organic chemistry ii
... formed upon reaction with only a mildly strong base such as an alkoxide (ii) a kinetic enolate is the less stable (less substituted) enolate which can be formed upon reaction with a very strong base such as LDA. Although the more stable enolate is also formed under these conditions, the less stable ...
... formed upon reaction with only a mildly strong base such as an alkoxide (ii) a kinetic enolate is the less stable (less substituted) enolate which can be formed upon reaction with a very strong base such as LDA. Although the more stable enolate is also formed under these conditions, the less stable ...
Unique Solutions
... During reduction reaction : a reactants gain oxygen b reactants lose hydrogen c reactants gain hydrogen d reactants lose nitrogen What is called the addition of oxygen to a substance? a reduction reaction b decomposition reaction c oxidation reaction d neutralization reaction c H2 ...
... During reduction reaction : a reactants gain oxygen b reactants lose hydrogen c reactants gain hydrogen d reactants lose nitrogen What is called the addition of oxygen to a substance? a reduction reaction b decomposition reaction c oxidation reaction d neutralization reaction c H2 ...
C h e m g u i d e ... HALOGENOALKANES: MAKING
... a) In the case of chloroalkanes, only tertiary ones can be made easily this way. Tertiary alcohols react readily with concentrated hydrochloric acid. (i) Draw a structure for a tertiary chloroalkane. (ii) Draw the structure of the alcohol it would be made from. (iii) Why aren’t primary or secondary ...
... a) In the case of chloroalkanes, only tertiary ones can be made easily this way. Tertiary alcohols react readily with concentrated hydrochloric acid. (i) Draw a structure for a tertiary chloroalkane. (ii) Draw the structure of the alcohol it would be made from. (iii) Why aren’t primary or secondary ...
Here is the Original File - University of New Hampshire
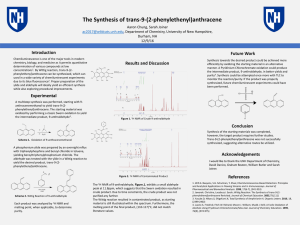
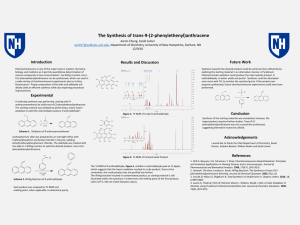
... chemistry, biology, and medicine as it permits quantitative determination of various compounds at low concentrations1. By Wittig reaction, trans-9-(2phenylethenyl)anthracene can be synthesized, which can used in a wide variety of chemiluminescent experiments due to its blue fluorescence2. Proper pre ...
... chemistry, biology, and medicine as it permits quantitative determination of various compounds at low concentrations1. By Wittig reaction, trans-9-(2phenylethenyl)anthracene can be synthesized, which can used in a wide variety of chemiluminescent experiments due to its blue fluorescence2. Proper pre ...
The Synthesis of trans-9-(2
... Chemiluminescence is one of the major tools in modern chemistry, biology, and medicine as it permits quantitative determination of various compounds at low concentrations1. By Wittig reaction, trans9-(2-phenylethenyl)anthracene can be synthesized, which can used in a wide variety of chemiluminescent ...
... Chemiluminescence is one of the major tools in modern chemistry, biology, and medicine as it permits quantitative determination of various compounds at low concentrations1. By Wittig reaction, trans9-(2-phenylethenyl)anthracene can be synthesized, which can used in a wide variety of chemiluminescent ...
Lecture 9a - University of California, Los Angeles
... reactive than ketones which means that both groups would react with the Grignard reagent, albeit with different rates The higher reactivity of the aldehyde is exploited in the formation of the cyclic acetal using 1,3-propanediol ...
... reactive than ketones which means that both groups would react with the Grignard reagent, albeit with different rates The higher reactivity of the aldehyde is exploited in the formation of the cyclic acetal using 1,3-propanediol ...
Chapter 7 - Alkenes and Alkynes I less substituted alkene due to
... - Hydrogenation reactions involve nely divided insoluble platinum, palladium, or nickel catalysts - If the catalyst is insoluble in the reaction mixture, it is heterogeneous catalysis while a soluble catalyst is homogeneous catalysis - An addition reaction has a product, an alkane, that results fro ...
... - Hydrogenation reactions involve nely divided insoluble platinum, palladium, or nickel catalysts - If the catalyst is insoluble in the reaction mixture, it is heterogeneous catalysis while a soluble catalyst is homogeneous catalysis - An addition reaction has a product, an alkane, that results fro ...
Kazzie`s Guide to Orgo 2
... How many H-bonds hold together Guanine and Cytosine? Which base appears in RNA but not DNA? Which carbon has it’s OH replaced by H in DNA? Draw the dinucleotide made up of thymine and adenine as it would appear in DNA: ...
