ch8 - Otterville R-VI School District
... organize reactants and products Be sure to include symbols showing states of each reactant and product Be sure to write the correct formula ...
... organize reactants and products Be sure to include symbols showing states of each reactant and product Be sure to write the correct formula ...
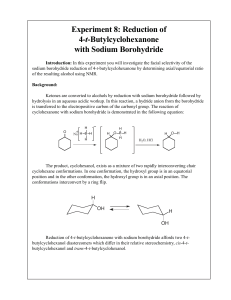
Experiment 8: Reduction of 4-t-Butylcyclohexanone with Sodium
... When water and an organic liquid are shaken together and than allowed to stand, the liquids separate into two layers or “phases” with the more dense liquid on the bottom. As a general rule of thumb, if the organic solvent is halogenated (dichloromethane) it will be more dense than water and thus on ...
... When water and an organic liquid are shaken together and than allowed to stand, the liquids separate into two layers or “phases” with the more dense liquid on the bottom. As a general rule of thumb, if the organic solvent is halogenated (dichloromethane) it will be more dense than water and thus on ...
chapter 8 lecture
... • There are close parallels between E2 and SN2 mechanisms in how the identity of the base, the leaving group and the solvent affect the rate. • The base appears in the rate equation, so the rate of the E2 reaction increases as the strength of the base increases. • E2 reactions are generally run wit ...
... • There are close parallels between E2 and SN2 mechanisms in how the identity of the base, the leaving group and the solvent affect the rate. • The base appears in the rate equation, so the rate of the E2 reaction increases as the strength of the base increases. • E2 reactions are generally run wit ...
Chemistry B11 Chapters 16-18 Amines, aldehydes, ketones and
... Physical properties of aldehydes and ketones: 1. Most aldehydes and ketones have strong odors (the odors of ketones are generally pleasant, and many are used in perfumes). 2. They are polar molecules (because of carbonyl group (C=O), carbon obtains the partial positive charge and oxygen obtains the ...
... Physical properties of aldehydes and ketones: 1. Most aldehydes and ketones have strong odors (the odors of ketones are generally pleasant, and many are used in perfumes). 2. They are polar molecules (because of carbonyl group (C=O), carbon obtains the partial positive charge and oxygen obtains the ...
- Iranian Chemical Communication
... in the presence of tetra n-butylammonium iodide ( TBAI) ( 1 mmol) as phase- transfer catalyst, various bases and solvents at 50 ºC and under reflux condition. ...
... in the presence of tetra n-butylammonium iodide ( TBAI) ( 1 mmol) as phase- transfer catalyst, various bases and solvents at 50 ºC and under reflux condition. ...
Alcohols - Science Skool!
... It is a reversible reaction and ends up at equilibrium with a mixture of reactants and products. Luckily enough you do not need to know the mechanism of this as it is very complex. Smaller esters tend to smell like most organic solvents (that gluey smell) though larger esters have the smell of “pear ...
... It is a reversible reaction and ends up at equilibrium with a mixture of reactants and products. Luckily enough you do not need to know the mechanism of this as it is very complex. Smaller esters tend to smell like most organic solvents (that gluey smell) though larger esters have the smell of “pear ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
... 11) Ionic bonds are formed when A) atoms share electrons. B) two or more atoms lose electrons at the same time. C) electrons are completely transferred from one atom to another. D) hydrogen forms bonds with negatively charged atoms in the same or different molecule. E) a pair of electrons is shared ...
... 11) Ionic bonds are formed when A) atoms share electrons. B) two or more atoms lose electrons at the same time. C) electrons are completely transferred from one atom to another. D) hydrogen forms bonds with negatively charged atoms in the same or different molecule. E) a pair of electrons is shared ...
Chapter 12 Review “Stoichiometry”
... “Stoichiometry” 30 Questions on this test, due to calculations taking more time; be sure to bring your CALCULATOR ...
... “Stoichiometry” 30 Questions on this test, due to calculations taking more time; be sure to bring your CALCULATOR ...
Oxidation and Reduction Reactions
... hydrogen to a carbonyl (using NaBH4 or LiAlH4 as the source of nucleophilic hydrogen). This was a chemoselective reaction – in other words, the reducing agent only reduced one functional group (the carbonyl) and left others alone (e.g. alkenes). If we want to reduce an alkene or alkyne, we need to u ...
