nomenclature continued… - Turner Fenton Secondary School
... An ester has two groups: the main part of the ester contains the –COO (parent acid). The carbonyl group is always position number 1. And the second part is the alkyl group. Naming: 1. Identify main ester chain = parent chain. 2. Replace oic acid with OATE for parent acid. 3. Second part name as alk ...
... An ester has two groups: the main part of the ester contains the –COO (parent acid). The carbonyl group is always position number 1. And the second part is the alkyl group. Naming: 1. Identify main ester chain = parent chain. 2. Replace oic acid with OATE for parent acid. 3. Second part name as alk ...
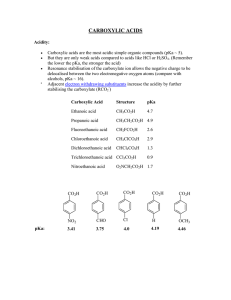
carboxylic acids - La Salle University
... 1o and 2o alkyl halides (X = Cl, Br, I) or tosylates undergo SN2 substitution with cyanide salts to give nitriles. Nitriles can be hydrolysed to carboxylic acids without the isolation of the amide intermediate. Note that the carbon skeleton is extended by 1 C atom during this reaction sequence. Alth ...
... 1o and 2o alkyl halides (X = Cl, Br, I) or tosylates undergo SN2 substitution with cyanide salts to give nitriles. Nitriles can be hydrolysed to carboxylic acids without the isolation of the amide intermediate. Note that the carbon skeleton is extended by 1 C atom during this reaction sequence. Alth ...
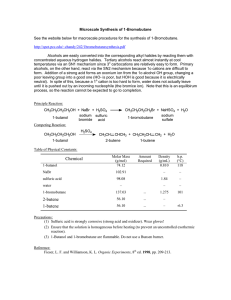
Synthesis of 1
... 1.11) to remove traces of acid, separate, and be careful to save the proper layer. In experiments of this type, it is good practice to save all layers until the product is in hand. • Dry the cloudy 1-bromobutane by adding anhydrous calcium chloride pellets and mixing until the liquid clears and the ...
... 1.11) to remove traces of acid, separate, and be careful to save the proper layer. In experiments of this type, it is good practice to save all layers until the product is in hand. • Dry the cloudy 1-bromobutane by adding anhydrous calcium chloride pellets and mixing until the liquid clears and the ...
A NEW APROACH TO N-SUBSTITUTED OXAZOLIDINE VIA NITRILIUM ION TRAPPING
... to amides with retention of configuration. This method involved the in situ formation of chlorosulfites followed by a reaction with nitrile complexes of Ti(IV) fluoride. We hypothesize that these amidation reactions involve the intermediacy of nitrilium ions which are subsequently hydrolyzed to form ...
... to amides with retention of configuration. This method involved the in situ formation of chlorosulfites followed by a reaction with nitrile complexes of Ti(IV) fluoride. We hypothesize that these amidation reactions involve the intermediacy of nitrilium ions which are subsequently hydrolyzed to form ...
CHEM 122: Introduction to Organic Chemistry Chapter 1: Organic
... 9. Draw a structural formula for the one tertiary (3 o) alcohol with the molecular formula C4H10O. 10. Draw condensed structural formulas for all compounds with the molecular formula C4H8O that contain a carbonyl group (there are two aldehydes and one ketone). 11. Draw structural formulas for the s ...
... 9. Draw a structural formula for the one tertiary (3 o) alcohol with the molecular formula C4H10O. 10. Draw condensed structural formulas for all compounds with the molecular formula C4H8O that contain a carbonyl group (there are two aldehydes and one ketone). 11. Draw structural formulas for the s ...
Name
... Another industrial process used to manufacture ethanol involves the addition of water to ethene using a catalyst. ...
... Another industrial process used to manufacture ethanol involves the addition of water to ethene using a catalyst. ...
CH30S Chemical Reactions Part 2 Unit Review
... 4Na + O2 2Na2O + 5.0KJ (10.85g Na2O, 0.438KJ) 23. The following reaction is exothermic and releases 7.5KJ of energy per mole of hydrogen gas consumed. Calculate the amount of energy released when 50.9g of iron(IV) oxide reacts with an excess of hydrogen gas according to the following unbalanced re ...
... 4Na + O2 2Na2O + 5.0KJ (10.85g Na2O, 0.438KJ) 23. The following reaction is exothermic and releases 7.5KJ of energy per mole of hydrogen gas consumed. Calculate the amount of energy released when 50.9g of iron(IV) oxide reacts with an excess of hydrogen gas according to the following unbalanced re ...
