1 Lecture 24: Carbohydrates I
... Cyclization of monosaccharides in solution. In general, alcohols can attack the C=O group in sugars to form hemiacetals. (or hemiketals). Since sugars have OH groups, they can form hemiacetals by an intramolecular reaction, forming closed rings. Only long (>C4) saccharides can form internal hemiacet ...
... Cyclization of monosaccharides in solution. In general, alcohols can attack the C=O group in sugars to form hemiacetals. (or hemiketals). Since sugars have OH groups, they can form hemiacetals by an intramolecular reaction, forming closed rings. Only long (>C4) saccharides can form internal hemiacet ...
February 13, 2008
... The system is at equilibrium; no change will occur. The concentrations of H2 and I2 will increase as the system approaches equilibrium. The concentration of HI will rise as the system approaches equilibrium. The concentrations of H2 and HI will fall as the system approaches equilibrium. The concentr ...
... The system is at equilibrium; no change will occur. The concentrations of H2 and I2 will increase as the system approaches equilibrium. The concentration of HI will rise as the system approaches equilibrium. The concentrations of H2 and HI will fall as the system approaches equilibrium. The concentr ...
Chapter 10 for 302
... this strong of a base o Grignards attacking carbonyls The negatively charged carbon of the Grignard is attracted to the partially positive carbon of the carbonyl In the following schemes, A and B are just the alkyl pieces attached to the carbonyl-containing molecules and C is the Grignard or oth ...
... this strong of a base o Grignards attacking carbonyls The negatively charged carbon of the Grignard is attracted to the partially positive carbon of the carbonyl In the following schemes, A and B are just the alkyl pieces attached to the carbonyl-containing molecules and C is the Grignard or oth ...
19.2 preparation of acyl chlorides
... the structure of the amide and the reaction conditions. One possible mechanism is shown in Figure 19.5. Under acidic conditions the equilibrium for the hydrolysis of an amide is driven toward the products by the protonation of the ammonia or amine that is formed. Under basic conditions the equilibri ...
... the structure of the amide and the reaction conditions. One possible mechanism is shown in Figure 19.5. Under acidic conditions the equilibrium for the hydrolysis of an amide is driven toward the products by the protonation of the ammonia or amine that is formed. Under basic conditions the equilibri ...
Phenols Like alcohols, phenols are starting materials for a wide
... Notice that the -ve charge can be delocalized into the benzene ring and can be written on the o and p positions relative to the original hydroxyl group. The carbanion is stabilized further by electron-withdrawing groups in these positions. ...
... Notice that the -ve charge can be delocalized into the benzene ring and can be written on the o and p positions relative to the original hydroxyl group. The carbanion is stabilized further by electron-withdrawing groups in these positions. ...
Sodium acetate ACS Reagent Product Number 24,124
... the presence of varying salts, including sodium acetate, at different ionic strengths has been ...
... the presence of varying salts, including sodium acetate, at different ionic strengths has been ...
biological sulfate reduction in alkaline waters for the reprocessing of
... Sodium carbonate, commonly known as soda ash, is used in the production of glass, detergents, and other products. In the production of soda ash from trona ore, crystallizer purge streams are disposed of in large tailings ponds. The sodium carbonate levels in these ponds are quite high (8 to 14 weigh ...
... Sodium carbonate, commonly known as soda ash, is used in the production of glass, detergents, and other products. In the production of soda ash from trona ore, crystallizer purge streams are disposed of in large tailings ponds. The sodium carbonate levels in these ponds are quite high (8 to 14 weigh ...
Chapter 11 Chemical Reactions
... Never change a subscript to balance an equation (You can only change coefficients) – If you change the subscript (formula) you are describing a different chemical. – H2O is a different compound than H2O2 Never put a coefficient in the middle of a formula; they must go only in the front ...
... Never change a subscript to balance an equation (You can only change coefficients) – If you change the subscript (formula) you are describing a different chemical. – H2O is a different compound than H2O2 Never put a coefficient in the middle of a formula; they must go only in the front ...
A2 Chemistry key word list
... The amount of any substance containing as many elementary particles as there are carbon atoms in exactly 12 g of the carbon-12 isotope. ...
... The amount of any substance containing as many elementary particles as there are carbon atoms in exactly 12 g of the carbon-12 isotope. ...
Chemical Reactions
... 2 substances combine to make one compound (also called “synthesis”) Ca + O2 CaO SO3 + H2O H2SO4 We can predict the products, especially if the reactants are two elements. Mg3N2 (symbols, charges, cross) Mg + N2 _______ ...
... 2 substances combine to make one compound (also called “synthesis”) Ca + O2 CaO SO3 + H2O H2SO4 We can predict the products, especially if the reactants are two elements. Mg3N2 (symbols, charges, cross) Mg + N2 _______ ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... Explorelearning.com Username – btesta Password - science Vocabulary: coefficient, combination, compound, decomposition, double replacement, element, molecule, product, reactant, single replacement, subscript ...
... Explorelearning.com Username – btesta Password - science Vocabulary: coefficient, combination, compound, decomposition, double replacement, element, molecule, product, reactant, single replacement, subscript ...
Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
... (a) Rectified spirit It contains 95% ethyl alcohol and 45% water. It is an azeotrope (constant boiling mixture) and boils at 74°(. (b) Absolute alcohol Alcohol containing no water, i.e; 100% C2H5OH is known as absolute alcohol. It is prepared as follows. (i) Quick lime process (ii) Azeotropic method ...
