of ethers that make them good anesthetics. Alcohols How are alcohols classified and named? • An alcohol is an organic compound with an — OH group. • The —OH functional group in alcohols is called a hydroxyl ...
Chapter 5-alcohol
... ◦ Phenols are weak acids and react with NaOH and other strong bases to form water-soluble salts. ...
... ◦ Phenols are weak acids and react with NaOH and other strong bases to form water-soluble salts. ...
Alkanes
... A carbon chain with an OH group attached. How do you name alcohols? The OH group takes priority. OH group gets lowest number along chain. Follow other rules after that. What is the general formula of alcohols? CnH2n+1O What does the dehydration of an alcohol look like? CnH2n+10 CnH2n + H2O What do ...
... A carbon chain with an OH group attached. How do you name alcohols? The OH group takes priority. OH group gets lowest number along chain. Follow other rules after that. What is the general formula of alcohols? CnH2n+1O What does the dehydration of an alcohol look like? CnH2n+10 CnH2n + H2O What do ...
Classification and Identification of Alcohols and Phenols
... Alcohols may be classified as either primary, secondary or tertiary depending on the number of carbon-containing groups attached to the carbon- bearing hydroxyl group. ...
... Alcohols may be classified as either primary, secondary or tertiary depending on the number of carbon-containing groups attached to the carbon- bearing hydroxyl group. ...
CHAPTER-6 DEHYDROHALOGENATION OF ALKYL HALIDES
... Dehydration of Alcohols to form Ethers • Simple, symmetrical ethers can be formed from the intermolecular acid‐catalyzed dehydration of 1° (or methyl) alcohols (a “substitution reaction”) • 2° and 3° alcohols can’t be used because they eliminate (intramolecular dehydration) to form alkenes ...
... Dehydration of Alcohols to form Ethers • Simple, symmetrical ethers can be formed from the intermolecular acid‐catalyzed dehydration of 1° (or methyl) alcohols (a “substitution reaction”) • 2° and 3° alcohols can’t be used because they eliminate (intramolecular dehydration) to form alkenes ...
Alcohols
... capable of hydrogen bonding between molecules –this means they will boil at a higher temp. than alkanes and halocarbons with a comparable number of atoms ...
... capable of hydrogen bonding between molecules –this means they will boil at a higher temp. than alkanes and halocarbons with a comparable number of atoms ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.