chm 103 general chemistry
... H. Organics Containing Oxygen 1. Alcohols: Organics containing –O—H (hydroxyl) groups a. Methanol (methyl alcohol): CH3OH Imagine methane (CH4) with one H replaced by OH (but it is not made this way) Generally manufactured from synthesis gas (CO + H2) under conditions of high temperature and pre ...
... H. Organics Containing Oxygen 1. Alcohols: Organics containing –O—H (hydroxyl) groups a. Methanol (methyl alcohol): CH3OH Imagine methane (CH4) with one H replaced by OH (but it is not made this way) Generally manufactured from synthesis gas (CO + H2) under conditions of high temperature and pre ...
File
... Properties of Alcohols and Ethers The properties of alcohols are a function of the hydrogen bonding associated with the highly polar "OH" bond. Short chain alcohols like methanol, ethanol, and propanols have the unique property of being soluble in nonpolar and polar solvents. This makes them very us ...
... Properties of Alcohols and Ethers The properties of alcohols are a function of the hydrogen bonding associated with the highly polar "OH" bond. Short chain alcohols like methanol, ethanol, and propanols have the unique property of being soluble in nonpolar and polar solvents. This makes them very us ...
Do you know the topic today?
... The sources are used Ethanol has been made by fermentation for several thousand years. The raw material is some form of starch or sugar such as : wheat ...
... The sources are used Ethanol has been made by fermentation for several thousand years. The raw material is some form of starch or sugar such as : wheat ...
Slides for Chapter 1-4 - Department of Chemistry and Physics
... Nucleophiles will replace the halide in C-X bonds of many alkyl halides(reaction as Lewis base) Nucleophiles that are Brønsted bases produce elimination ...
... Nucleophiles will replace the halide in C-X bonds of many alkyl halides(reaction as Lewis base) Nucleophiles that are Brønsted bases produce elimination ...
bond enthalpy activity sheet - Deans Community High School
... A pupil was investigating the enthalpy of combustion of an alcohol. Water was heated in a copper calorimeter using an alcohol burner. (a) Write down 5 measurements he would need to take during the experiment. (b) The answer that was obtained was very different to the value given in data booklet. Giv ...
... A pupil was investigating the enthalpy of combustion of an alcohol. Water was heated in a copper calorimeter using an alcohol burner. (a) Write down 5 measurements he would need to take during the experiment. (b) The answer that was obtained was very different to the value given in data booklet. Giv ...
Organic Compounds
... or more hydrogen atoms replaced by another nonmetallic atom eg. bromomethane - CH3Br methanol - CH3OH ...
... or more hydrogen atoms replaced by another nonmetallic atom eg. bromomethane - CH3Br methanol - CH3OH ...
notes fill in File
... hydrocarbon chain or ring is ______________ by a different atom or group of atoms Example: alcohols, organic acids, esters, and halogen derivatives ________________ = (substituted hydrocarbons) have one or more hydrogen atoms replaced by an -OH group (hydroxyl group) The simplest alcohol is methanol ...
... hydrocarbon chain or ring is ______________ by a different atom or group of atoms Example: alcohols, organic acids, esters, and halogen derivatives ________________ = (substituted hydrocarbons) have one or more hydrogen atoms replaced by an -OH group (hydroxyl group) The simplest alcohol is methanol ...
N.b. A catalyst is a species which speeds up a chemical reaction but
... i) React with aldehydes and ketones forming secondary and tertiary alcohols respectively. ii) React with carbon dioxide. RMgBr + CO2 ...
... i) React with aldehydes and ketones forming secondary and tertiary alcohols respectively. ii) React with carbon dioxide. RMgBr + CO2 ...
1 - contentextra
... Saturated A compound which contains only single bonds between carbon atoms, no carbon–carbon double or triple bonds. Secondary carbon atom A carbon atom that is attached to the functional group and also to one hydrogen atom. SN1 Substitution nucleophilic unimolecular. A substitution reaction in whic ...
