The Synthesis and Analysis of Copper (II) Carboxylates
... best method of analysis. 1n eaehcasekxceptthe "se afthe carboxylic aeid as an unknown, the student can be expected to rationalize differences in procedure for different carboxylate acids. ...
... best method of analysis. 1n eaehcasekxceptthe "se afthe carboxylic aeid as an unknown, the student can be expected to rationalize differences in procedure for different carboxylate acids. ...
Activity Series Unit
... Explain 1: Why do some ions interact with other in a reaction while others do not? 4. Consider the reactions that took place between the metals and hydrochloric acid. Write a chemical equation of each reaction that took place. (Be sure to write each species as it exists in solution) This is called ...
... Explain 1: Why do some ions interact with other in a reaction while others do not? 4. Consider the reactions that took place between the metals and hydrochloric acid. Write a chemical equation of each reaction that took place. (Be sure to write each species as it exists in solution) This is called ...
Chapter 21 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
... • Two molecules of acid combine with the loss of water to form the anhydride. • Anhydrides are more reactive than acids, but less reactive than acid chlorides. • A carboxylate ion is the leaving group in ...
... • Two molecules of acid combine with the loss of water to form the anhydride. • Anhydrides are more reactive than acids, but less reactive than acid chlorides. • A carboxylate ion is the leaving group in ...
Organic synthesis
... • Condenser must have outer tube for water that is sealed at top and bottom • Condenser must have two openings for water in and out that are open ...
... • Condenser must have outer tube for water that is sealed at top and bottom • Condenser must have two openings for water in and out that are open ...
Chemistry 100
... completion? Each involves the reaction symbolized by the equation: N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g) A) B) C) D) ...
... completion? Each involves the reaction symbolized by the equation: N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g) A) B) C) D) ...
Chapter 5 - Skyline AP Biology
... 19) Enzymes that break down DNA catalyze the hydrolysis of the covalent bonds that join nucleotides 19) together. What would happen to DNA molecules treated with these enzymes? A) The purines would be separated from the deoxyribose sugars. B) All bases would be separated from the deoxyribose sugars. ...
... 19) Enzymes that break down DNA catalyze the hydrolysis of the covalent bonds that join nucleotides 19) together. What would happen to DNA molecules treated with these enzymes? A) The purines would be separated from the deoxyribose sugars. B) All bases would be separated from the deoxyribose sugars. ...
Ethers - ThinkChemistry
... water but as their chain length increases their solubility in water decreases. ...
... water but as their chain length increases their solubility in water decreases. ...
File
... and an un-saturated aliphatic using the addition of aqueous bromine or potassium permanganate solutions. Formation of two layers means no reaction took place, therefore aliphatic was saturated. If a color change takes place or a precipitated forms, a reaction occurred, which means the aliphatic was ...
... and an un-saturated aliphatic using the addition of aqueous bromine or potassium permanganate solutions. Formation of two layers means no reaction took place, therefore aliphatic was saturated. If a color change takes place or a precipitated forms, a reaction occurred, which means the aliphatic was ...
Study Guide KEY Exam III F 2012
... non-bonding pair on the carbonyl oxygen (C=O) in the backbone. Tertiary (3o) structure refers to the location of each atom of the protein relative to every other atom in three dimensional space. This structure is maintained by hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonding, covalent (disulfide, -S-S-) b ...
... non-bonding pair on the carbonyl oxygen (C=O) in the backbone. Tertiary (3o) structure refers to the location of each atom of the protein relative to every other atom in three dimensional space. This structure is maintained by hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonding, covalent (disulfide, -S-S-) b ...
Test Booklet
... 22 Using the solubility graph provided, a student performs an experiment to find the solubility of a substance. The student finds the amount of substance needed to make a saturated solution in 100 g of water at different temperatures. The student’s data are shown in the table below the graph. ...
... 22 Using the solubility graph provided, a student performs an experiment to find the solubility of a substance. The student finds the amount of substance needed to make a saturated solution in 100 g of water at different temperatures. The student’s data are shown in the table below the graph. ...
