4 - GEOCITIES.ws
... Carbon atoms are the most versatile building blocks of molecules 4. Explain how the tetravalence of the carbon atom contributes the structural complexity of organic compounds. a. Carbon has 4 valence electrons, forms 4 covalent bonds b. Is not very electronegative, the bonds are relatively stable c. ...
... Carbon atoms are the most versatile building blocks of molecules 4. Explain how the tetravalence of the carbon atom contributes the structural complexity of organic compounds. a. Carbon has 4 valence electrons, forms 4 covalent bonds b. Is not very electronegative, the bonds are relatively stable c. ...
Microsoft Word - Final Exam Study Guide
... A. How many hydrogens? How many lone pairs? B. Label the structure with any missing formal charges. C. Draw at least two more resonance structures and rank them from most major contributor to most minor contributor. D. Mark all the chiral centers and label any designated chiral centers R or S. B. Wo ...
... A. How many hydrogens? How many lone pairs? B. Label the structure with any missing formal charges. C. Draw at least two more resonance structures and rank them from most major contributor to most minor contributor. D. Mark all the chiral centers and label any designated chiral centers R or S. B. Wo ...
Lecture Review of Organic Chemistry and Herbicide Chemistry
... tend to be degraded readily by microbes e.g. Roundup (glyphosate), Liberty/Ignite/Finale (glufosinate), and several thiocarbamate herbicides ...
... tend to be degraded readily by microbes e.g. Roundup (glyphosate), Liberty/Ignite/Finale (glufosinate), and several thiocarbamate herbicides ...
Exam 3 Key - Chemistry
... 11. (3) The first step of the reaction between a ketone and a Grignard reagent is: a) initial protonation of the C=O oxygen by H+ b) attack of the C=O oxygen upon the Mg c) attack by R- upon the C=O oxygen d) attack by R- upon the C=O carbon e) protonation of the Grignard reagent 12. (4) One of the ...
... 11. (3) The first step of the reaction between a ketone and a Grignard reagent is: a) initial protonation of the C=O oxygen by H+ b) attack of the C=O oxygen upon the Mg c) attack by R- upon the C=O oxygen d) attack by R- upon the C=O carbon e) protonation of the Grignard reagent 12. (4) One of the ...
Alkanes
... Alcohols An alcohol is an organic compound with an — ____ group. The —OH functional group in alcohols is called a hydroxyl group or hydroxy function. ...
... Alcohols An alcohol is an organic compound with an — ____ group. The —OH functional group in alcohols is called a hydroxyl group or hydroxy function. ...
lecture 3 - aldehydes and ketones
... Because aldehydes and ketones lack a hydrogen on the oxygen, they cannot form hydrogen bonds between other aldehyde or ketone molecules. O ...
... Because aldehydes and ketones lack a hydrogen on the oxygen, they cannot form hydrogen bonds between other aldehyde or ketone molecules. O ...
Aldehydes and Ketones - University of Nebraska Omaha
... • The parent chain is the longest chain that contains the carbonyl group. • For an aldehyde, change the suffix from –e to –al; for a ketone change the suffix from –e to –one • For an unsaturated aldehyde or ketone, show the carbon-carbon double bond by changing the infix from –an– to –en–; the locat ...
... • The parent chain is the longest chain that contains the carbonyl group. • For an aldehyde, change the suffix from –e to –al; for a ketone change the suffix from –e to –one • For an unsaturated aldehyde or ketone, show the carbon-carbon double bond by changing the infix from –an– to –en–; the locat ...
Organic Chemistry Notes
... Ethers, like alcohols, contain a single oxygen atom but it is bonded between two C atoms instead of attached to only one. Dimethyl ether, until recently used in oxygenated gasoline, will lower the amount of CO produced in combustion since additional oxygen is introduced intimately with the fuel. How ...
... Ethers, like alcohols, contain a single oxygen atom but it is bonded between two C atoms instead of attached to only one. Dimethyl ether, until recently used in oxygenated gasoline, will lower the amount of CO produced in combustion since additional oxygen is introduced intimately with the fuel. How ...
Phy Properties - Rosebank Progress College
... liquids and more than 17 solids at room temperature. Alkenes – two to four gasses, 5 to15 liquids and more than 15 are solids at room temperature. Alkynes – two to four gasses, 5 to 17 liquids and more than 17 solids at room temperature. ...
... liquids and more than 17 solids at room temperature. Alkenes – two to four gasses, 5 to15 liquids and more than 15 are solids at room temperature. Alkynes – two to four gasses, 5 to 17 liquids and more than 17 solids at room temperature. ...
Organic and Biochemistry
... Organic substances that are soluble in water and other polar solvents have polar groups. • Examples: glucose and ascorbic acid (vitamin C). Soaps and detergents are examples of molecules that have both a polar part (which is water soluble) and a nonpolar part (which is soluble in nonpolar substances ...
... Organic substances that are soluble in water and other polar solvents have polar groups. • Examples: glucose and ascorbic acid (vitamin C). Soaps and detergents are examples of molecules that have both a polar part (which is water soluble) and a nonpolar part (which is soluble in nonpolar substances ...
