Chromatography Spectroscopy HW
... Compare the reagents and conditions for the nitration of phenol with those used for the nitration of benzene. State and explain the effect of the –OH group on the reactivity of the benzene ring in phenol. ...
... Compare the reagents and conditions for the nitration of phenol with those used for the nitration of benzene. State and explain the effect of the –OH group on the reactivity of the benzene ring in phenol. ...
11. 5-member heterocycles with 1 and heteroatoms
... attached to one of the carbon atoms of the tetrahydrothiophene ring. Biotin supplements are often recommended as a natural product to counteract the problem of hair loss in both children and adults. The signs and symptoms of biotin deficiency include hair loss which progresses in severity to include ...
... attached to one of the carbon atoms of the tetrahydrothiophene ring. Biotin supplements are often recommended as a natural product to counteract the problem of hair loss in both children and adults. The signs and symptoms of biotin deficiency include hair loss which progresses in severity to include ...
UNIT 1—Water AB
... d) How many grams of the excess reactant will remain when the reaction has stopped? Predicting products of Chemical Reaction 1. A synthesis (combination) reaction occurs between solid Lithium and Oxygen gas. The product is Lithium Oxide. 2. A double replacement reaction occurs. Ca(NO3)2 (aq) + Na2CO ...
... d) How many grams of the excess reactant will remain when the reaction has stopped? Predicting products of Chemical Reaction 1. A synthesis (combination) reaction occurs between solid Lithium and Oxygen gas. The product is Lithium Oxide. 2. A double replacement reaction occurs. Ca(NO3)2 (aq) + Na2CO ...
Answer Key to Sample Questions
... a. What is the sign of S for this reaction? positive because one molecule breaks to form two molecules b. What is the sign of H for this reaction? positive because a bond is broken, but none is formed. c. In which temperature range will this reaction be thermodynamically favored? It is entropy fav ...
... a. What is the sign of S for this reaction? positive because one molecule breaks to form two molecules b. What is the sign of H for this reaction? positive because a bond is broken, but none is formed. c. In which temperature range will this reaction be thermodynamically favored? It is entropy fav ...
Reduction Reactions
... Although the reactive component of sodium borohydride is the hydridic anion, the counterion can also be used to modulate the reactivity of the reagent system. A number of other borohydride reagents are available including LiBH4 and Ca(BH4)2. Both these reagents are more reactive and readily reduce e ...
... Although the reactive component of sodium borohydride is the hydridic anion, the counterion can also be used to modulate the reactivity of the reagent system. A number of other borohydride reagents are available including LiBH4 and Ca(BH4)2. Both these reagents are more reactive and readily reduce e ...
C6_rev - boswellsrcd
... Method 1. Write a balanced equation for the reaction. sodium hydroxide + hydrochloric acid NaOH(aq) HCl(aq) ...
... Method 1. Write a balanced equation for the reaction. sodium hydroxide + hydrochloric acid NaOH(aq) HCl(aq) ...
Lecture Notes 7 - La Salle University
... The iron(II) protoporphyrin-IX complex is the prosthetic group in hemoglobins and myoglobins, which are responsible for oxygen transport and storage in living tissues. Heme can also be found in the enzyme peroxidase, which catalyzes the oxidation of substrates with hydrogen peroxide. The related enz ...
... The iron(II) protoporphyrin-IX complex is the prosthetic group in hemoglobins and myoglobins, which are responsible for oxygen transport and storage in living tissues. Heme can also be found in the enzyme peroxidase, which catalyzes the oxidation of substrates with hydrogen peroxide. The related enz ...
Combining transition metal catalysis and organocatalysis
... e.g.) using a "soft" Lewis acid (metal such as Cu(I), Ag(I), Au(I), and Pd(0)) and a "hard" Lewis base (amine) 1. combining enamine catalysis and -allyl palladium complexes 2. combining enamine catalysis and -activation of C-C triple bond 4. combining enamine catalysis and SOMO photoredox catalysis ...
... e.g.) using a "soft" Lewis acid (metal such as Cu(I), Ag(I), Au(I), and Pd(0)) and a "hard" Lewis base (amine) 1. combining enamine catalysis and -allyl palladium complexes 2. combining enamine catalysis and -activation of C-C triple bond 4. combining enamine catalysis and SOMO photoredox catalysis ...
CHEM1100 Practice Exam 2 You have 120 minutes to complete this
... 1. Salts containing Group I elements are soluble (Li+, Na+, K+, Cs+, Rb+). Exceptions to this rule are rare. Salts containing the ammonium ion (NH4+) are also soluble. 2. Salts containing nitrate ion (NO3-) are generally soluble. 3. Salts containing Cl–, Br–, I– are generally soluble. Important exce ...