File - need help with revision notes?
... 4. Oxidation (of primary and secondary alcohols) A primary alcohol can be oxidised to form an Aldehyde, and then further oxidised to form a carboxylic acid. The reagents used are acidified potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) and concentrated sulphuric acid H2SO4 (source of H+ ions). If an oxidisation rea ...
... 4. Oxidation (of primary and secondary alcohols) A primary alcohol can be oxidised to form an Aldehyde, and then further oxidised to form a carboxylic acid. The reagents used are acidified potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) and concentrated sulphuric acid H2SO4 (source of H+ ions). If an oxidisation rea ...
Chapter 4
... Acid-Base Reactions • Reminder: Arrhenius (irrelevant) acids/bases • Brønsted-Lowry acids/bases (protons only): Acids are proton donors, bases are proton acceptors • Acid-Base Reactions are called neutralization reactions because the acid/base becomes neutralized by the base/acid added to it. • *OH ...
... Acid-Base Reactions • Reminder: Arrhenius (irrelevant) acids/bases • Brønsted-Lowry acids/bases (protons only): Acids are proton donors, bases are proton acceptors • Acid-Base Reactions are called neutralization reactions because the acid/base becomes neutralized by the base/acid added to it. • *OH ...
Basic Chemistry – Terminology and Reactions
... 2O 3O In order to balance an equation we have to follow these steps. Step 1: Start by finding out how many atoms of each type are on each side of the equation. Step 2: Next, look for an element which is in only one chemical on the left and in only one on the right of the equation. Step 3: Balance th ...
... 2O 3O In order to balance an equation we have to follow these steps. Step 1: Start by finding out how many atoms of each type are on each side of the equation. Step 2: Next, look for an element which is in only one chemical on the left and in only one on the right of the equation. Step 3: Balance th ...
doc
... Why does this reaction work better for primary and secondary alcohols? These reagents are less acidic and less likely to cause acid catalyzed rearrangements. (Mechanisms are covered in Chapter 11.) ...
... Why does this reaction work better for primary and secondary alcohols? These reagents are less acidic and less likely to cause acid catalyzed rearrangements. (Mechanisms are covered in Chapter 11.) ...
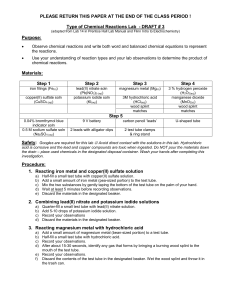
Type of Chemical Reactions Lab
... iv. Return the solution to the dispensing container and rinse the U-tube with water. v. Return the materials to their original location. ...
... iv. Return the solution to the dispensing container and rinse the U-tube with water. v. Return the materials to their original location. ...
Exp`t 70
... Guide. DO NOT ADD DICHLOROMETHANE, but instead analyze the pure liquid as a “neat” sample on the gas chromatograph. (Check the GC compendium in 206 W for GC conditions). In analyzing your results, consider that the carbocation can lose any of 6 primary hydrogen atoms, but only 2 secondary hydrogen a ...
... Guide. DO NOT ADD DICHLOROMETHANE, but instead analyze the pure liquid as a “neat” sample on the gas chromatograph. (Check the GC compendium in 206 W for GC conditions). In analyzing your results, consider that the carbocation can lose any of 6 primary hydrogen atoms, but only 2 secondary hydrogen a ...
Chemistry Review Name: Date: __B__1. An element is to a (an
... e. 10p+;8n0;10ec. 9p+;9n0;9e__C_ 5. The atomic number of sulfur is 16. Sulfur combines with hydrogen by covalent bonding to form a compound, hydrogen sulfide. Based on the electron configuration of sulfur, we can predict that the molecular formula of the compound will be (explain your answer) a. HS ...
