Chapter 9. Addition Reactions of Alkenes
... The reaction below, which provides compound M as its major product, appears to defy the principles that we discussed in class. Draw the structures of the intermediate carbocations that form in this reaction, then clearly but briefly explain why M, and not L, is the major product of this reaction. Hi ...
... The reaction below, which provides compound M as its major product, appears to defy the principles that we discussed in class. Draw the structures of the intermediate carbocations that form in this reaction, then clearly but briefly explain why M, and not L, is the major product of this reaction. Hi ...
Class X Chemistry-Carbon and its compounds
... 6. Classify the following compounds as alkanes, alkenes and alkynes. C2H4 , C3H4 , C4H8 , C5H12 , C5H8 , C3H8 7. Write the electron dot structure for: (a) Ammonia (NH3) (b) Nitrogen (N2) (d) Carbon dioxide (CO2) (e) Cyclohexane (C6H12) (g) Methane (CH4) (h) Oxygen (O2) ...
... 6. Classify the following compounds as alkanes, alkenes and alkynes. C2H4 , C3H4 , C4H8 , C5H12 , C5H8 , C3H8 7. Write the electron dot structure for: (a) Ammonia (NH3) (b) Nitrogen (N2) (d) Carbon dioxide (CO2) (e) Cyclohexane (C6H12) (g) Methane (CH4) (h) Oxygen (O2) ...
-1- GLOSSARY OF CHEM 1110 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY TERMS
... -4halogenation: the addition of a halogen molecule (only Cl2 or Br2) to an alkene to produce an alkyl dihalide or alkyne to produce an alkyl tetrahalide. heteroatoms: elements other than carbon and hydrogen that are commonly found in organic molecules, such as nitrogen, oxygen and the halogens. hom ...
... -4halogenation: the addition of a halogen molecule (only Cl2 or Br2) to an alkene to produce an alkyl dihalide or alkyne to produce an alkyl tetrahalide. heteroatoms: elements other than carbon and hydrogen that are commonly found in organic molecules, such as nitrogen, oxygen and the halogens. hom ...
S2-2-07 - Classifying Chemical Reactions
... ionic and covalent bonds, naming compounds, and balancing chemical equations. In last class we learned about synthesis and decomposition reactions. Today we will cover the remainder of the reaction types (single and double displacement and combustion) using discussion, analogy, hands-on experiments, ...
... ionic and covalent bonds, naming compounds, and balancing chemical equations. In last class we learned about synthesis and decomposition reactions. Today we will cover the remainder of the reaction types (single and double displacement and combustion) using discussion, analogy, hands-on experiments, ...
FINAL EXAM Review Sheet / Study Guide Honors Chemistry
... 2) Explain the difference between dissociation and dissolving. Use an example compound for each. ...
... 2) Explain the difference between dissociation and dissolving. Use an example compound for each. ...
Exp 19 - Diphenylacetylene_2015
... (DCM) to a 5 mL conical vial containing a spin vane. Place the vial on the stir-plate in the aluminum block and stir until the stilbene has dissolved. In a test-tube, obtain approximately 1.2 mL of the 5% Br2 in DCM solution. This solution is approximately 1.0 M in Br2. Support this test tube in a s ...
... (DCM) to a 5 mL conical vial containing a spin vane. Place the vial on the stir-plate in the aluminum block and stir until the stilbene has dissolved. In a test-tube, obtain approximately 1.2 mL of the 5% Br2 in DCM solution. This solution is approximately 1.0 M in Br2. Support this test tube in a s ...
Chemistry 212 Name:
... 8. In a certain oxidation state, copper behaves as if it were a main group element instead of a transition metal. What oxidation state is that and why would you expect this to be observed. (5 points) Cu+, its electron configuration is [Ar] 4d10. This is the same as Zn2+ and leads to reactivity as th ...
... 8. In a certain oxidation state, copper behaves as if it were a main group element instead of a transition metal. What oxidation state is that and why would you expect this to be observed. (5 points) Cu+, its electron configuration is [Ar] 4d10. This is the same as Zn2+ and leads to reactivity as th ...
Chapter 8 - Chemical Equations
... it is located to the left side of the staircase line on the Periodic Table. Step 2 – You will compare the type of element by itself to the similar type of element in the compound. In this case, aluminum is a metal, so I will compare it with the metal in the compound (which is Pb). Step 3 – RULE: The ...