... 1. Salts containing Group I elements are soluble (Li+, Na+, K+, Cs+, Rb+). Exceptions to this rule are rare. Salts containing the ammonium ion (NH4+) are also soluble. 2. Salts containing nitrate ion (NO3-) are generally soluble. 3. Salts containing Cl–, Br–, I– are generally soluble. Important exce ...
ORGANIC REACTIONS IN A CLAY MICROENVIRONMENT
... Both primary and secondary thiols readily underwent inter-molecular elimination of hydrogen sulphide under the influence of Al-bentonite in a sealed reactor at 200~ Little alkene production took place. (Ballantine et al., 1981d). Butan-l-thiol was found to produce di-(but-l-yl) sulphide (21%) with 7 ...
... Both primary and secondary thiols readily underwent inter-molecular elimination of hydrogen sulphide under the influence of Al-bentonite in a sealed reactor at 200~ Little alkene production took place. (Ballantine et al., 1981d). Butan-l-thiol was found to produce di-(but-l-yl) sulphide (21%) with 7 ...
Key III
... a) The sigma bond formed between the carbon and oxygen atoms is best described as being between the overlap of a(n) _ __ hybrid orbital on C with a(n) _ __ hybrid orbital on O. b) The sigma bonds formed between the hydrogen and carbon is best described as being the overlap of an __ _ hybrid orbital ...
... a) The sigma bond formed between the carbon and oxygen atoms is best described as being between the overlap of a(n) _ __ hybrid orbital on C with a(n) _ __ hybrid orbital on O. b) The sigma bonds formed between the hydrogen and carbon is best described as being the overlap of an __ _ hybrid orbital ...
Final Review
... equivalence point c. The molarity of a NaOH solution, if 20.0 mL of the solution was neutralized by 28.0 mL of a 1.0 M H3PO4 solution Chapter 19 Oxidation—Reduction Reactions Define the following terms: a. oxidation b. reduction c. half-reaction d. oxidation number e. oxidizing agent f. reducing age ...
... equivalence point c. The molarity of a NaOH solution, if 20.0 mL of the solution was neutralized by 28.0 mL of a 1.0 M H3PO4 solution Chapter 19 Oxidation—Reduction Reactions Define the following terms: a. oxidation b. reduction c. half-reaction d. oxidation number e. oxidizing agent f. reducing age ...
Gas-Forming reactions Reactions that form a
... (b). Cl, Br and I has an oxidation number of -1 in compounds, except when combined with oxygen or fluorine (c). Hydrogen, in all its compounds except hydrides, has an oxidation number of +1. (d). Oxygen, in all its compounds except when connected to another oxygen or a fluorine, has an oxidation num ...
... (b). Cl, Br and I has an oxidation number of -1 in compounds, except when combined with oxygen or fluorine (c). Hydrogen, in all its compounds except hydrides, has an oxidation number of +1. (d). Oxygen, in all its compounds except when connected to another oxygen or a fluorine, has an oxidation num ...
Chapter 1--Title
... A calculated electrostatic potential map of benzyne shows added electron density at the site of the benzyne p bond ...
... A calculated electrostatic potential map of benzyne shows added electron density at the site of the benzyne p bond ...
Chapter 19
... (primary amines are oxidized to nitro and secondary amines are oxidized to hydroxylamines) ...
... (primary amines are oxidized to nitro and secondary amines are oxidized to hydroxylamines) ...
Chemistry 223 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State University
... Primary structure is the order that the amino acids are connected. Ala-Gly-Glu-Ala denotes the order in which the amino acids are connected. What is meant by secondary structure? Give an example. Secondary structure is the orientation the primary structure obtains (alpha helix or ...
... Primary structure is the order that the amino acids are connected. Ala-Gly-Glu-Ala denotes the order in which the amino acids are connected. What is meant by secondary structure? Give an example. Secondary structure is the orientation the primary structure obtains (alpha helix or ...
ch12 by dina
... Reaction of ESTER AND KETONS + Grignard reagent The final product contains two identical groups at the alcohol carbon that are both derived from the Grignard reagent Esters react with two molar equivalents of a Grignard reagent to yield a tertiary alcohol A ketone is formed by the first molar equ ...
... Reaction of ESTER AND KETONS + Grignard reagent The final product contains two identical groups at the alcohol carbon that are both derived from the Grignard reagent Esters react with two molar equivalents of a Grignard reagent to yield a tertiary alcohol A ketone is formed by the first molar equ ...
or H - No Brain Too Small
... o conversion of primary alcohol to carboxylic acid using heat and H+/Cr2O72- or H+/MnO4- (both oxidising agents) o conversion of an alkene to a diol using H+/MnO4- (no heat needed) ...