1. Absorption of what type electromagnetic radiation results in
... proceeds more rapidly than the nitration of benzene and yields predominantly the meta product. proceeds more rapidly than the nitration of benzene and yields predominantly the ortho, para products. proceeds more slowly than the nitration of benzene and yields predominantly the meta product. proceeds ...
... proceeds more rapidly than the nitration of benzene and yields predominantly the meta product. proceeds more rapidly than the nitration of benzene and yields predominantly the ortho, para products. proceeds more slowly than the nitration of benzene and yields predominantly the meta product. proceeds ...
Lecture 39 - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... Progressively Oxidizing (adding Oxygen) the alcohol allows us to go from an alcohol to a carboxylic acid ...
... Progressively Oxidizing (adding Oxygen) the alcohol allows us to go from an alcohol to a carboxylic acid ...
I I I I I I
... YTS9,!M Z!R��CL'M �a931;M \l.Ul9�t·'C"1 ·+�rtJl�4TI1� m;'Toln.:.l.l' ;1t1l.,t03'"A\1 IlAl·j:()'61.!.l '''ltlslt ...
... YTS9,!M Z!R��CL'M �a931;M \l.Ul9�t·'C"1 ·+�rtJl�4TI1� m;'Toln.:.l.l' ;1t1l.,t03'"A\1 IlAl·j:()'61.!.l '''ltlslt ...
chemistry ch4 - The Student Room
... The reaction of this compound with hot aqueous sodium hydroxide shows, as with chlorobenzene, that it is difficult to remove the chlorine in this way, by hydrolysis. Explain why this is relatively difficult to achieve when compared to the alkaline hydrolysis of 1-chlorobutane. In your answer you sho ...
... The reaction of this compound with hot aqueous sodium hydroxide shows, as with chlorobenzene, that it is difficult to remove the chlorine in this way, by hydrolysis. Explain why this is relatively difficult to achieve when compared to the alkaline hydrolysis of 1-chlorobutane. In your answer you sho ...
inorganic-chemistry-gp-i-alkali-metals
... Na + O2 Na2O2 (colourless peroxide) sometimes the formation of superoxide gives a colour. M + O2 MO2 (coloured superoxide) where M= K, Rb, Cs The colour of the superoxide’s is due to the paramagnetic behaviour, the O2- is having two covalent bonds and a single electron, which when move from one ...
... Na + O2 Na2O2 (colourless peroxide) sometimes the formation of superoxide gives a colour. M + O2 MO2 (coloured superoxide) where M= K, Rb, Cs The colour of the superoxide’s is due to the paramagnetic behaviour, the O2- is having two covalent bonds and a single electron, which when move from one ...
Chemistry_
... Synthetic means artificial (man-made), TeflonTM is an example of another synthetic substance 3. Can you list three properties of KevlarTM that make it so useful? Properties include fire resistance, high tensile strength, lightweight(ness) and flexibility ...
... Synthetic means artificial (man-made), TeflonTM is an example of another synthetic substance 3. Can you list three properties of KevlarTM that make it so useful? Properties include fire resistance, high tensile strength, lightweight(ness) and flexibility ...
Enzymatic synthesis of sialic acid derivative by immobilized lipase
... catalyzed by Novozym 435. Higher activity of Novozym 435 was also found in the kinetic resolution of secondary alcohols in monoether-functionalized ionic liquids (Zhou et al., 2011). Thus, Novozym 435 was observed to efficiently catalyze the esterification of N-acetyl neuraminic acid methyl ester with ...
... catalyzed by Novozym 435. Higher activity of Novozym 435 was also found in the kinetic resolution of secondary alcohols in monoether-functionalized ionic liquids (Zhou et al., 2011). Thus, Novozym 435 was observed to efficiently catalyze the esterification of N-acetyl neuraminic acid methyl ester with ...
Chemical Reactions
... • Synthesis – 2 substances (reactants) combine to form a new substance (product). – Substances are either atoms (elements) or compounds in this case. A + ...
... • Synthesis – 2 substances (reactants) combine to form a new substance (product). – Substances are either atoms (elements) or compounds in this case. A + ...
amine
... amides into a nitro compound. 1° amines are created by reducing a nitro compound with a reducing agent Ex. Nitrobenzene is reduced to aniline The symbol [H] is often used to show that any reduction agent can be used. ...
... amides into a nitro compound. 1° amines are created by reducing a nitro compound with a reducing agent Ex. Nitrobenzene is reduced to aniline The symbol [H] is often used to show that any reduction agent can be used. ...
Organic Chemistry I Mario Lintz 1st Year MD/PhD Candidate Mario
... o 1) introduce protecting group to block interfering function o 2) carry out desired reaction o 3) remove the protecting group Alcohol behaves as the nucleophile. (As is often the case) OH easily transfer H to a basic reagent, a problem in some reactions. Conversion of the OH to a removable fu ...
