LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034 PART-A
... 11. Give an example for α, β, γ and δ-elimination reaction. 12. State and explain the Hammond postulate to the bromination of n-propane. 13. How will you determine the reaction mechanism of hydrolysis of an ester using isotoping labeling method? 14. Write and explain the Steven’s rearrangement. 15. ...
... 11. Give an example for α, β, γ and δ-elimination reaction. 12. State and explain the Hammond postulate to the bromination of n-propane. 13. How will you determine the reaction mechanism of hydrolysis of an ester using isotoping labeling method? 14. Write and explain the Steven’s rearrangement. 15. ...
Name Page 1 F.05.215e3p1 I.
... related oxidizing agents, a 1,2-diol is formed. When phenylacetylene (Compound E) is treated with oxidizing agents such as OsO4, the corresponding addition reaction product is not observed; instead it is proposed that the initial addition reaction product, which is an ene-diol, undergoes an isomeriz ...
... related oxidizing agents, a 1,2-diol is formed. When phenylacetylene (Compound E) is treated with oxidizing agents such as OsO4, the corresponding addition reaction product is not observed; instead it is proposed that the initial addition reaction product, which is an ene-diol, undergoes an isomeriz ...
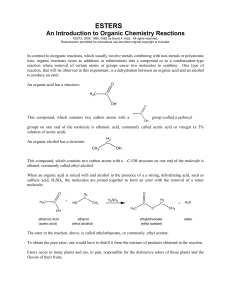
Synthesis of Esters
... alcohol, which you will identify simply by its aroma!! HOW ESTERS ARE MADE: There are several ways to make an ester from an alcohol or a phenol. Reaction (1), mixing a carboxylic acid with an alcohol (or phenol) is not effective - these two react with each other only slowly and, worse, it's an equil ...
... alcohol, which you will identify simply by its aroma!! HOW ESTERS ARE MADE: There are several ways to make an ester from an alcohol or a phenol. Reaction (1), mixing a carboxylic acid with an alcohol (or phenol) is not effective - these two react with each other only slowly and, worse, it's an equil ...
Catalytic Hydrogenation of Alkenes: Relative Stability of
... Secondary and tertiary alcohols dehydrate by an E1 mechanism. The protonated hydroxy forms an alkyloxonium ion providing a good leaving group: water. Loss of water forms a secondary or tertiary carbocation. Deprotonation forms the alkene. Carbocation side reactions (hydrogen shifts, alkyl shifts, e ...
... Secondary and tertiary alcohols dehydrate by an E1 mechanism. The protonated hydroxy forms an alkyloxonium ion providing a good leaving group: water. Loss of water forms a secondary or tertiary carbocation. Deprotonation forms the alkene. Carbocation side reactions (hydrogen shifts, alkyl shifts, e ...
hydrocarbons summary
... Choose the correct ending (-ane for alkanes, -ene for alkenes, -diene for dienes, -triene for trienes, -yne for alkynes) Determine the longest carbon chain. Where a double or triple bond is present, choose the longest chain that includes this bond. Attach a prefix that corresponds to the number of c ...
... Choose the correct ending (-ane for alkanes, -ene for alkenes, -diene for dienes, -triene for trienes, -yne for alkynes) Determine the longest carbon chain. Where a double or triple bond is present, choose the longest chain that includes this bond. Attach a prefix that corresponds to the number of c ...
CHEMISTRY
... (2) [Zn2+] < [Cu2+] (3) The Zn electrode has twice the surface of Cu electrode (4) Mole ratio of Zn2+ : Cu2+ is 2 :1 21. The compound which does not leave any residue on heating is: ...
... (2) [Zn2+] < [Cu2+] (3) The Zn electrode has twice the surface of Cu electrode (4) Mole ratio of Zn2+ : Cu2+ is 2 :1 21. The compound which does not leave any residue on heating is: ...
File
... • Each group should have 4 people and 20 cards. Split the cards up so each person has 5. • On your own piece of paper, write out your 5 chemical equations and balance them. • Then, once all equations are balanced, look at the 20 as a group. You need to split the 20 cards up in to 5 different react ...
... • Each group should have 4 people and 20 cards. Split the cards up so each person has 5. • On your own piece of paper, write out your 5 chemical equations and balance them. • Then, once all equations are balanced, look at the 20 as a group. You need to split the 20 cards up in to 5 different react ...
