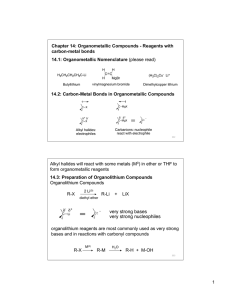
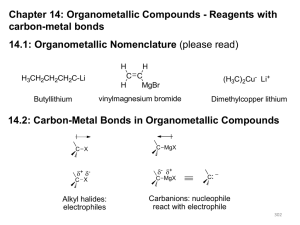
Organometallic Compounds - Reagents
... to a starting compound using known and reliable reactions. “it is a problem solving technique for transforming the structure of a synthetic target molecule (TM) to a sequence of progressively simpler structures along the pathway which ultimately leads to simple or commercially available starting mat ...
... to a starting compound using known and reliable reactions. “it is a problem solving technique for transforming the structure of a synthetic target molecule (TM) to a sequence of progressively simpler structures along the pathway which ultimately leads to simple or commercially available starting mat ...
File - the prayas tutorial
... Ans. Because Grignard reagents have a very strong affinity for H+ ions. In presence of water, they abstract H+ ions from water and form alkanes. To prevent this, they should be prepared under anhydrous conditions. Q. 7. Haloalkanes react with KCN to form alkyl cyanides as major product while AgCN fo ...
... Ans. Because Grignard reagents have a very strong affinity for H+ ions. In presence of water, they abstract H+ ions from water and form alkanes. To prevent this, they should be prepared under anhydrous conditions. Q. 7. Haloalkanes react with KCN to form alkyl cyanides as major product while AgCN fo ...
Carboxylic Acid Questions 1.-Arrange the following in order of (i
... CCl3CO2H < CH3CO2H < CH3CH2SH < CH3CH2OH Remember the lower the pKa the stronger the acid, so once you have part (i), this is just the opposite. Tip: When asked about pKa trends, it may be easier to think in terms of acidity then remember to flip the order. 2: Note the identical nature of the reacti ...
... CCl3CO2H < CH3CO2H < CH3CH2SH < CH3CH2OH Remember the lower the pKa the stronger the acid, so once you have part (i), this is just the opposite. Tip: When asked about pKa trends, it may be easier to think in terms of acidity then remember to flip the order. 2: Note the identical nature of the reacti ...
Classification of Organic Compounds
... The emphasis in this experiment is on the methods of organic qualitative analysis. Nevertheless, a brief discussion of the properties and molecular structures of the substances to be tested should prove useful. Organic compounds are often defined as those substances containing carbon; most contain h ...
... The emphasis in this experiment is on the methods of organic qualitative analysis. Nevertheless, a brief discussion of the properties and molecular structures of the substances to be tested should prove useful. Organic compounds are often defined as those substances containing carbon; most contain h ...
26-2: Aldehydes and Ketones
... Carbonyl is in the middle of a hydrocarbon chain General formula: _____ (or R-CORl) Naming: ...
... Carbonyl is in the middle of a hydrocarbon chain General formula: _____ (or R-CORl) Naming: ...
Grignard Reagents
... to a starting compound using known and reliable reactions. “it is a problem solving technique for transforming the structure of a synthetic target molecule (TM) to a sequence of progressively simpler structures along the pathway which ultimately leads to simple or commercially available starting mat ...
... to a starting compound using known and reliable reactions. “it is a problem solving technique for transforming the structure of a synthetic target molecule (TM) to a sequence of progressively simpler structures along the pathway which ultimately leads to simple or commercially available starting mat ...
Organic Reactions
... CAUTION - Sodium hydroxide is a very caustic material that can cause severe skin burns. Eye burns caused by sodium hydroxide are progressive: what at rst appears to be a minor irritation can develop into a severe injury unless the chemical is completely ushed from the eye. If sodium hydroxide come ...
... CAUTION - Sodium hydroxide is a very caustic material that can cause severe skin burns. Eye burns caused by sodium hydroxide are progressive: what at rst appears to be a minor irritation can develop into a severe injury unless the chemical is completely ushed from the eye. If sodium hydroxide come ...
Esters, fats and oils
... Esters can be named from the names of the carboxylic acid and alcohol used to make them e.g. methyl ethanoate is made from ethanoic acid and methanol. ...
... Esters can be named from the names of the carboxylic acid and alcohol used to make them e.g. methyl ethanoate is made from ethanoic acid and methanol. ...
Improvements & new technologies
... Biodiesel is defined as fatty acid methyl or ethyl esters from vegetable oils or animal fats when they are used as fuel in diesel engines and heating systems. ...
... Biodiesel is defined as fatty acid methyl or ethyl esters from vegetable oils or animal fats when they are used as fuel in diesel engines and heating systems. ...
