Carbonyl Chemistry (12 Lectures) Aldehydes and Ketones
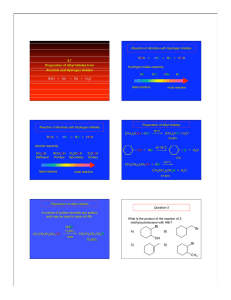
... Formation of alcohols via addition of Grignard reagents to aldehydes and ketones is carried out in two separate steps Step 1: Addition of the nucleophilic alkyl group to the carbonyl carbon, aided by Lewis acid interaction between MgX+ and the carbonyl oxygen. The product of this step is a halomagne ...
... Formation of alcohols via addition of Grignard reagents to aldehydes and ketones is carried out in two separate steps Step 1: Addition of the nucleophilic alkyl group to the carbonyl carbon, aided by Lewis acid interaction between MgX+ and the carbonyl oxygen. The product of this step is a halomagne ...
top organomet chem-2006-19-207 pauson
... With the focus on green chemistry, it is actually impossible to think on an industrial chemical reaction, which involves transition metal complexes, that is not efficiently catalytic. The chemical industry demands atom economical reactions, that is, those in which substrates are transformed into prod ...
... With the focus on green chemistry, it is actually impossible to think on an industrial chemical reaction, which involves transition metal complexes, that is not efficiently catalytic. The chemical industry demands atom economical reactions, that is, those in which substrates are transformed into prod ...
New Applications for Sulfur-Based Leaving Groups in Synthesis
... Kharasch et al. therefore hypothesised that the presence of trace oxygen in the reaction mixure allowed for the formation of small amounts of allyl bromide peroxide which could undergo cleavage to yield a peroxide radical. This radical can then abstract a hydrogen atom from hydrogen bromide to form ...
... Kharasch et al. therefore hypothesised that the presence of trace oxygen in the reaction mixure allowed for the formation of small amounts of allyl bromide peroxide which could undergo cleavage to yield a peroxide radical. This radical can then abstract a hydrogen atom from hydrogen bromide to form ...
Chapter: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
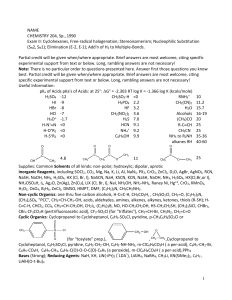
... For C4H9Br, two primary halides are possible CH3CH2CH2CH2Br (n-butyl bromide) and (CH3)2CHCH2Br (iso-butyl bromide). Since A is not normal –butyl bromide, it must be isobutyl bromide. ...
... For C4H9Br, two primary halides are possible CH3CH2CH2CH2Br (n-butyl bromide) and (CH3)2CHCH2Br (iso-butyl bromide). Since A is not normal –butyl bromide, it must be isobutyl bromide. ...
4.7 Preparation of Alkyl Halides from Alcohols and Hydrogen
... A) the alkyloxonium ion intermediate B) the transition step of the bimolecular proton transfer C) the transition state of the attack of the nucleophile on the carbocation D) the transition state of the unimolecular ...
... A) the alkyloxonium ion intermediate B) the transition step of the bimolecular proton transfer C) the transition state of the attack of the nucleophile on the carbocation D) the transition state of the unimolecular ...
Synthesis of Amide Bond Isosteres Incorporated
... Susceptibility to collagen induced arthritis is associated with the mouse MHCII molecule H2Aq. The rat CII260-267 sequence has been identified as the minimal glycopeptide required for binding to H-2Aq and for eliciting a proper T cell response. This master thesis describes the synthesis and incorpor ...
... Susceptibility to collagen induced arthritis is associated with the mouse MHCII molecule H2Aq. The rat CII260-267 sequence has been identified as the minimal glycopeptide required for binding to H-2Aq and for eliciting a proper T cell response. This master thesis describes the synthesis and incorpor ...
3.2 Organic Synthesis (Reaction Pathways)
... is the Radical Substitution of an alkane using halogens such as bromine and chlorine. ...
... is the Radical Substitution of an alkane using halogens such as bromine and chlorine. ...
ALCOHOLS AND ETHERS
... (Figure 15-2b). However, there is a relatively broad band around 3350 cm-l, which is characteristic of hydrogen-bonded hydroxyl groups. The shift in frequency of about 300 cm-I arises because hydrogen bonding weakens the 0 - H bond; its absorption frequency then will be lower. The association band i ...
... (Figure 15-2b). However, there is a relatively broad band around 3350 cm-l, which is characteristic of hydrogen-bonded hydroxyl groups. The shift in frequency of about 300 cm-I arises because hydrogen bonding weakens the 0 - H bond; its absorption frequency then will be lower. The association band i ...
amine
... • A large number of physiologically active compounds are derived from 2-phenethylamine (C6H5CH2CH2NH2). These compounds include adrenaline, noradrenaline, methamphetamine, and mescaline. Each contains a benzene ring bonded to a two-carbon unit with a nitrogen atom (shown in red). ...