... e. 10p+;8n0;10ec. 9p+;9n0;9e__C_ 5. The atomic number of sulfur is 16. Sulfur combines with hydrogen by covalent bonding to form a compound, hydrogen sulfide. Based on the electron configuration of sulfur, we can predict that the molecular formula of the compound will be (explain your answer) a. HS ...
Alcohol - djkuranui
... primary alcohols). Secondary alcohols don’t create aldehydes – they create ketones. Ergo, Tollen’s test can be used to tell the difference b/w aldehydes and ketones ...
... primary alcohols). Secondary alcohols don’t create aldehydes – they create ketones. Ergo, Tollen’s test can be used to tell the difference b/w aldehydes and ketones ...
HIGHER TIER CHEMISTRY MINI-MOCK UNIT 2
... CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) The rate at which this reaction takes place can be studied by measuring the amount of carbon dioxide gas produced. The graph below shows the results of four experiments, 1 to 4. In each experiment the amount of calcium carbonate, the volume of acid a ...
... CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) The rate at which this reaction takes place can be studied by measuring the amount of carbon dioxide gas produced. The graph below shows the results of four experiments, 1 to 4. In each experiment the amount of calcium carbonate, the volume of acid a ...
SG5 Chemical Reactions and Quantities
... A gas may form (bubbling, new odors, etc.) A solid may form (precipitation) Colors, odors, and textures may change 3) Write a balanced chemical equation 1. Make sure all your formulas are correct; you may not change them 2. Remember the elements that form diatomic molecules: H2 N2 O2 F2 Cl2 Br2 I2 3 ...
... A gas may form (bubbling, new odors, etc.) A solid may form (precipitation) Colors, odors, and textures may change 3) Write a balanced chemical equation 1. Make sure all your formulas are correct; you may not change them 2. Remember the elements that form diatomic molecules: H2 N2 O2 F2 Cl2 Br2 I2 3 ...
Name: Northwest Vista College Chem 1311
... 9. Based on the solubility rules, which of the following will occur if solutions of CuSO 4(aq) and BaCl2(aq) are mixed? A) CuCl2 will precipitate; Ba2+ and SO42- are spectator ions. B) CuSO4 will precipitate; Ba2+ and Cl- are spectator ions. C) BaSO4 will precipitate; Cu2+ and Cl- are spectator ions ...
... 9. Based on the solubility rules, which of the following will occur if solutions of CuSO 4(aq) and BaCl2(aq) are mixed? A) CuCl2 will precipitate; Ba2+ and SO42- are spectator ions. B) CuSO4 will precipitate; Ba2+ and Cl- are spectator ions. C) BaSO4 will precipitate; Cu2+ and Cl- are spectator ions ...
Strychnine total synthesis

Strychnine total synthesis in chemistry describes the total synthesis of the complex biomolecule strychnine. The first reported method by the group of Robert Burns Woodward in 1954 is considered a classic in this research field. At the time it formed the natural conclusion to an elaborate process of molecular structure elucidation that started with the isolation of strychnine from the beans of Strychnos ignatii by Pierre Joseph Pelletier and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou in 1818. Major contributors to the entire effort were Sir Robert Robinson with over 250 publications and Hermann Leuchs with another 125 papers in a time span of 40 years. Robinson was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1947 for his work on alkaloids, strychnine included. The process of chemical identification was completed with publications in 1946 by Robinson and later confirmed by Woodward in 1947. X-ray structures establishing the absolute configuration became available between 1947 and 1951 with publications from J. M. Bijvoet and J.H. Robertson .Woodward published a very brief account on the strychnine synthesis in 1954 (just 3 pages) and a lengthy one (42 pages) in 1963.Many more methods exist and reported by the research groups of Magnus, Overman, Kuehne, Rawal, Bosch, Vollhardt, Mori, Shibasaki, Li, Fukuyama Vanderwal and MacMillan. Synthetic (+)-strychnine is also known. Racemic synthesises were published by Padwa in 2007 and in 2010 by Andrade and by Reissig.In his 1963 publication Woodward quoted Sir Robert Robinson who said for its molecular size it is the most complex substance known.