Chap. 3 : Biochemistry - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... - Can bond with itself to form straight, branched, or ringed chains. - These differences in bonding arrangements provide the many differences in living things. *** Formation of carbon compounds -- polymers – compound made up of repeated linked units (monomers) ...
... - Can bond with itself to form straight, branched, or ringed chains. - These differences in bonding arrangements provide the many differences in living things. *** Formation of carbon compounds -- polymers – compound made up of repeated linked units (monomers) ...
Final Exam Review
... Topics that may be covered on the final: What are the products of free radical halogenation of an alkane (ex: Cl2/hv light)? What is the electivity for brominations vs. chlorinations? How are alkyne anions formed from terminal alkynes? Which radical or anion is most stable? Proper names for compound ...
... Topics that may be covered on the final: What are the products of free radical halogenation of an alkane (ex: Cl2/hv light)? What is the electivity for brominations vs. chlorinations? How are alkyne anions formed from terminal alkynes? Which radical or anion is most stable? Proper names for compound ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... Define and give general equations for synthesis, decomposition, singlereplacement, and double-replacement reactions. Classify a reaction as synthesis, decomposition, single-replacement, single-replacement, doublereplacement, or combustion. ...
... Define and give general equations for synthesis, decomposition, singlereplacement, and double-replacement reactions. Classify a reaction as synthesis, decomposition, single-replacement, single-replacement, doublereplacement, or combustion. ...
Esters - chymist.com
... In contrast to inorganic reactions, which usually involve metals combining with non-metals or polyatomic ions, organic reactions occur as additions or substitutions into a compound or as a condensation-type reaction where removal of certain atoms or groups cause two molecules to combine. One type of ...
... In contrast to inorganic reactions, which usually involve metals combining with non-metals or polyatomic ions, organic reactions occur as additions or substitutions into a compound or as a condensation-type reaction where removal of certain atoms or groups cause two molecules to combine. One type of ...
Functional Groups - Waterford Public Schools
... Naming Primary Amines • When the amino group is attached to a hydrocarbon family like CC, C=C, X- and RO-, the amine group is always treated as the principal functional group and expressed as a suffix • Ending changes to –amine ...
... Naming Primary Amines • When the amino group is attached to a hydrocarbon family like CC, C=C, X- and RO-, the amine group is always treated as the principal functional group and expressed as a suffix • Ending changes to –amine ...
ExamView - sch4u organic test.tst
... ____ 16. Which of the following is a property of all alcohols? A) contain a C=O group C) insoluble in water B) √ toxic D) none of the above ____ 17. The IUPAC name for CH3CH2CH2CH2CH(OH)CH3 is A) √ 2-hexanol C) 4-hexanol B) hexanol D) both b and c ____ 18. The IUPAC name for CH3CH2OH is A) 1-methano ...
... ____ 16. Which of the following is a property of all alcohols? A) contain a C=O group C) insoluble in water B) √ toxic D) none of the above ____ 17. The IUPAC name for CH3CH2CH2CH2CH(OH)CH3 is A) √ 2-hexanol C) 4-hexanol B) hexanol D) both b and c ____ 18. The IUPAC name for CH3CH2OH is A) 1-methano ...
Slide 1
... Any type can be a straight chain, branchedchain, or ring. An Isomer – is a compound that has the same chemical formula but different structural formulas. ...
... Any type can be a straight chain, branchedchain, or ring. An Isomer – is a compound that has the same chemical formula but different structural formulas. ...
Topic 8 Assessed Homework Task - A
... Ethanol is an important fuel. A dilute aqueous solution of ethanol can be produced by the fermentation of an aqueous solution of glucose. It is claimed that the ethanol obtained from this solution is a carbon-neutral biofuel. Write an equation for this fermentation reaction. Give two other essential ...
... Ethanol is an important fuel. A dilute aqueous solution of ethanol can be produced by the fermentation of an aqueous solution of glucose. It is claimed that the ethanol obtained from this solution is a carbon-neutral biofuel. Write an equation for this fermentation reaction. Give two other essential ...
Reactions of Alcohols
... SN2 reaction between R-X and R-OWE NEED TO CONSIDER STERIC HINDERANCE. This might lead to E2! ...
... SN2 reaction between R-X and R-OWE NEED TO CONSIDER STERIC HINDERANCE. This might lead to E2! ...