... How many H-bonds hold together Guanine and Cytosine? Which base appears in RNA but not DNA? Which carbon has it’s OH replaced by H in DNA? Draw the dinucleotide made up of thymine and adenine as it would appear in DNA: ...
Going Bananas Over Isoamyl Acetate
... the equilibrium can be shifted by adding more of the acid or of the alcohol, depending on cost or availability. The mechanism of the reaction involves initial protonation of the carboxyl group, attack by the nucleophilic hydroxyl, a proton transfer, and loss of water followed by loss of the catalyzi ...
... the equilibrium can be shifted by adding more of the acid or of the alcohol, depending on cost or availability. The mechanism of the reaction involves initial protonation of the carboxyl group, attack by the nucleophilic hydroxyl, a proton transfer, and loss of water followed by loss of the catalyzi ...
Going Bananas Over Isoamyl Acetate
... the equilibrium can be shifted by adding more of the acid or of the alcohol, depending on cost or availability. The mechanism of the reaction involves initial protonation of the carboxyl group, attack by the nucleophilic hydroxyl, a proton transfer, and loss of water followed by loss of the catalyzi ...
... the equilibrium can be shifted by adding more of the acid or of the alcohol, depending on cost or availability. The mechanism of the reaction involves initial protonation of the carboxyl group, attack by the nucleophilic hydroxyl, a proton transfer, and loss of water followed by loss of the catalyzi ...
Alkenes - MsReenChemistry
... alkene that has the greater number of hydrogen substituents, and the halogen to the carbon of the alkene with the fewer ...
... alkene that has the greater number of hydrogen substituents, and the halogen to the carbon of the alkene with the fewer ...
Organic Chemistry (HL) Revision Questions
... If the conditions of the reaction in (b) are changed so that a hot solution of sodium hydroxide in ethanol is used then a different reaction occurs. The reaction with 2-bromo-2-methylbutane gives two different organic products. State the type of reaction taking place and suggest the identity (name o ...
... If the conditions of the reaction in (b) are changed so that a hot solution of sodium hydroxide in ethanol is used then a different reaction occurs. The reaction with 2-bromo-2-methylbutane gives two different organic products. State the type of reaction taking place and suggest the identity (name o ...
The Acid-Catalyzed Reaction of Acetic
... notice the special odors associated with esters - some fruity, some more like nail polish. In contrast, the acids which are used in their syntheses usually have a rotten odor. The reverse reaction, hydrolysis of the ester, gives the alcohol and the acid from which it was synthesized. Because the hyd ...
... notice the special odors associated with esters - some fruity, some more like nail polish. In contrast, the acids which are used in their syntheses usually have a rotten odor. The reverse reaction, hydrolysis of the ester, gives the alcohol and the acid from which it was synthesized. Because the hyd ...
Chapter 5. An Overview of Organic Reactions
... C-H bonds only (no functional groups) Connecting carbons can lead to large or small molecules The formula for an alkane with no rings in it must be CnH2n+2 where the number of C’s is n Alkanes are saturated with hydrogen (no more can be added They are also called aliphatic compounds ...
... C-H bonds only (no functional groups) Connecting carbons can lead to large or small molecules The formula for an alkane with no rings in it must be CnH2n+2 where the number of C’s is n Alkanes are saturated with hydrogen (no more can be added They are also called aliphatic compounds ...
Lecture 14a - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... Solvent: DMSO (cannot be used in Chem 30CL), PTC conditions, solid state reaction An one-pot reaction is not advisable here because the reactants, the intermediate and the product are very difficult to separate from each other (anhydrous ZnI2 is not available!) The Corey-Chaykovsky reagent can ...
... Solvent: DMSO (cannot be used in Chem 30CL), PTC conditions, solid state reaction An one-pot reaction is not advisable here because the reactants, the intermediate and the product are very difficult to separate from each other (anhydrous ZnI2 is not available!) The Corey-Chaykovsky reagent can ...
Mechanism of Aldol Condensation
... Aldol condensations are important in organic synthesis, providing a good way to form carbon– carbon bonds. For example, the Robinson annulation reaction sequence features an aldol condensation; the Wieland-Miescher ketone product is an important starting material for many organic syntheses. Aldol co ...
... Aldol condensations are important in organic synthesis, providing a good way to form carbon– carbon bonds. For example, the Robinson annulation reaction sequence features an aldol condensation; the Wieland-Miescher ketone product is an important starting material for many organic syntheses. Aldol co ...
Dissertation:
... In the case of PLLA alcoholysis process that was proceeded rapidly in the presence of metal alkoxides such as LiOEt and KOEt, the complete conversion of PLLA into ethyl esters of lactic and lactyllactic acid was observed after 1 h. Here, no catalytic activity of zinc, aluminum and sodium alkoxides w ...
... In the case of PLLA alcoholysis process that was proceeded rapidly in the presence of metal alkoxides such as LiOEt and KOEt, the complete conversion of PLLA into ethyl esters of lactic and lactyllactic acid was observed after 1 h. Here, no catalytic activity of zinc, aluminum and sodium alkoxides w ...