Organic Chemistry & Polymers
... - MEK – methyl ethyl ketone – solvent in oil paints and glues. Also formed in the blood stream in ketosis (a problem in diabetes). ...
... - MEK – methyl ethyl ketone – solvent in oil paints and glues. Also formed in the blood stream in ketosis (a problem in diabetes). ...
CARBONYL COMPOUNDS - Aldehydes and Ketones C=O C C C
... C2H5COCH2CH3(l) + 3 [O] ——> C2H5COOH(l) + ...
... C2H5COCH2CH3(l) + 3 [O] ——> C2H5COOH(l) + ...
Organic Chemistry
... General formula can be written to represent all member of a series Each successive member of the series differs by a common structural unit The chemistry of any one member is similar to that of the other members ...
... General formula can be written to represent all member of a series Each successive member of the series differs by a common structural unit The chemistry of any one member is similar to that of the other members ...
Click for Section 2.9 notes
... Some Derivatives of Alkanes • When H atoms in alkanes are replaced by heteroatoms (atoms other than C or H), then we have introduced a functional group into the alkane • When H is replaced by –OH, the compound is an alcohol • Alcohols are also named by the number of C atoms ...
... Some Derivatives of Alkanes • When H atoms in alkanes are replaced by heteroatoms (atoms other than C or H), then we have introduced a functional group into the alkane • When H is replaced by –OH, the compound is an alcohol • Alcohols are also named by the number of C atoms ...
The next bullet point down, tells us that the 1 H NMR spectra of
... contains four carbon atoms and the hydroxyl group is on carbon-2. The fifth bullet point shows us the 1H NMR of compound 3. From the spectrum, we can identify four different peaks, three of which are labelled as A, B and C. Since there are four different peaks in the 1H NMR spectrum, this alcohol mu ...
... contains four carbon atoms and the hydroxyl group is on carbon-2. The fifth bullet point shows us the 1H NMR of compound 3. From the spectrum, we can identify four different peaks, three of which are labelled as A, B and C. Since there are four different peaks in the 1H NMR spectrum, this alcohol mu ...
Carbohydrates Typical formula: C (H O) , eg glucose: C H O
... The chiral center that determines D- or L- is the one furtherest from the carbonyl. Most naturally occurring sugars are in the D- family. The family name for sugars has the suffix -ose. Monosaccharides can be characterized as to how many ...
... The chiral center that determines D- or L- is the one furtherest from the carbonyl. Most naturally occurring sugars are in the D- family. The family name for sugars has the suffix -ose. Monosaccharides can be characterized as to how many ...
CHM230 OXIDATION OF CYCLOHEXANOL TO CYCLOHEXANONE
... As you can see from its formula, the chlorine in hypochlorous acid has an oxidation state of +1. Recall that chlorine normally has an oxidation number of -1. This deficiency of electrons makes this particular species very reactive. Since this is a very strong oxidizing agent, we will be generating i ...
... As you can see from its formula, the chlorine in hypochlorous acid has an oxidation state of +1. Recall that chlorine normally has an oxidation number of -1. This deficiency of electrons makes this particular species very reactive. Since this is a very strong oxidizing agent, we will be generating i ...
Chapter 5. An Overview of Organic Reactions
... Branched substituents are numbered starting from the carbon of the substituent attached to the parent chain. From this carbon, count the number of carbons in the longest chain of the substituent. The substituent is named as an alkyl group based on the number of carbons in this chain. Numbering of th ...
... Branched substituents are numbered starting from the carbon of the substituent attached to the parent chain. From this carbon, count the number of carbons in the longest chain of the substituent. The substituent is named as an alkyl group based on the number of carbons in this chain. Numbering of th ...
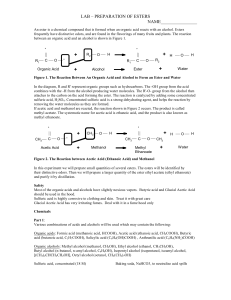
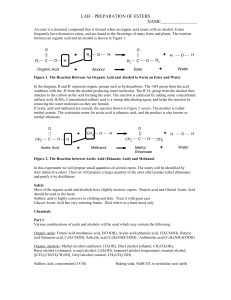
An ester is a chemical compound that is formed when an organic
... In the diagram, R and R' represent organic groups such as hydrocarbons. The -OH group from the acid combines with the -H from the alcohol producing water molecules. The R'-O- group from the alcohol then attaches to the carbon on the acid forming the ester. The reaction is catalyzed by adding some co ...
... In the diagram, R and R' represent organic groups such as hydrocarbons. The -OH group from the acid combines with the -H from the alcohol producing water molecules. The R'-O- group from the alcohol then attaches to the carbon on the acid forming the ester. The reaction is catalyzed by adding some co ...
Organic Chemistry : Ch. 19
... The molecular formula for both of these is C4H10 Even though the formula is the same the properties of these compounds is very different. This is an example of isomers. Isomers are compounds with the same formula but different chemical and physical properties. (Boiling point, etc…) ...
... The molecular formula for both of these is C4H10 Even though the formula is the same the properties of these compounds is very different. This is an example of isomers. Isomers are compounds with the same formula but different chemical and physical properties. (Boiling point, etc…) ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.