... Saturated A compound which contains only single bonds between carbon atoms, no carbon–carbon double or triple bonds. Secondary carbon atom A carbon atom that is attached to the functional group and also to one hydrogen atom. SN1 Substitution nucleophilic unimolecular. A substitution reaction in whic ...
Non-Heme Iron Catalyzed Oxidation of Alkanes to Alcohols via
... The ability of the binuclear non-heme ferrous complex Fe22+(H2Hbamb)2(NMeIm)2 (H2Hbamb: 2,3-bis(2-hydroxybenzamido)2,3-dimethylbutane) to react with oxygen atom donor molecules, peroxides or peracids and catalyze the hydroxylation of alkanes and arenes will be discussed. Mechanistic studies demonstr ...
... The ability of the binuclear non-heme ferrous complex Fe22+(H2Hbamb)2(NMeIm)2 (H2Hbamb: 2,3-bis(2-hydroxybenzamido)2,3-dimethylbutane) to react with oxygen atom donor molecules, peroxides or peracids and catalyze the hydroxylation of alkanes and arenes will be discussed. Mechanistic studies demonstr ...
Organic Reactions
... distinguish between alkenes and alkanes. If reddishbrown color of Br2 disappears when added to unknown, the unknown has alkenes in it. ...
... distinguish between alkenes and alkanes. If reddishbrown color of Br2 disappears when added to unknown, the unknown has alkenes in it. ...
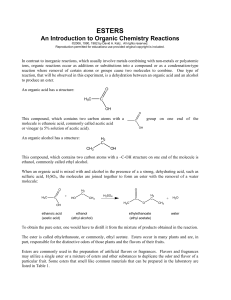
Preparation of Esters
... An ester has the functional group , which is also known as an ester link. In the laboratory, an ester is usually formed from the reaction of a carboxylic (organic) acid and an alcohol, giving an ester and water as the products. This is an example of a condensation reaction, in which two molecules li ...
... An ester has the functional group , which is also known as an ester link. In the laboratory, an ester is usually formed from the reaction of a carboxylic (organic) acid and an alcohol, giving an ester and water as the products. This is an example of a condensation reaction, in which two molecules li ...
C7 Revision Notes 2015
... reacting an alcohol with an organic acid. A little sulfuric acid is needed as a catalyst. •They have distinctive pleasant (usually) smells. •They are responsible for the smells and flavours of fruits •They are used in products such as food, perfumes, solvents and plasticisers •Some esters used in pe ...
... reacting an alcohol with an organic acid. A little sulfuric acid is needed as a catalyst. •They have distinctive pleasant (usually) smells. •They are responsible for the smells and flavours of fruits •They are used in products such as food, perfumes, solvents and plasticisers •Some esters used in pe ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... (Source: California State Chemistry Standard 10. Organic and Biochemistry) Scientific progress is made by asking meaningful questions and conducting careful investigations. As a basis for understanding this concept, and to address the content the other four strands, students should develop their o ...
... (Source: California State Chemistry Standard 10. Organic and Biochemistry) Scientific progress is made by asking meaningful questions and conducting careful investigations. As a basis for understanding this concept, and to address the content the other four strands, students should develop their o ...
Lab Evaporation and Intermolecular Attraction
... alkanes are pentane, C5H12, and hexane, C6H14. In addition to carbon and hydrogen atoms, alcohols also contain the -OH functional group. Methanol, CH3OH, and ethanol, C2H5OH, are two of the alcohols that we will use in this experiment. You will examine the molecular structure of alkanes and alcohols ...
... alkanes are pentane, C5H12, and hexane, C6H14. In addition to carbon and hydrogen atoms, alcohols also contain the -OH functional group. Methanol, CH3OH, and ethanol, C2H5OH, are two of the alcohols that we will use in this experiment. You will examine the molecular structure of alkanes and alcohols ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.