Acidity of Alcohols
... • Alcohols and phenols form hydrogen bonds, and hence they have relatively high boiling points. This also makes the lower alcohols miscible with water. As the R group becomes larger, the solubility of alcohols in water ...
... • Alcohols and phenols form hydrogen bonds, and hence they have relatively high boiling points. This also makes the lower alcohols miscible with water. As the R group becomes larger, the solubility of alcohols in water ...
Isoindolone Formation via Intramolecular Diels
... solution in toluene which could be used directly in the next stage without the need for purification. Reductive amination with 4-trifluoromethoxybenzylamine (4) and a NaBH4/EtOH mixture worked well and, satisfyingly, gave an excellent purification procedure, the inseparable input mixture of 2formyl-3-c ...
... solution in toluene which could be used directly in the next stage without the need for purification. Reductive amination with 4-trifluoromethoxybenzylamine (4) and a NaBH4/EtOH mixture worked well and, satisfyingly, gave an excellent purification procedure, the inseparable input mixture of 2formyl-3-c ...
Development of Multi-Component Reactions using Catalytically Generated Allyl Metal Reagents
... In the past decades, the development of effective multi-component based synthesis has played an important role to achieve high atom economy and sustainable chemistry.1-7 The major challenges in this field are compatibility between the reagents and catalysts present to prevent catalyst inhibition and ...
... In the past decades, the development of effective multi-component based synthesis has played an important role to achieve high atom economy and sustainable chemistry.1-7 The major challenges in this field are compatibility between the reagents and catalysts present to prevent catalyst inhibition and ...
Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
... water. The reaction with R’ COCI is carried out in the presence of pyridine so as to neutralise HCI which is formed during the reaction. The introduction of acetyl (CH3CO-) group in phenols is known as acetylation. Acetylation of salicylic acid produces aspirin. ...
... water. The reaction with R’ COCI is carried out in the presence of pyridine so as to neutralise HCI which is formed during the reaction. The introduction of acetyl (CH3CO-) group in phenols is known as acetylation. Acetylation of salicylic acid produces aspirin. ...
Aromatic Substitution Reactions
... ophile, in a fashion very similar to the addition reactions described in Chapter 11, which begin by reaction of an electrophile with the pi electrons of an alkene. This results in the formation of a carbocation called an arenium ion. Removal of a proton from the arenium ion by some weak base that is ...
... ophile, in a fashion very similar to the addition reactions described in Chapter 11, which begin by reaction of an electrophile with the pi electrons of an alkene. This results in the formation of a carbocation called an arenium ion. Removal of a proton from the arenium ion by some weak base that is ...
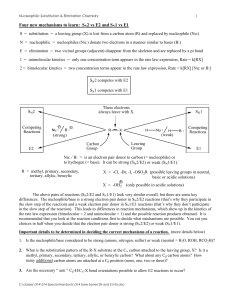
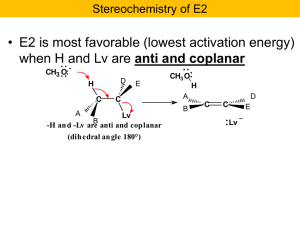
Four new mechanisms to learn: SN2 vs E2 and SN1 vs E1
... The above pairs of reactions (SN2/E2 and SN1/E1) look very similar overall, but there are some key differences. The nucleophile/base is a strong electron pair donor in SN2/E2 reactions (that’s why they participate in the slow step of the reaction) and a weak electron pair donor in SN1/E1 reactions ( ...
... The above pairs of reactions (SN2/E2 and SN1/E1) look very similar overall, but there are some key differences. The nucleophile/base is a strong electron pair donor in SN2/E2 reactions (that’s why they participate in the slow step of the reaction) and a weak electron pair donor in SN1/E1 reactions ( ...
Applications of Phosphorus, Sulfur, Silicon and Boron Chemistry:
... Summary of key points A single diastereoisomer of the starting β-hydroxysilane gives a single isomer of the alkene, and the other diastereoisomer will always give the other alkene isomer as product. Thus the elimination step is stereospecific. The synthesis of the β-hydroxysilane is diastereoselect ...
... Summary of key points A single diastereoisomer of the starting β-hydroxysilane gives a single isomer of the alkene, and the other diastereoisomer will always give the other alkene isomer as product. Thus the elimination step is stereospecific. The synthesis of the β-hydroxysilane is diastereoselect ...
Crystallization and Determination of Melting and Boiling Points
... components in complex mixtures can be separated for identification or purification purposes. (Adsorption is the binding of molecules to the surface of another substance.) The utilization of a moving (or mobile) phase and a stationary phase is common to all chromatographic separation techniques. A mi ...