... o conversion of primary alcohol to carboxylic acid using heat and H+/Cr2O72- or H+/MnO4- (both oxidising agents) o conversion of an alkene to a diol using H+/MnO4- (no heat needed) ...
Problem Set 12-2: Organic Chemistry
... 4. How could you test for an optical isomer? 5. Locate chrial centers in the structures you drew above. 6. Rank from acidic to basic: a. Methanol b. Methanoic acid c. Methanamine d. Methanal 7. Why is ethanoic acid considered an acid? (i.e. what is the definition of an acid?) 8. Which of the 12 func ...
... 4. How could you test for an optical isomer? 5. Locate chrial centers in the structures you drew above. 6. Rank from acidic to basic: a. Methanol b. Methanoic acid c. Methanamine d. Methanal 7. Why is ethanoic acid considered an acid? (i.e. what is the definition of an acid?) 8. Which of the 12 func ...
Organic Chemistry The Chemistry Of Life / The Chemistry of Carbon
... 4. Weak enough to metabolize and recycle but strong enough for stability ...
... 4. Weak enough to metabolize and recycle but strong enough for stability ...
Aldehydes and Ketones
... ketone with a phosphonium ylide- a compound with a negatively-charged carbon bonded to a positively-charged phosphorus atom. The result is the replacement of the carbonyl oxygen with the carbon group on the ylide. We will learn how to prepare this Wittig reagent (the ylide), and how it reacts with t ...
... ketone with a phosphonium ylide- a compound with a negatively-charged carbon bonded to a positively-charged phosphorus atom. The result is the replacement of the carbonyl oxygen with the carbon group on the ylide. We will learn how to prepare this Wittig reagent (the ylide), and how it reacts with t ...
TYPES OF SOLUTION CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... a. endpoint- the point (volume of standard) at which the unknown changes color b. equivalence point--# moles of standard solution = # moles of unknown solution. c. standardize- titration the unknown solution with the standard of known concentration. Exercise 14 A student carries out an experiment to ...
... a. endpoint- the point (volume of standard) at which the unknown changes color b. equivalence point--# moles of standard solution = # moles of unknown solution. c. standardize- titration the unknown solution with the standard of known concentration. Exercise 14 A student carries out an experiment to ...
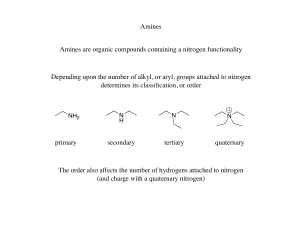
Nitrogen Compounds
... In aqueous solution depending on the pH, they form either the neutral form, or the carboxylate will lose a proton, or the amino group will gain a proton. ...
... In aqueous solution depending on the pH, they form either the neutral form, or the carboxylate will lose a proton, or the amino group will gain a proton. ...
Nexera UC Scouting - Shimadzu Europa GmbH
... safer drugs, therapeutics and diagnostics. During API (active pharmaceutical ingredient) development, drug stereoisomerism is recognized as an issue having clinical and regulatory implications. Enantiomers have essentially identical physical and chemical properties, while potentially showing large d ...
... safer drugs, therapeutics and diagnostics. During API (active pharmaceutical ingredient) development, drug stereoisomerism is recognized as an issue having clinical and regulatory implications. Enantiomers have essentially identical physical and chemical properties, while potentially showing large d ...
Strychnine total synthesis

Strychnine total synthesis in chemistry describes the total synthesis of the complex biomolecule strychnine. The first reported method by the group of Robert Burns Woodward in 1954 is considered a classic in this research field. At the time it formed the natural conclusion to an elaborate process of molecular structure elucidation that started with the isolation of strychnine from the beans of Strychnos ignatii by Pierre Joseph Pelletier and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou in 1818. Major contributors to the entire effort were Sir Robert Robinson with over 250 publications and Hermann Leuchs with another 125 papers in a time span of 40 years. Robinson was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1947 for his work on alkaloids, strychnine included. The process of chemical identification was completed with publications in 1946 by Robinson and later confirmed by Woodward in 1947. X-ray structures establishing the absolute configuration became available between 1947 and 1951 with publications from J. M. Bijvoet and J.H. Robertson .Woodward published a very brief account on the strychnine synthesis in 1954 (just 3 pages) and a lengthy one (42 pages) in 1963.Many more methods exist and reported by the research groups of Magnus, Overman, Kuehne, Rawal, Bosch, Vollhardt, Mori, Shibasaki, Li, Fukuyama Vanderwal and MacMillan. Synthetic (+)-strychnine is also known. Racemic synthesises were published by Padwa in 2007 and in 2010 by Andrade and by Reissig.In his 1963 publication Woodward quoted Sir Robert Robinson who said for its molecular size it is the most complex substance known.