Nitrogen and its compounds - kcpe-kcse
... or phosphorus (V) oxide or fused calcium chloride cannot dry an alkaline gas like ammonia. Sulphuric acid and phosphorus (V) oxide are both acidic. They react with ammonia, forming their respective ammonium salt. ...
... or phosphorus (V) oxide or fused calcium chloride cannot dry an alkaline gas like ammonia. Sulphuric acid and phosphorus (V) oxide are both acidic. They react with ammonia, forming their respective ammonium salt. ...
EXPERIMENT 4 Objectives Principles
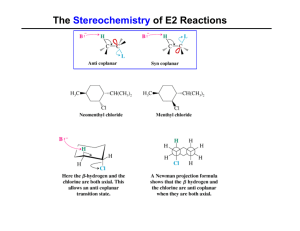
... concentration of alkyl halide. This reaction works best with methyl and primary halides because bulky alkyl groups block the backside attack of the nucleophile, but the reaction does work with secondary halides (although it is usually accompanied by elimination), and will not react at all with terti ...
... concentration of alkyl halide. This reaction works best with methyl and primary halides because bulky alkyl groups block the backside attack of the nucleophile, but the reaction does work with secondary halides (although it is usually accompanied by elimination), and will not react at all with terti ...
Student Instructions from Laboratory Manual
... bar. With vigorous stirring, slowly add 2.5 equiv of lithium triethylborohydride [aka, SuperHydride®] (1.0-M solution in THF) by syringe, cap the flask, and allow the reaction to proceed for 20 min. Add 3 equiv of methyl iodide slowly by calibrated micropipette and stir the resulting reaction mixtur ...
... bar. With vigorous stirring, slowly add 2.5 equiv of lithium triethylborohydride [aka, SuperHydride®] (1.0-M solution in THF) by syringe, cap the flask, and allow the reaction to proceed for 20 min. Add 3 equiv of methyl iodide slowly by calibrated micropipette and stir the resulting reaction mixtur ...
Chapter 4
... the left side and the correct formula(s) for the product(s) on the right side of the equation. Ethane reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water C2H6 + O2 ...
... the left side and the correct formula(s) for the product(s) on the right side of the equation. Ethane reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water C2H6 + O2 ...
Chapter 1 Review, pages 72–77
... 37. (a) The compound on the right, benzoic acid, has two polar groups—a carbonyl group and a hydroxyl group—located close together, adding polarity to the molecule, which contributes to its solubility in water. However, the non-polar ring makes benzoic acid less soluble. Consequently, benzoic acid ...
... 37. (a) The compound on the right, benzoic acid, has two polar groups—a carbonyl group and a hydroxyl group—located close together, adding polarity to the molecule, which contributes to its solubility in water. However, the non-polar ring makes benzoic acid less soluble. Consequently, benzoic acid ...
Equilibrium Review worksheet
... 10. A 0.10 mol/L solution of the essential amino acid tryptophan has a measured pH of 5.19 at 25 °C. Predict the percent ionization of this tryptophan solution, and the Ka value for aqueous tryptophan. The molecular formula for tryptophan may be written as C 10H11N2COOH. ...
... 10. A 0.10 mol/L solution of the essential amino acid tryptophan has a measured pH of 5.19 at 25 °C. Predict the percent ionization of this tryptophan solution, and the Ka value for aqueous tryptophan. The molecular formula for tryptophan may be written as C 10H11N2COOH. ...
Group Activity 3 [10 PTS]
... 1. Write the condensed structural formula of each of the following alcohols a. 1-propanol ...
... 1. Write the condensed structural formula of each of the following alcohols a. 1-propanol ...
Chapter 6
... 2. Zinc Metal, used as a coating in galvanized iron, also reacts with air to form a coating that resists further corrosion. zinc+ oxygen → ___________________ 3. When aluminum foil is placed in a solution of copper (II) chloride, copper metal and another solution are formed: aluminum + copper (II) c ...
... 2. Zinc Metal, used as a coating in galvanized iron, also reacts with air to form a coating that resists further corrosion. zinc+ oxygen → ___________________ 3. When aluminum foil is placed in a solution of copper (II) chloride, copper metal and another solution are formed: aluminum + copper (II) c ...
Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life
... Carbon has little tendency to gain or lose electrons. It has a valence number of 4 and forms four covalent bonds. Each carbon atom in a carbon compound is an intersection point and so a molecule can branch off in four directions. This makes it TETRAVALENT. Single covalent bonds form a tetrahedron li ...
... Carbon has little tendency to gain or lose electrons. It has a valence number of 4 and forms four covalent bonds. Each carbon atom in a carbon compound is an intersection point and so a molecule can branch off in four directions. This makes it TETRAVALENT. Single covalent bonds form a tetrahedron li ...
Organic Chemistry – Summary of Reactions and Conditions
... made from vegetable oils but the triglycerides in the oils need to be converted into methyl or ethyl esters in order for the oil to be a suitable fuel for the engine. e.g. ...
... made from vegetable oils but the triglycerides in the oils need to be converted into methyl or ethyl esters in order for the oil to be a suitable fuel for the engine. e.g. ...
Alkene/Alkyne Addition Reactions
... unsymmetrical reagent such as H-Br, H-Cl, or H-OH to an alkene or alkyne is the one obtained when the H atom of the reagent is added to the C atom of the multiple bond that already has the greater number of H atoms. “The rich get richer” ...
... unsymmetrical reagent such as H-Br, H-Cl, or H-OH to an alkene or alkyne is the one obtained when the H atom of the reagent is added to the C atom of the multiple bond that already has the greater number of H atoms. “The rich get richer” ...