... components in complex mixtures can be separated for identification or purification purposes. (Adsorption is the binding of molecules to the surface of another substance.) The utilization of a moving (or mobile) phase and a stationary phase is common to all chromatographic separation techniques. A mi ...
Limitations in Determining Enantiomeric Excess of Alcohols by 31P
... assuming that meso 1/meso 2 ratio follows the same value observed for the racemic mixture (Table 1). This strategy was necessary because the meso 2 signal, in this particular example, is overlapped by the monoalkyl phosphonated derivative (Table 1, Figs. 2d and 2e). This result was compatible with t ...
... assuming that meso 1/meso 2 ratio follows the same value observed for the racemic mixture (Table 1). This strategy was necessary because the meso 2 signal, in this particular example, is overlapped by the monoalkyl phosphonated derivative (Table 1, Figs. 2d and 2e). This result was compatible with t ...
Oxidation of Diols and Ethers by NaBr03
... NaBr03/NaHS03 reagent was found to be efficient for the oxidation of ethers to esters under mild conditions. In order to confirm the optimum reaction conditions, dioctyl ether (33) was chosen as a model substrate and allowed to react with NaBr03/NaHS03 under various reaction conditions (Eq. 2 and Ta ...
... NaBr03/NaHS03 reagent was found to be efficient for the oxidation of ethers to esters under mild conditions. In order to confirm the optimum reaction conditions, dioctyl ether (33) was chosen as a model substrate and allowed to react with NaBr03/NaHS03 under various reaction conditions (Eq. 2 and Ta ...
Ch04-04-alkenes-2
... resembles reactants (I). Endergonic reaction: late transition state resembles products (II). ...
... resembles reactants (I). Endergonic reaction: late transition state resembles products (II). ...
102 Lecture Ch19
... melting and boiling points than primary or secondary • Amides have higher melting and boiling points than carboxylic acids because they are more flat (due to delocalization of electrons), so they stack better • Amides (except formamide) are solids at room temperature • Smaller amides (5 carbons or l ...
... melting and boiling points than primary or secondary • Amides have higher melting and boiling points than carboxylic acids because they are more flat (due to delocalization of electrons), so they stack better • Amides (except formamide) are solids at room temperature • Smaller amides (5 carbons or l ...
No Slide Title
... • Need a nonpolar, nonreactive solvent to dissolve argenine without interfering with the reaction. • Methyl Sulfoxide NOT efficient as a solvent for this reaction due to its exothermicity. – i.e (Broken Manifold and intense sulfur scent) • Length of complete reaction and temperature requirements are ...
... • Need a nonpolar, nonreactive solvent to dissolve argenine without interfering with the reaction. • Methyl Sulfoxide NOT efficient as a solvent for this reaction due to its exothermicity. – i.e (Broken Manifold and intense sulfur scent) • Length of complete reaction and temperature requirements are ...
amines - Gneet`s
... and conc.H2SO4 ( Liebermann’s test) Tertiary amines : Forms nitrite in cold which on heating gives nitrosoamine which responds to Liebermann’s test. 4. Action of acetyl chloride Primary amines : Acetyl derivative is formed Secondary amines: Acetyl derivatives is formed Tertiary amines : No action 5. ...
... and conc.H2SO4 ( Liebermann’s test) Tertiary amines : Forms nitrite in cold which on heating gives nitrosoamine which responds to Liebermann’s test. 4. Action of acetyl chloride Primary amines : Acetyl derivative is formed Secondary amines: Acetyl derivatives is formed Tertiary amines : No action 5. ...
carboxylic acid
... reactions • Aldehydes and ketones do not possess a suitable leaving group • C=O bond is not restored • Carbon of original carbonyl group remains sp3-hybridized, singly bonded to four substituents ...
... reactions • Aldehydes and ketones do not possess a suitable leaving group • C=O bond is not restored • Carbon of original carbonyl group remains sp3-hybridized, singly bonded to four substituents ...
Answers / Solutions
... d does nott undergo d addition reaction easily because a)) It has h a cyclic li structure t t b) Double bonds in it are very strong c)) Resonance R stabilised t bili d system t iis to t be preserved d) It has h six i hydrogen h d atoms t Benzene is resonance stabilised and as such resistant to addit ...
... d does nott undergo d addition reaction easily because a)) It has h a cyclic li structure t t b) Double bonds in it are very strong c)) Resonance R stabilised t bili d system t iis to t be preserved d) It has h six i hydrogen h d atoms t Benzene is resonance stabilised and as such resistant to addit ...
cleavage of methyl ethers with iodotrimethylsilane
... as a result of hydrolysis by contact with moisture. The amount of by-products, including cyclohexyl iodide, is reduced by the presence of pyridine. Hindered pyridine bases such as 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4methylpyridine5 have also been used for this purpose, by the submitters. The pyridine bases do not ap ...