... it is located to the left side of the staircase line on the Periodic Table. Step 2 – You will compare the type of element by itself to the similar type of element in the compound. In this case, aluminum is a metal, so I will compare it with the metal in the compound (which is Pb). Step 3 – RULE: The ...
Document
... can be increased by decreasing the … A In the same state as the reactants A particle size ...
... can be increased by decreasing the … A In the same state as the reactants A particle size ...
Synthesis of (−)-Epibatidine - David A. Evans
... molecular SN2 displacement by nitrogen would follow. Although the reduction proceeded without affecting the chloropyridine ring,21 a 75:25 mixture of inseparable alcohols was obtained. The structural assignment of the major diastereomer was complicated as a result of slowly interconverting conformat ...
... molecular SN2 displacement by nitrogen would follow. Although the reduction proceeded without affecting the chloropyridine ring,21 a 75:25 mixture of inseparable alcohols was obtained. The structural assignment of the major diastereomer was complicated as a result of slowly interconverting conformat ...
Edexcel GCE - The Student Room
... (c) Lithium can react with chlorine to produce lithium chloride. When a sample of lithium chloride is heated in a Bunsen flame, a red colour is seen. (i) Draw a ‘dot and cross’ diagram of lithium chloride showing all the electrons. Indicate the charges clearly on your diagram. ...
... (c) Lithium can react with chlorine to produce lithium chloride. When a sample of lithium chloride is heated in a Bunsen flame, a red colour is seen. (i) Draw a ‘dot and cross’ diagram of lithium chloride showing all the electrons. Indicate the charges clearly on your diagram. ...
Chemistry: Selected Topics
... The aim of the course is to acquaint the students with the properties and synthesis of some important types of chemical compounds. In the first part of the course, the general concepts of chemical reaction kinetics are presented with emphasis on the relation between reaction rate and reaction mechan ...
... The aim of the course is to acquaint the students with the properties and synthesis of some important types of chemical compounds. In the first part of the course, the general concepts of chemical reaction kinetics are presented with emphasis on the relation between reaction rate and reaction mechan ...
Introduction to Organic Chemistry
... Proteins • Elements: C, H, O, N • Monomer: amino acid • Examples: enzymes, hemoglobin, collagen, antibodies ...
... Proteins • Elements: C, H, O, N • Monomer: amino acid • Examples: enzymes, hemoglobin, collagen, antibodies ...
document
... G. A reaction in which two reactant compounds switch ions. 9. Decomposition Reaction A H. This number tells the number of atoms of one element in a 10. Single Displacement Reaction O compound. I. Bonds formed by gaining and losing 11. Double Displacement Reaction G electrons. J. A group of atoms tha ...
... G. A reaction in which two reactant compounds switch ions. 9. Decomposition Reaction A H. This number tells the number of atoms of one element in a 10. Single Displacement Reaction O compound. I. Bonds formed by gaining and losing 11. Double Displacement Reaction G electrons. J. A group of atoms tha ...
Final Exam review semester 1
... 1. Ninety-nine percent of all the matter that can be observed in the universe exists as 2. Hydrochloric acid, HCl, is added to solid NaOH. After the reaction is complete, NaCl dissolved in water remains. What are the products of this chemical reaction? ____ ...
... 1. Ninety-nine percent of all the matter that can be observed in the universe exists as 2. Hydrochloric acid, HCl, is added to solid NaOH. After the reaction is complete, NaCl dissolved in water remains. What are the products of this chemical reaction? ____ ...
Sample Questions
... 5. A sample of ammonia has a mass of 43.5 g. How many molecules are in this sample? 6. What is the molar mass of ethanol (C2H5OH)? 7. Roundup, an herbicide manufactured by Monsanto, has the formula C3H8NO5P. How many moles of molecules are there in a 295.1-g sample of Roundup? 8. Phosphoric acid can ...
... 5. A sample of ammonia has a mass of 43.5 g. How many molecules are in this sample? 6. What is the molar mass of ethanol (C2H5OH)? 7. Roundup, an herbicide manufactured by Monsanto, has the formula C3H8NO5P. How many moles of molecules are there in a 295.1-g sample of Roundup? 8. Phosphoric acid can ...
Microsoft Word
... phenylephrine and related analogs and is divided into two sections. Chapter 2: deals with the application of Wittig-Horner approach/Heck coupling reaction towards the synthesis of tamoxifen and mintlactone and is divided into three sections. Chapter 3: includes the synthesis, characterization and ca ...