... hydrogen to a carbonyl (using NaBH4 or LiAlH4 as the source of nucleophilic hydrogen). This was a chemoselective reaction – in other words, the reducing agent only reduced one functional group (the carbonyl) and left others alone (e.g. alkenes). If we want to reduce an alkene or alkyne, we need to u ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... (s) after the formula –solid Cu(s) (g) after the formula –gas H2 (g) (l) after the formula -liquid H2O(l) (aq) after the formula - dissolved in water, an aqueous solution. CaCl2 (aq) used after a product indicates a gas (same as (g)) O2 used after a product indicates a solid (same as (s)) ...
... (s) after the formula –solid Cu(s) (g) after the formula –gas H2 (g) (l) after the formula -liquid H2O(l) (aq) after the formula - dissolved in water, an aqueous solution. CaCl2 (aq) used after a product indicates a gas (same as (g)) O2 used after a product indicates a solid (same as (s)) ...
Chemistry EOC Review 2015 Name Per ___ This review is part of
... Describe trends in properties (e.g., ionization energy or reactivity as a function of location on the periodic table, boiling point of organic liquids as a function of molecular weight). Atomic radius is one-half of the distance between the center of identical atoms that are not bonded together. Ion ...
... Describe trends in properties (e.g., ionization energy or reactivity as a function of location on the periodic table, boiling point of organic liquids as a function of molecular weight). Atomic radius is one-half of the distance between the center of identical atoms that are not bonded together. Ion ...
Chemistry-Bridging
... 26. Balance the symbol equations for the following reactions: a. K + H2SO4 K2SO4 + H2 b. C3H8 + O2 CO2 + H2O c. Na2O + HCl NaCl + H2O d. KOH + H2SO4 K2SO4 + H2O 27. Write balanced equations for the following reactions: a. The complete combustion of the fuel ethanol (C2H5OH) in oxygen. b. The ...
... 26. Balance the symbol equations for the following reactions: a. K + H2SO4 K2SO4 + H2 b. C3H8 + O2 CO2 + H2O c. Na2O + HCl NaCl + H2O d. KOH + H2SO4 K2SO4 + H2O 27. Write balanced equations for the following reactions: a. The complete combustion of the fuel ethanol (C2H5OH) in oxygen. b. The ...
solutions - UMass Chemistry
... Place an X in the boxes corresponding to the correct answers. Any number of answers may be correct, including none of them. 9. (10 pts) 2 grams of octane are burned in a calorimeter. The calorimeter has a heat capacity of 900 J/K. There are 1200 grams of water in the calorimeter surrounding the bomb ...
... Place an X in the boxes corresponding to the correct answers. Any number of answers may be correct, including none of them. 9. (10 pts) 2 grams of octane are burned in a calorimeter. The calorimeter has a heat capacity of 900 J/K. There are 1200 grams of water in the calorimeter surrounding the bomb ...
File
... volume of the oxygen will be A) 20.0 liters B) 40.0 liters C) 60.0 liters D) 160. liters 30. Sodium nitrate is very soluble in water. The bonding force most responsible for this large solubility is best described as A) an interionic attraction C) a dipole-dipole attraction B) an ion-dipole attractio ...
... volume of the oxygen will be A) 20.0 liters B) 40.0 liters C) 60.0 liters D) 160. liters 30. Sodium nitrate is very soluble in water. The bonding force most responsible for this large solubility is best described as A) an interionic attraction C) a dipole-dipole attraction B) an ion-dipole attractio ...
File - Mrs. LeCompte
... same way, regardless of the C-skeleton it is bonded to Are often the chemically reactive part of the molecule Determine the unique chemical properties of the organic molecules in which they occur Please note that chemists use the letter R to represent the C-skeleton these groups are attached to, ...
... same way, regardless of the C-skeleton it is bonded to Are often the chemically reactive part of the molecule Determine the unique chemical properties of the organic molecules in which they occur Please note that chemists use the letter R to represent the C-skeleton these groups are attached to, ...
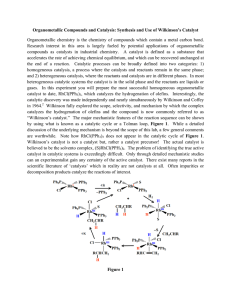
Lecture Review of Organic Chemistry and Herbicide Chemistry
... calcium and magnesium bind to the 2,4-D anion causing formation of precipitates that clog filters and nozzles amine salts are less susceptible than the alkali salts to forming precipitates; the esters have excellent stability in water example of Roundup (glyphosate): in hard water, the isopropyl ami ...
... calcium and magnesium bind to the 2,4-D anion causing formation of precipitates that clog filters and nozzles amine salts are less susceptible than the alkali salts to forming precipitates; the esters have excellent stability in water example of Roundup (glyphosate): in hard water, the isopropyl ami ...