... (a) Rectified spirit It contains 95% ethyl alcohol and 45% water. It is an azeotrope (constant boiling mixture) and boils at 74°(. (b) Absolute alcohol Alcohol containing no water, i.e; 100% C2H5OH is known as absolute alcohol. It is prepared as follows. (i) Quick lime process (ii) Azeotropic method ...
CHEM1102 2014-J-8 June 2014 • Complete the following table
... Give the constitutional formula(s) of the organic product(s) formed when each of the following compounds is treated with 4 M sodium hydroxide. The first three reactions proceed at room temperature; the last two require heating. ...
... Give the constitutional formula(s) of the organic product(s) formed when each of the following compounds is treated with 4 M sodium hydroxide. The first three reactions proceed at room temperature; the last two require heating. ...
AROMATIC COMPOUNDS A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1
... c) Upon hydrogenation, cyclohexene releases 120 kJ mol-1 of energy. Benzene might be expected to release 3 x 120 or 360 kJ mol-1, but it releases only 208 kJ mol-1. This is (360 - 208) / 3) 69.3 kJ mol-1 of energy less per mole of H2 added. (It is not important that you know the precise numbers. You ...
... c) Upon hydrogenation, cyclohexene releases 120 kJ mol-1 of energy. Benzene might be expected to release 3 x 120 or 360 kJ mol-1, but it releases only 208 kJ mol-1. This is (360 - 208) / 3) 69.3 kJ mol-1 of energy less per mole of H2 added. (It is not important that you know the precise numbers. You ...
MCQ plus answers
... The following multiple choice questions are provided to illustrate the type of questions used in this section of the paper and to provide you with extra practice. It is not a sample quiz. The questions in the paper will be in the style of these questions but may well cover different topics. In the e ...
... The following multiple choice questions are provided to illustrate the type of questions used in this section of the paper and to provide you with extra practice. It is not a sample quiz. The questions in the paper will be in the style of these questions but may well cover different topics. In the e ...
Unit 2
... • During fermentation glucose is broken down to form ethanol; carbon dioxide is also produced. • Fermentation is brought about by enzymes present in yeast. • There is a limit to the amount of ethanol which can be produced by fermentation. ...
... • During fermentation glucose is broken down to form ethanol; carbon dioxide is also produced. • Fermentation is brought about by enzymes present in yeast. • There is a limit to the amount of ethanol which can be produced by fermentation. ...
Lab 2 - Academic Computer Center
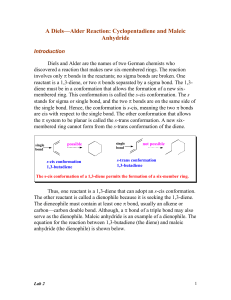
... reactant. One of the reactants (the diene) must have a conjugated diene system, and the other reactant (the dienophile) must contain a double bond or triple bond. The diene might have EDGs and the dienophile might have EWGs. You should be able to show the product of any diene with any dienophile fro ...
... reactant. One of the reactants (the diene) must have a conjugated diene system, and the other reactant (the dienophile) must contain a double bond or triple bond. The diene might have EDGs and the dienophile might have EWGs. You should be able to show the product of any diene with any dienophile fro ...
OCR_Organic_Chemistry_AS_summary
... Formulae of organic molecules • Structural formulae – the minimal detail that shows the arrangement of atoms, e.g. CH3CH3 for ethane • Displayed formulae – shows the relative position of all atoms and bonds between them, e.g. ethene • Skeleton formulae – the simplest representation of organic molec ...
... Formulae of organic molecules • Structural formulae – the minimal detail that shows the arrangement of atoms, e.g. CH3CH3 for ethane • Displayed formulae – shows the relative position of all atoms and bonds between them, e.g. ethene • Skeleton formulae – the simplest representation of organic molec ...
Chapters 20 & 21
... Arrangements have different names, cis and trans cis – same side of the molecule trans – different side of the molecule ...
... Arrangements have different names, cis and trans cis – same side of the molecule trans – different side of the molecule ...
Strychnine total synthesis

Strychnine total synthesis in chemistry describes the total synthesis of the complex biomolecule strychnine. The first reported method by the group of Robert Burns Woodward in 1954 is considered a classic in this research field. At the time it formed the natural conclusion to an elaborate process of molecular structure elucidation that started with the isolation of strychnine from the beans of Strychnos ignatii by Pierre Joseph Pelletier and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou in 1818. Major contributors to the entire effort were Sir Robert Robinson with over 250 publications and Hermann Leuchs with another 125 papers in a time span of 40 years. Robinson was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1947 for his work on alkaloids, strychnine included. The process of chemical identification was completed with publications in 1946 by Robinson and later confirmed by Woodward in 1947. X-ray structures establishing the absolute configuration became available between 1947 and 1951 with publications from J. M. Bijvoet and J.H. Robertson .Woodward published a very brief account on the strychnine synthesis in 1954 (just 3 pages) and a lengthy one (42 pages) in 1963.Many more methods exist and reported by the research groups of Magnus, Overman, Kuehne, Rawal, Bosch, Vollhardt, Mori, Shibasaki, Li, Fukuyama Vanderwal and MacMillan. Synthetic (+)-strychnine is also known. Racemic synthesises were published by Padwa in 2007 and in 2010 by Andrade and by Reissig.In his 1963 publication Woodward quoted Sir Robert Robinson who said for its molecular size it is the most complex substance known.