Study Guide Exam 2 and 3 Sp2011
... If you are trying to determine if an amine is a primary, secondary or tertiary, you now replace the C with the N and the OH with lone pair of electrons on the picture for alcohols. Depending on how many other carbon atoms are bound to the nitrogen determines if it is primary, secondary or tertiary. ...
... If you are trying to determine if an amine is a primary, secondary or tertiary, you now replace the C with the N and the OH with lone pair of electrons on the picture for alcohols. Depending on how many other carbon atoms are bound to the nitrogen determines if it is primary, secondary or tertiary. ...
Ultrasonic acceleration of ester hydrolysis in ethanol–water
... maximum points. In our previous study [8] it was concluded that these phenomena should be related to the molecular structure of the binary solvent rather than to the reaction mechanism. However, replacement of ethyl acetate by more hydrophobic butyl acetate changed beyond recognition the dependence ...
... maximum points. In our previous study [8] it was concluded that these phenomena should be related to the molecular structure of the binary solvent rather than to the reaction mechanism. However, replacement of ethyl acetate by more hydrophobic butyl acetate changed beyond recognition the dependence ...
Thermochemistry 2 Matching Match each item with the correct
... Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. heat of reaction d. heat of fusion b. heat of formation e. heat of solution c. Hess's law of heat summation ____ ...
... Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. heat of reaction d. heat of fusion b. heat of formation e. heat of solution c. Hess's law of heat summation ____ ...
final1-final_report
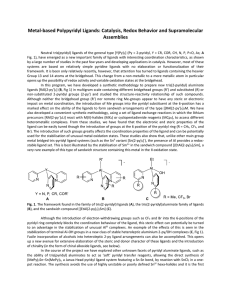
... also developed a convenient synthetic methodology, using a set of ligand exchange reactions in which the lithium precursors [RAl(2-py´)3Li] react with M(II)-halides (MX2) or cyclopentadienide reagents (MCp2), to access different heterometallic complexes. From these studies, we have found that the el ...
... also developed a convenient synthetic methodology, using a set of ligand exchange reactions in which the lithium precursors [RAl(2-py´)3Li] react with M(II)-halides (MX2) or cyclopentadienide reagents (MCp2), to access different heterometallic complexes. From these studies, we have found that the el ...
Page 1 - WordPress.com
... Q7.Haloalkanes are used in the synthesis of other organic compounds. (a) Hot concentrated ethanolic potassium hydroxide reacts with 2-‐bromo-‐3-‐methylbutane to form two alkenes that are structural iso ...
... Q7.Haloalkanes are used in the synthesis of other organic compounds. (a) Hot concentrated ethanolic potassium hydroxide reacts with 2-‐bromo-‐3-‐methylbutane to form two alkenes that are structural iso ...
organic functional group analysis
... 2. Solubility in 5% NaOH: Diagnosis of a High Molecular Weight Organic Acid Add ~1 mL of 5% NaOH dropwise, with agitation, to ~0.5 mL of the known compound. A high molecular weight carboxylic acid will be soluble in 5% NaOH because of the formation of the sodium salt of the acid. High molecular weig ...
... 2. Solubility in 5% NaOH: Diagnosis of a High Molecular Weight Organic Acid Add ~1 mL of 5% NaOH dropwise, with agitation, to ~0.5 mL of the known compound. A high molecular weight carboxylic acid will be soluble in 5% NaOH because of the formation of the sodium salt of the acid. High molecular weig ...
- Iranian Journal of Science and Technology (Sciences)
... chlorodiphenylphosphine was selected as the most suitable reagent and media for performing the esterification reactions. Apart from the ease of handling and preparation of this IL, the phosphine oxide formed in the reaction is taken up by the ionic liquid and the ester product forms a separate phase ...
... chlorodiphenylphosphine was selected as the most suitable reagent and media for performing the esterification reactions. Apart from the ease of handling and preparation of this IL, the phosphine oxide formed in the reaction is taken up by the ionic liquid and the ester product forms a separate phase ...
Strychnine total synthesis

Strychnine total synthesis in chemistry describes the total synthesis of the complex biomolecule strychnine. The first reported method by the group of Robert Burns Woodward in 1954 is considered a classic in this research field. At the time it formed the natural conclusion to an elaborate process of molecular structure elucidation that started with the isolation of strychnine from the beans of Strychnos ignatii by Pierre Joseph Pelletier and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou in 1818. Major contributors to the entire effort were Sir Robert Robinson with over 250 publications and Hermann Leuchs with another 125 papers in a time span of 40 years. Robinson was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1947 for his work on alkaloids, strychnine included. The process of chemical identification was completed with publications in 1946 by Robinson and later confirmed by Woodward in 1947. X-ray structures establishing the absolute configuration became available between 1947 and 1951 with publications from J. M. Bijvoet and J.H. Robertson .Woodward published a very brief account on the strychnine synthesis in 1954 (just 3 pages) and a lengthy one (42 pages) in 1963.Many more methods exist and reported by the research groups of Magnus, Overman, Kuehne, Rawal, Bosch, Vollhardt, Mori, Shibasaki, Li, Fukuyama Vanderwal and MacMillan. Synthetic (+)-strychnine is also known. Racemic synthesises were published by Padwa in 2007 and in 2010 by Andrade and by Reissig.In his 1963 publication Woodward quoted Sir Robert Robinson who said for its molecular size it is the most complex substance known.







![Group Activity 3 [10 PTS]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010780770_1-3445600a9b56e890a0f283c789afe8fb-300x300.png)