... • A large number of physiologically active compounds are derived from 2-phenethylamine (C6H5CH2CH2NH2). These compounds include adrenaline, noradrenaline, methamphetamine, and mescaline. Each contains a benzene ring bonded to a two-carbon unit with a nitrogen atom (shown in red). ...
synthetic approaches for quinoline and isoquinoline
... Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, S.I.T.M, LKO, India Received: 10 March 2011, Revised and Accepted: 11 April 2011 ABSTRACT The Quinoline and Isoquinoline nucleus is found to be very important in pharmacy field. In recent years, a lot of synthetic drugs have been sy ...
... Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, S.I.T.M, LKO, India Received: 10 March 2011, Revised and Accepted: 11 April 2011 ABSTRACT The Quinoline and Isoquinoline nucleus is found to be very important in pharmacy field. In recent years, a lot of synthetic drugs have been sy ...
Title The Cyanide-Ion Cleavage of Organic Disulfides
... alkyl aryl sulfides in high yields in the presence of cyanide ion. The results of this novel reaction are summarized in Table 4. It is expected that alkyl aryl sulfides would be derived from aryl thiocyanates. Thus, aryl thiocyanates were found to react with alcohols in the presence of cyanide ion t ...
... alkyl aryl sulfides in high yields in the presence of cyanide ion. The results of this novel reaction are summarized in Table 4. It is expected that alkyl aryl sulfides would be derived from aryl thiocyanates. Thus, aryl thiocyanates were found to react with alcohols in the presence of cyanide ion t ...
Organic Chemistry Notes by Jim Maxka jim.maxka
... reaction through. PBr3 to make R-Br and SOCl2.to make R-Cl (can use PCl5 as well). In general, we use Al, P, S, and Si reagents with C-O because, the formation of the Al-O P-O, S-O, and Si-O bond is more stabilizing than the C-O. That means that there is a thermodynamic driving force for the C-O bon ...
... reaction through. PBr3 to make R-Br and SOCl2.to make R-Cl (can use PCl5 as well). In general, we use Al, P, S, and Si reagents with C-O because, the formation of the Al-O P-O, S-O, and Si-O bond is more stabilizing than the C-O. That means that there is a thermodynamic driving force for the C-O bon ...
Chapter 1
... 2. Dropping the final –e of the parent name and adding the suffix –amine 3. Number the parent chain to give the amine carbon the lowest possible number 4. Name and number all substituents as usual ...
... 2. Dropping the final –e of the parent name and adding the suffix –amine 3. Number the parent chain to give the amine carbon the lowest possible number 4. Name and number all substituents as usual ...
Presentation
... c) the formation of bond between oxygen of COO group of acid and carbon of alcohol d) the cleavage of C–OH bond of acid ...
... c) the formation of bond between oxygen of COO group of acid and carbon of alcohol d) the cleavage of C–OH bond of acid ...
HMDS - Sigma
... as necessary to meet the needs of a specific application. Always take proper safety precautions when using a silylating reagent – consult MSDS for specific handling information. HMDS is extremely sensitive to moisture and should be handled under dry conditions. Prepare a reagent blank (all component ...
... as necessary to meet the needs of a specific application. Always take proper safety precautions when using a silylating reagent – consult MSDS for specific handling information. HMDS is extremely sensitive to moisture and should be handled under dry conditions. Prepare a reagent blank (all component ...
Chloroperbenzoic_aci..
... Secondary amines have been oxidized to hydroxylamines with m-CPBA.26b In this reaction, substantial amounts of nitrone as byproduct are expected. (The best method for the preparation of hydroxylamines is to oxidize the secondary amine with 2-(phenylsulfonyl)-3-aryloxaziridine (see e.g. (±) trans-2(P ...
... Secondary amines have been oxidized to hydroxylamines with m-CPBA.26b In this reaction, substantial amounts of nitrone as byproduct are expected. (The best method for the preparation of hydroxylamines is to oxidize the secondary amine with 2-(phenylsulfonyl)-3-aryloxaziridine (see e.g. (±) trans-2(P ...
Learning Guide for Chapter 16
... I. Introduction to ethers, sulfides, and epoxides II. Nomenclature of ethers III. Synthesis of ethers and sulfides IV. Reactions of ethers and sulfides V. Synthesis of epoxides VI. Reactions of epoxides VII. Review of reactions I. Introduction to ethers, epoxides, and thioethers Defintion and exampl ...