Template for calculating the ΔH° in a multiple step chemical reaction
... The chemical reaction: 2 H2O2 → 2 H2O + O2 is a a. synthesis reaction b. decomposition reaction c. single displacement reaction d. double displacement reaction e. combustion reaction The chemical reaction: Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2 is a a. synthesis reaction b. decomposition reaction c. single displac ...
... The chemical reaction: 2 H2O2 → 2 H2O + O2 is a a. synthesis reaction b. decomposition reaction c. single displacement reaction d. double displacement reaction e. combustion reaction The chemical reaction: Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2 is a a. synthesis reaction b. decomposition reaction c. single displac ...
effective: september 2003 curriculum guidelines
... The course will be presented using lectures, problem sessions and class discussion. Films and other audiovisual aids as well as programmed material will be used where appropriate. Problems will be assigned on a regular basis, to be handed in and evaluated. The laboratory course will be used to illus ...
... The course will be presented using lectures, problem sessions and class discussion. Films and other audiovisual aids as well as programmed material will be used where appropriate. Problems will be assigned on a regular basis, to be handed in and evaluated. The laboratory course will be used to illus ...
Quiz 3 – Aldehydes and Ketones 1 Which of the following reactions
... 7 You have two C6H10O ketones, I and II. Both are optically active, but I is racemized by treatment with base and II is not. Wolff-Kishner reduction of both ketones gives the same achiral hydrocarbon, formula C6H12. What reasonable structures may be assigned to I and II? A) I is 3-methyl-4-penten-2- ...
... 7 You have two C6H10O ketones, I and II. Both are optically active, but I is racemized by treatment with base and II is not. Wolff-Kishner reduction of both ketones gives the same achiral hydrocarbon, formula C6H12. What reasonable structures may be assigned to I and II? A) I is 3-methyl-4-penten-2- ...
• Pergamon
... MetaHoporphyrins have been used extensively as models for studying cytochrome P-450 monooxygenase activity.! Although these catalysts are known to carry out many useful reactions such as alkene epoxidation and hydrocarbon oxidation, their utility in organic synthesis has been limited. Recently we re ...
... MetaHoporphyrins have been used extensively as models for studying cytochrome P-450 monooxygenase activity.! Although these catalysts are known to carry out many useful reactions such as alkene epoxidation and hydrocarbon oxidation, their utility in organic synthesis has been limited. Recently we re ...
Diels-Alder Reaction
... of a reaction type known as a cycloaddition reaction, in which the conjugated p-systems of two reactants join to generate a new ring. The reactants in the Diels-Alder reaction are a 1,3-diene and an alkene called the dienophile. The carbon-carbon double bond in the dienophile is usually conjugated w ...
... of a reaction type known as a cycloaddition reaction, in which the conjugated p-systems of two reactants join to generate a new ring. The reactants in the Diels-Alder reaction are a 1,3-diene and an alkene called the dienophile. The carbon-carbon double bond in the dienophile is usually conjugated w ...
Lecture 18
... medulla during stressful situations They raise the blood glucose level and move blood to the muscles. The prefix nor in a drug name means there is one less —CH3 group on the nitrogen atom. Norepinephrine is used in remedies for colds, hay fever, and asthma because it contracts the capillaries in the ...
... medulla during stressful situations They raise the blood glucose level and move blood to the muscles. The prefix nor in a drug name means there is one less —CH3 group on the nitrogen atom. Norepinephrine is used in remedies for colds, hay fever, and asthma because it contracts the capillaries in the ...
Exam 1 from 2008
... a) Draw an accurate 3D structure of allene. (Hint: It is not planar.) On this structure show the p-orbitals and how they overlap to form the pi bonds in allene. Clearly indicate the 3D orientation of the p-orbitals relative to the atoms in the molecule and to each other. b) Label the hybridization o ...
... a) Draw an accurate 3D structure of allene. (Hint: It is not planar.) On this structure show the p-orbitals and how they overlap to form the pi bonds in allene. Clearly indicate the 3D orientation of the p-orbitals relative to the atoms in the molecule and to each other. b) Label the hybridization o ...
Hofmann–Löffler reaction

The Hofmann–Löffler reaction (also referred to as Hofmann–Löffler–Freytag reaction, Löffler–Freytag reaction, Löffler–Hofmann reaction, as well as Löffler's method) is an organic reaction in which a cyclic amine 2 (pyrrolidine or, in some cases, piperidine) is generated by thermal or photochemical decomposition of N-halogenated amine 1 in the presence of a strong acid (concentrated sulfuric acid or concentrated CF3CO2H). The Hofmann–Löffler–Freytag reaction proceeds via an intramolecular hydrogen atom transfer to a nitrogen-centered radical and is an example of a remote intramolecular free radical C–H functionalization.