Stoichiometry Review Package Answer Key
... For a visual practice on balancing equations and limiting/excess reagents go to: https://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/balancing-chemical-equations https://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/reactants-products-and-leftovers The following questions are based on the material covered so far. I will post ...
... For a visual practice on balancing equations and limiting/excess reagents go to: https://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/balancing-chemical-equations https://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/reactants-products-and-leftovers The following questions are based on the material covered so far. I will post ...
Functional Groups
... from the OH group and one from the adjacent carbon atom, resulting in a C=O group. A water molecule is also produced in the reaction. 1. When a primary alcohol is oxidized an H atom remains on the carbon atom and an aldehyde is produced. ...
... from the OH group and one from the adjacent carbon atom, resulting in a C=O group. A water molecule is also produced in the reaction. 1. When a primary alcohol is oxidized an H atom remains on the carbon atom and an aldehyde is produced. ...
Ionic Compounds 1. What is the formula for aluminum phosphate
... 3. How many grams of NaCl are contained in 350. mL of a 0.171 M solution of sodium chloride? 4. What mass of calcium chloride, CaCl2, is in 3.576 L of a 1.56 M solution? 5. Which of the following ion will produce an INSOLUBLE precipitate with a sulfate ion? 6. Which of the following compounds is SOL ...
... 3. How many grams of NaCl are contained in 350. mL of a 0.171 M solution of sodium chloride? 4. What mass of calcium chloride, CaCl2, is in 3.576 L of a 1.56 M solution? 5. Which of the following ion will produce an INSOLUBLE precipitate with a sulfate ion? 6. Which of the following compounds is SOL ...
SNC2D – Science 10 Tuesday April 26th, 2010 Mr. Sourlis and Mr
... e. gold 2. Which one of the following elements has 5 valence electrons? a. boron b. lithium c. hydrogen d. iodine e. phosphorus 3. When a chemical reaction takes place, the total mass of the products is always a. Greater than the total mass of the reactants b. Less than the total mass of the reactan ...
... e. gold 2. Which one of the following elements has 5 valence electrons? a. boron b. lithium c. hydrogen d. iodine e. phosphorus 3. When a chemical reaction takes place, the total mass of the products is always a. Greater than the total mass of the reactants b. Less than the total mass of the reactan ...
chemistry_23 - Bonar Law Memorial
... A Generalized Equation and a Specific One Treating benzene with a halogen in the presence of a catalyst causes the substitution of a hydrogen atom in the ring. Halogens on carbon chains are readily displaced by hydroxide ions to produce an alcohol and a salt. The general reaction is as follows. Hal ...
... A Generalized Equation and a Specific One Treating benzene with a halogen in the presence of a catalyst causes the substitution of a hydrogen atom in the ring. Halogens on carbon chains are readily displaced by hydroxide ions to produce an alcohol and a salt. The general reaction is as follows. Hal ...
Strychnine total synthesis

Strychnine total synthesis in chemistry describes the total synthesis of the complex biomolecule strychnine. The first reported method by the group of Robert Burns Woodward in 1954 is considered a classic in this research field. At the time it formed the natural conclusion to an elaborate process of molecular structure elucidation that started with the isolation of strychnine from the beans of Strychnos ignatii by Pierre Joseph Pelletier and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou in 1818. Major contributors to the entire effort were Sir Robert Robinson with over 250 publications and Hermann Leuchs with another 125 papers in a time span of 40 years. Robinson was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1947 for his work on alkaloids, strychnine included. The process of chemical identification was completed with publications in 1946 by Robinson and later confirmed by Woodward in 1947. X-ray structures establishing the absolute configuration became available between 1947 and 1951 with publications from J. M. Bijvoet and J.H. Robertson .Woodward published a very brief account on the strychnine synthesis in 1954 (just 3 pages) and a lengthy one (42 pages) in 1963.Many more methods exist and reported by the research groups of Magnus, Overman, Kuehne, Rawal, Bosch, Vollhardt, Mori, Shibasaki, Li, Fukuyama Vanderwal and MacMillan. Synthetic (+)-strychnine is also known. Racemic synthesises were published by Padwa in 2007 and in 2010 by Andrade and by Reissig.In his 1963 publication Woodward quoted Sir Robert Robinson who said for its molecular size it is the most complex substance known.