... I. Introduction to ethers, sulfides, and epoxides II. Nomenclature of ethers III. Synthesis of ethers and sulfides IV. Reactions of ethers and sulfides V. Synthesis of epoxides VI. Reactions of epoxides VII. Review of reactions I. Introduction to ethers, epoxides, and thioethers Defintion and exampl ...
Dehydration of ROH
... depends primarily on the degree of stabilization and solvation of the alkoxide ion. • The negatively charged oxygens of methoxide and ethoxide are about as accessible as the oxygen of hydroxide ion for solvation; these alcohol are about as acidic as water. • As the bulk of the alkyl group increases, ...
... depends primarily on the degree of stabilization and solvation of the alkoxide ion. • The negatively charged oxygens of methoxide and ethoxide are about as accessible as the oxygen of hydroxide ion for solvation; these alcohol are about as acidic as water. • As the bulk of the alkyl group increases, ...
Catalytic Nucleophilic Fluorination of Secondary and Tertiary
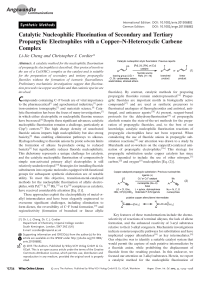
... catalyzed the formation of propargylic fluoride 2 a in good yield from propargylic tosylate 1 a-OTs in the presence of Et3N·3 HF as the fluoride source at 30 8C,[27] with the formation of only a trace amount of enyne 3 (Table 1, entry 1). To our knowledge, Cu(NHC) complexes have not previously been ...
... catalyzed the formation of propargylic fluoride 2 a in good yield from propargylic tosylate 1 a-OTs in the presence of Et3N·3 HF as the fluoride source at 30 8C,[27] with the formation of only a trace amount of enyne 3 (Table 1, entry 1). To our knowledge, Cu(NHC) complexes have not previously been ...
Chapter 13. Alcohols, Diols, and Ethers
... Can be cleaved by heating with HI (more common) or HBr. Need a strong Brönsted or Lewis acid and a strong nucleophile. Usually, methyl ether C-O and benzyl ether C-O are those that can be cleaved. Modern methods for cleaving ethers include the use of BBr3 and AlCl3 + HSCH2CH3. O ...
... Can be cleaved by heating with HI (more common) or HBr. Need a strong Brönsted or Lewis acid and a strong nucleophile. Usually, methyl ether C-O and benzyl ether C-O are those that can be cleaved. Modern methods for cleaving ethers include the use of BBr3 and AlCl3 + HSCH2CH3. O ...
215-216 HH W12-notes
... Can be cleaved by heating with HI (more common) or HBr. Need a strong Brönsted or Lewis acid and a strong nucleophile. Usually, methyl ether C-O and benzyl ether C-O are those that can be cleaved. Modern methods for cleaving ethers include the use of BBr3 and AlCl3 + HSCH2CH3. O ...
... Can be cleaved by heating with HI (more common) or HBr. Need a strong Brönsted or Lewis acid and a strong nucleophile. Usually, methyl ether C-O and benzyl ether C-O are those that can be cleaved. Modern methods for cleaving ethers include the use of BBr3 and AlCl3 + HSCH2CH3. O ...
Chapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones
... addition forming the conjugate acid of C=O Addition yields a hydroxy ether, called a hemiacetal (reversible); further reaction can occur Protonation of the –OH and loss of water leads to an oxonium ion, R2C=OR+ to which a second alcohol adds to form the acetal ...
... addition forming the conjugate acid of C=O Addition yields a hydroxy ether, called a hemiacetal (reversible); further reaction can occur Protonation of the –OH and loss of water leads to an oxonium ion, R2C=OR+ to which a second alcohol adds to form the acetal ...
Chem 240 - Napa Valley College
... mean that you would get a lot of by-products but you would end up getting more product also (SN1 major, E1 minor). 4) There are a number of ways of substituting a halogen for an alcohol group, but some ways are better than others. What advantage is there in using PCl3 rather than HCl in the chloride ...
... mean that you would get a lot of by-products but you would end up getting more product also (SN1 major, E1 minor). 4) There are a number of ways of substituting a halogen for an alcohol group, but some ways are better than others. What advantage is there in using PCl3 rather than HCl in the chloride ...
Hofmann–Löffler reaction

The Hofmann–Löffler reaction (also referred to as Hofmann–Löffler–Freytag reaction, Löffler–Freytag reaction, Löffler–Hofmann reaction, as well as Löffler's method) is an organic reaction in which a cyclic amine 2 (pyrrolidine or, in some cases, piperidine) is generated by thermal or photochemical decomposition of N-halogenated amine 1 in the presence of a strong acid (concentrated sulfuric acid or concentrated CF3CO2H). The Hofmann–Löffler–Freytag reaction proceeds via an intramolecular hydrogen atom transfer to a nitrogen-centered radical and is an example of a remote intramolecular free radical C–H functionalization.