... phenylephrine and related analogs and is divided into two sections. Chapter 2: deals with the application of Wittig-Horner approach/Heck coupling reaction towards the synthesis of tamoxifen and mintlactone and is divided into three sections. Chapter 3: includes the synthesis, characterization and ca ...
AP Review Chp 1 and Chp 2 Wed 10/9/2013 1. Near room
... A copper(II) sulfate solution is mixed by dissolving 25.000 g of copper(II) sulfate, and then it is treated with an excess of magnesium metal. The mass of copper collected is 8.786 g after drying. Calculate the percent yield of copper. II) In a particular experiment, 225 g of phosphorus, P4, reacted ...
... A copper(II) sulfate solution is mixed by dissolving 25.000 g of copper(II) sulfate, and then it is treated with an excess of magnesium metal. The mass of copper collected is 8.786 g after drying. Calculate the percent yield of copper. II) In a particular experiment, 225 g of phosphorus, P4, reacted ...
Chemistry Crunch #12.2: Organic Reactions KEY Why? Learning
... No! Depending on how big or small the hydrocarbon is, a different amount of CO2 and H2O would be produced. 2. Write the balanced equation for the complete combustion of hexene (C6H12). ...
... No! Depending on how big or small the hydrocarbon is, a different amount of CO2 and H2O would be produced. 2. Write the balanced equation for the complete combustion of hexene (C6H12). ...
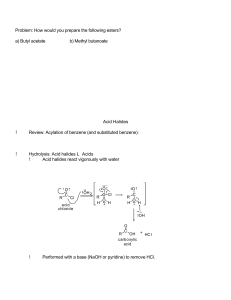
Ester - SCH4U-SRB
... Esters are responsible for the “fruity” odours and flavours of many naturally occurring products. Chemists can reproduce these odours or flavours in the lab by mixing the right alcohol and carboxylic acid together; thus, producing “artificial” or “synthetic” versions of these naturally occurring com ...
... Esters are responsible for the “fruity” odours and flavours of many naturally occurring products. Chemists can reproduce these odours or flavours in the lab by mixing the right alcohol and carboxylic acid together; thus, producing “artificial” or “synthetic” versions of these naturally occurring com ...
Making Macromolecule Activity - Mercer Island School District
... 1. In your group, make a glucose molecule. Glucose is a monosaccharide. Make the ring structure first using 5 carbon atoms and 1 oxygen. Then add the other atoms (1 more carbon, 12 hydrogens, 5 more Oxygens). 2. When you are done. Make sure there are no empty spots for making bonds. All bonds should ...
... 1. In your group, make a glucose molecule. Glucose is a monosaccharide. Make the ring structure first using 5 carbon atoms and 1 oxygen. Then add the other atoms (1 more carbon, 12 hydrogens, 5 more Oxygens). 2. When you are done. Make sure there are no empty spots for making bonds. All bonds should ...
Strychnine total synthesis

Strychnine total synthesis in chemistry describes the total synthesis of the complex biomolecule strychnine. The first reported method by the group of Robert Burns Woodward in 1954 is considered a classic in this research field. At the time it formed the natural conclusion to an elaborate process of molecular structure elucidation that started with the isolation of strychnine from the beans of Strychnos ignatii by Pierre Joseph Pelletier and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou in 1818. Major contributors to the entire effort were Sir Robert Robinson with over 250 publications and Hermann Leuchs with another 125 papers in a time span of 40 years. Robinson was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1947 for his work on alkaloids, strychnine included. The process of chemical identification was completed with publications in 1946 by Robinson and later confirmed by Woodward in 1947. X-ray structures establishing the absolute configuration became available between 1947 and 1951 with publications from J. M. Bijvoet and J.H. Robertson .Woodward published a very brief account on the strychnine synthesis in 1954 (just 3 pages) and a lengthy one (42 pages) in 1963.Many more methods exist and reported by the research groups of Magnus, Overman, Kuehne, Rawal, Bosch, Vollhardt, Mori, Shibasaki, Li, Fukuyama Vanderwal and MacMillan. Synthetic (+)-strychnine is also known. Racemic synthesises were published by Padwa in 2007 and in 2010 by Andrade and by Reissig.In his 1963 publication Woodward quoted Sir Robert Robinson who said for its molecular size it is the most complex substance known.