Name (Last, First):
... Make a model of ethanal. The organic chemist uses the term “oxidize” to refer to either of two processes: 1. The removal of two hydrogen atoms, with the formation of water (as in 2 a above) OR 2. The addition of an oxygen atom into the molecule. How would either of these two processes affect the “ox ...
... Make a model of ethanal. The organic chemist uses the term “oxidize” to refer to either of two processes: 1. The removal of two hydrogen atoms, with the formation of water (as in 2 a above) OR 2. The addition of an oxygen atom into the molecule. How would either of these two processes affect the “ox ...
ALDEHYDES & KETONES - Rogue Community College
... Aliphatic chains NOT as part of ... Aliphatic rings or Aromatic rings ...
... Aliphatic chains NOT as part of ... Aliphatic rings or Aromatic rings ...
Quiz #3 will be concerning Types of Organic Compounds and types
... 5. Ketone – any of a class of organic compounds containing the carbonyl group (C=O) whose carbon atom is joined to two other carbon atoms. 6. Ester – a compound with the general formula RCOOR’ (where R is a hydrocarbon group or a hydrogen and R’ is a hydrocarbon group.) It is formed from an alcohol ...
... 5. Ketone – any of a class of organic compounds containing the carbonyl group (C=O) whose carbon atom is joined to two other carbon atoms. 6. Ester – a compound with the general formula RCOOR’ (where R is a hydrocarbon group or a hydrogen and R’ is a hydrocarbon group.) It is formed from an alcohol ...
IUBAC naming organic compounds
... appropriate IUPAC suffix in the designated answer box. In the second answer box enter a number indicating the number of carbon atoms in the longest chain. ...
... appropriate IUPAC suffix in the designated answer box. In the second answer box enter a number indicating the number of carbon atoms in the longest chain. ...
Module: 3 Lecture: 15 BUTYL ALCOHOL
... INTRODUCTION Butyl alcohol or butanol, C4H9OH is a primary alcohol with 4 carbon atoms. It belongs to the higher alcohols and branched-chain alcohols. Butanol can be produced by fermentation of biomass by bacteria. When produced biologically called as bio-butanol. It is primarily used as a solvent, ...
... INTRODUCTION Butyl alcohol or butanol, C4H9OH is a primary alcohol with 4 carbon atoms. It belongs to the higher alcohols and branched-chain alcohols. Butanol can be produced by fermentation of biomass by bacteria. When produced biologically called as bio-butanol. It is primarily used as a solvent, ...
Biehl PPT Part2
... From ethyl benzene? Side-chain oxidation!!!! Appears as if we could start with benzoic acid and introduce ethyl group by EtLi. ...
... From ethyl benzene? Side-chain oxidation!!!! Appears as if we could start with benzoic acid and introduce ethyl group by EtLi. ...
SCH4U Unit Test Name
... ____ 16. Which statement below is incorrect? a. the smallest aldehyde has the formula HCOH b. a carbonyl carbon consists of a carbon-oxygen double bond c. in an aldehyde, the carbonyl carbon is always bonded to a hydrogen atom d. Ketones are more soluble in water than alcohols with the equivalent n ...
... ____ 16. Which statement below is incorrect? a. the smallest aldehyde has the formula HCOH b. a carbonyl carbon consists of a carbon-oxygen double bond c. in an aldehyde, the carbonyl carbon is always bonded to a hydrogen atom d. Ketones are more soluble in water than alcohols with the equivalent n ...
Microsoft Word
... conditions such as with hydrides, alkylating reagents, Griganard reagents and organometallic reagents In addition, they also serve as stable protecting group in peptide, nucleoside and nucleotide, carbohydrate and steroid chemistry. Tetrahydropyranylation is a general and important protecting group ...
... conditions such as with hydrides, alkylating reagents, Griganard reagents and organometallic reagents In addition, they also serve as stable protecting group in peptide, nucleoside and nucleotide, carbohydrate and steroid chemistry. Tetrahydropyranylation is a general and important protecting group ...
Eötvös Loránd Science University
... Preparation of acid chlorides and anhydrides. 8. lecture (Week 9) Halogenation of -carbon atom. Reactivity of halogenated acids. Carboxylic acid derivatives - Structure of carboxylic acid derivatives (acid chlorides, anhydrides, esters, amides, nitriles). Important acid derivatives. Chemical prope ...
... Preparation of acid chlorides and anhydrides. 8. lecture (Week 9) Halogenation of -carbon atom. Reactivity of halogenated acids. Carboxylic acid derivatives - Structure of carboxylic acid derivatives (acid chlorides, anhydrides, esters, amides, nitriles). Important acid derivatives. Chemical prope ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.