... o 1) introduce protecting group to block interfering function o 2) carry out desired reaction o 3) remove the protecting group Alcohol behaves as the nucleophile. (As is often the case) OH easily transfer H to a basic reagent, a problem in some reactions. Conversion of the OH to a removable fu ...
Aim # 8: How do we write and balance a chemical equation?
... 3. Balance the equation by supplying coefficients that will make the number of atoms of each element the same on both sides of the arrow. 2Mg + O2 → 2MgO ...
... 3. Balance the equation by supplying coefficients that will make the number of atoms of each element the same on both sides of the arrow. 2Mg + O2 → 2MgO ...
Chapter 18 - Aldehydes and Ketones
... LiAlH4 reduces all carbonyl compounds to the corresponding alcohols. Acid chlorides are also reduced by this reagent to the 1o alcohols. ...
... LiAlH4 reduces all carbonyl compounds to the corresponding alcohols. Acid chlorides are also reduced by this reagent to the 1o alcohols. ...
Part I Power generation in fuel cells
... It must also be remembered that electrode potentials change as the conditions become non-standard, and this must be taken into account when discussing the feasibility of the corrosion process. The iron half reaction coupled to a half reaction such as described above produces what is known as a corr ...
... It must also be remembered that electrode potentials change as the conditions become non-standard, and this must be taken into account when discussing the feasibility of the corrosion process. The iron half reaction coupled to a half reaction such as described above produces what is known as a corr ...
name - cloudfront.net
... 19. Which of the following will occur when solutions of CuSO4(aq) and BaCl2(aq) are mixed? A. A precipitate of CuCl2 will form; Ba2+ and SO42– are spectator ions. B. A precipitate of CuSO4 will form; Ba2+ and Cl– are spectator ions. C. A precipitate of BaSO4 will form; Cu2+ and Cl– are spectator ion ...
... 19. Which of the following will occur when solutions of CuSO4(aq) and BaCl2(aq) are mixed? A. A precipitate of CuCl2 will form; Ba2+ and SO42– are spectator ions. B. A precipitate of CuSO4 will form; Ba2+ and Cl– are spectator ions. C. A precipitate of BaSO4 will form; Cu2+ and Cl– are spectator ion ...
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Amides
... Fatty acids are derived from the coupling of acetic acid. Acetic acid is the primary building block for the biosynthesis of more naturally occurring compounds than any other single precursor substance. The substance 3-methyl-3-butenyl pyrophosphate is the crucial intermediate in the synthesis of ter ...
... Fatty acids are derived from the coupling of acetic acid. Acetic acid is the primary building block for the biosynthesis of more naturally occurring compounds than any other single precursor substance. The substance 3-methyl-3-butenyl pyrophosphate is the crucial intermediate in the synthesis of ter ...
1 - contentextra
... respectively have one or two of the hydrogen atoms substituted by alkyl groups. Carbocation A species formed as an intermediate during a reaction that has a positive charge on a carbon atom. Tertiary carbocations are more stable than secondary which are more stable than primary, due to the positive ...
... respectively have one or two of the hydrogen atoms substituted by alkyl groups. Carbocation A species formed as an intermediate during a reaction that has a positive charge on a carbon atom. Tertiary carbocations are more stable than secondary which are more stable than primary, due to the positive ...
Strychnine total synthesis

Strychnine total synthesis in chemistry describes the total synthesis of the complex biomolecule strychnine. The first reported method by the group of Robert Burns Woodward in 1954 is considered a classic in this research field. At the time it formed the natural conclusion to an elaborate process of molecular structure elucidation that started with the isolation of strychnine from the beans of Strychnos ignatii by Pierre Joseph Pelletier and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou in 1818. Major contributors to the entire effort were Sir Robert Robinson with over 250 publications and Hermann Leuchs with another 125 papers in a time span of 40 years. Robinson was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1947 for his work on alkaloids, strychnine included. The process of chemical identification was completed with publications in 1946 by Robinson and later confirmed by Woodward in 1947. X-ray structures establishing the absolute configuration became available between 1947 and 1951 with publications from J. M. Bijvoet and J.H. Robertson .Woodward published a very brief account on the strychnine synthesis in 1954 (just 3 pages) and a lengthy one (42 pages) in 1963.Many more methods exist and reported by the research groups of Magnus, Overman, Kuehne, Rawal, Bosch, Vollhardt, Mori, Shibasaki, Li, Fukuyama Vanderwal and MacMillan. Synthetic (+)-strychnine is also known. Racemic synthesises were published by Padwa in 2007 and in 2010 by Andrade and by Reissig.In his 1963 publication Woodward quoted Sir Robert Robinson who said for its molecular size it is the most complex substance known.