... as a result of hydrolysis by contact with moisture. The amount of by-products, including cyclohexyl iodide, is reduced by the presence of pyridine. Hindered pyridine bases such as 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4methylpyridine5 have also been used for this purpose, by the submitters. The pyridine bases do not ap ...
Imbalanced tunneling ready states in alcohol dehydrogenase
... The secondary kinetic isotope effects for the hydride transfer reactions from aliphatic alcohols to two carbocations (NAD+ models) in acetonitrile were determined. The results suggest that the hydride transfer takes place by tunneling and that the rehybridizations of both donor and acceptor carbons l ...
... The secondary kinetic isotope effects for the hydride transfer reactions from aliphatic alcohols to two carbocations (NAD+ models) in acetonitrile were determined. The results suggest that the hydride transfer takes place by tunneling and that the rehybridizations of both donor and acceptor carbons l ...
CH 2
... with the idea that the carbon-carbon double bond in alkenes is stronger than the carbon-carbon single bond in alkanes, however, as the majority of the reactions of alkenes involve the rupture of this bond to form two new single bonds. ...
... with the idea that the carbon-carbon double bond in alkenes is stronger than the carbon-carbon single bond in alkanes, however, as the majority of the reactions of alkenes involve the rupture of this bond to form two new single bonds. ...
Nucleophilic Substitution and b
... Here is the crux of the matter: how can the non-reacting carbon change its configuration??? Further it does not always change but only if configuration of the reacting carbon changes!! We got a mixture of enantiomers, a racemic mixture. Something strange is happening!! Expect sulfur to attack the C- ...
... Here is the crux of the matter: how can the non-reacting carbon change its configuration??? Further it does not always change but only if configuration of the reacting carbon changes!! We got a mixture of enantiomers, a racemic mixture. Something strange is happening!! Expect sulfur to attack the C- ...
Improved Synthesis of (3E,6Z,9Z)-1,3,6,9
... The winter moth, Operophtera brumata (Lepidoptera: Geometridae), is an early-season defoliator that attacks a wide variety of hardwoods and, in some cases, conifers. The insect is native to Europe but has become established in at least three areas of North America including southeastern New England. ...
... The winter moth, Operophtera brumata (Lepidoptera: Geometridae), is an early-season defoliator that attacks a wide variety of hardwoods and, in some cases, conifers. The insect is native to Europe but has become established in at least three areas of North America including southeastern New England. ...
Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
... An alcohol reacts with conc. HCl and ZnCl2 (Lucas reagent) to give carbocation. More stable is the carbocation, faster is the reaction. ...
... An alcohol reacts with conc. HCl and ZnCl2 (Lucas reagent) to give carbocation. More stable is the carbocation, faster is the reaction. ...
Amines - ncert
... with three or more carbon atoms are liquid and still higher ones are solid. Aniline and other arylamines are usually colourless but get coloured on storage due to atmospheric oxidation. Lower aliphatic amines are soluble in water because they can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. However, so ...
... with three or more carbon atoms are liquid and still higher ones are solid. Aniline and other arylamines are usually colourless but get coloured on storage due to atmospheric oxidation. Lower aliphatic amines are soluble in water because they can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. However, so ...
Exam 3 - Napa Valley College
... mean that you would get a lot of by-products but you would end up getting more product also (SN1 major, E1 minor). 4) There are a number of ways of substituting a halogen for an alcohol group, but some ways are better than others. What advantage is there in using PCl3 rather than HCl in the chloride ...
... mean that you would get a lot of by-products but you would end up getting more product also (SN1 major, E1 minor). 4) There are a number of ways of substituting a halogen for an alcohol group, but some ways are better than others. What advantage is there in using PCl3 rather than HCl in the chloride ...
Hofmann–Löffler reaction

The Hofmann–Löffler reaction (also referred to as Hofmann–Löffler–Freytag reaction, Löffler–Freytag reaction, Löffler–Hofmann reaction, as well as Löffler's method) is an organic reaction in which a cyclic amine 2 (pyrrolidine or, in some cases, piperidine) is generated by thermal or photochemical decomposition of N-halogenated amine 1 in the presence of a strong acid (concentrated sulfuric acid or concentrated CF3CO2H). The Hofmann–Löffler–Freytag reaction proceeds via an intramolecular hydrogen atom transfer to a nitrogen-centered radical and is an example of a remote intramolecular free radical C–H functionalization.