Properties of , -Unsaturated Aldehydes and Ketones
... The conjugated carbonyl group of ,-unsaturated aldehydes and ketones can undergo reactions involving the entire functional system by: Acid-catalyzed mechanisms Radical mechanisms ...
... The conjugated carbonyl group of ,-unsaturated aldehydes and ketones can undergo reactions involving the entire functional system by: Acid-catalyzed mechanisms Radical mechanisms ...
SCH 4U
... b. Explain how you could use physical properties to tell the substances apart – be sure to be specific as to what would be observed. (3 marks) ...
... b. Explain how you could use physical properties to tell the substances apart – be sure to be specific as to what would be observed. (3 marks) ...
No Slide Title
... Often by a free radical process involving high pressure, high temperature and a catalyst. The catalyst is usually a substance (e.g. an organic peroxide) which readily breaks up to form radicals which initiate a chain reaction. Another catalyst is a Ziegler-Natta catalyst (named after the scientists ...
... Often by a free radical process involving high pressure, high temperature and a catalyst. The catalyst is usually a substance (e.g. an organic peroxide) which readily breaks up to form radicals which initiate a chain reaction. Another catalyst is a Ziegler-Natta catalyst (named after the scientists ...
POLYPP - Knockhardy
... Often by a free radical process involving high pressure, high temperature and a catalyst. The catalyst is usually a substance (e.g. an organic peroxide) which readily breaks up to form radicals which initiate a chain reaction. Another catalyst is a Ziegler-Natta catalyst (named after the scientists ...
... Often by a free radical process involving high pressure, high temperature and a catalyst. The catalyst is usually a substance (e.g. an organic peroxide) which readily breaks up to form radicals which initiate a chain reaction. Another catalyst is a Ziegler-Natta catalyst (named after the scientists ...
Organic Compound - TangHua2012-2013
... bond to a carbon atom. The general formula for a simple alcohol containing no rings is CnH(2n+1)OH. *Classification: Three major subsets of alcohols- 'primary' (1°), 'secondary' (2°) and 'tertiary' (3°), based upon the number of carbons the C-OH carbon is bonded to. A primary (1°) alcohol is one in ...
... bond to a carbon atom. The general formula for a simple alcohol containing no rings is CnH(2n+1)OH. *Classification: Three major subsets of alcohols- 'primary' (1°), 'secondary' (2°) and 'tertiary' (3°), based upon the number of carbons the C-OH carbon is bonded to. A primary (1°) alcohol is one in ...
91165 Organic Chemistry Cornell Notes.
... double bond opens up and atoms join to the carbon atoms. The one product molecule is now unsaturated. Shaking a small amount of bromine water with an alkane and an alkene lets you easily distinguish between them as the bromine water decolourises instantly with the alkene (and only very slowly with t ...
... double bond opens up and atoms join to the carbon atoms. The one product molecule is now unsaturated. Shaking a small amount of bromine water with an alkane and an alkene lets you easily distinguish between them as the bromine water decolourises instantly with the alkene (and only very slowly with t ...
Strychnine total synthesis

Strychnine total synthesis in chemistry describes the total synthesis of the complex biomolecule strychnine. The first reported method by the group of Robert Burns Woodward in 1954 is considered a classic in this research field. At the time it formed the natural conclusion to an elaborate process of molecular structure elucidation that started with the isolation of strychnine from the beans of Strychnos ignatii by Pierre Joseph Pelletier and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou in 1818. Major contributors to the entire effort were Sir Robert Robinson with over 250 publications and Hermann Leuchs with another 125 papers in a time span of 40 years. Robinson was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1947 for his work on alkaloids, strychnine included. The process of chemical identification was completed with publications in 1946 by Robinson and later confirmed by Woodward in 1947. X-ray structures establishing the absolute configuration became available between 1947 and 1951 with publications from J. M. Bijvoet and J.H. Robertson .Woodward published a very brief account on the strychnine synthesis in 1954 (just 3 pages) and a lengthy one (42 pages) in 1963.Many more methods exist and reported by the research groups of Magnus, Overman, Kuehne, Rawal, Bosch, Vollhardt, Mori, Shibasaki, Li, Fukuyama Vanderwal and MacMillan. Synthetic (+)-strychnine is also known. Racemic synthesises were published by Padwa in 2007 and in 2010 by Andrade and by Reissig.In his 1963 publication Woodward quoted Sir Robert Robinson who said for its molecular size it is the most complex substance known.