Conformations
... between two species on adjacent carbons (often refers to eclipsing strain). Gauche Interactions: Torsional strain when two non-H are at a 60° torsional angle. Cyclohexane: "Puckering" (an atom bending out of the plane of three other atoms) relieves all of the angle and torsional strain. The chair co ...
... between two species on adjacent carbons (often refers to eclipsing strain). Gauche Interactions: Torsional strain when two non-H are at a 60° torsional angle. Cyclohexane: "Puckering" (an atom bending out of the plane of three other atoms) relieves all of the angle and torsional strain. The chair co ...
Chapter 21: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nucleophilic Acyl
... cannot be controlled to add only one RLi or RMgX; the intermediate ketone is too reactive ...
... cannot be controlled to add only one RLi or RMgX; the intermediate ketone is too reactive ...
Chemistry1100 Practice Exam 4 Choose the best answer for
... 11. A compound has an empirical formula CH2- An independent analysis gave a value of 70 for its molar mass. What is the correct molecular formula? a. C2H4 b. C3H6 c. C4O8 d. C5H10 e. C5H11 12. Given the balanced chemical equation, C4H4 + 5 O2 → 4 CO2 + 2 H2O. If 0.3618 moles of C4H4 are allowed to ...
... 11. A compound has an empirical formula CH2- An independent analysis gave a value of 70 for its molar mass. What is the correct molecular formula? a. C2H4 b. C3H6 c. C4O8 d. C5H10 e. C5H11 12. Given the balanced chemical equation, C4H4 + 5 O2 → 4 CO2 + 2 H2O. If 0.3618 moles of C4H4 are allowed to ...
cork institute of technology
... Calculate the dissociation constant (Ka) value of a 0.253 M aqueous solution of propionic acid, CH3CH2CO2H, with a pH of 4.88. CH3CH2CO2H + H2O ⇋ H3O+ + CH3CH2CO−2 (4 marks) Calculate the following: i) The pH of a 0.042 Ba(OH)2 solution. ii) The hydrogen ion concentration of an aqueous solution whos ...
... Calculate the dissociation constant (Ka) value of a 0.253 M aqueous solution of propionic acid, CH3CH2CO2H, with a pH of 4.88. CH3CH2CO2H + H2O ⇋ H3O+ + CH3CH2CO−2 (4 marks) Calculate the following: i) The pH of a 0.042 Ba(OH)2 solution. ii) The hydrogen ion concentration of an aqueous solution whos ...
Chapter 1 Chemical Bonding and Chemical Structure
... • Recall priorities: carboxylic acid > anhydride > ester > acid halide > amide > nitrile > aldehyde > ketone > alcohol (phenol) > thiol > amine 16.1 Nomenclature of Benzene Derivatives ...
... • Recall priorities: carboxylic acid > anhydride > ester > acid halide > amide > nitrile > aldehyde > ketone > alcohol (phenol) > thiol > amine 16.1 Nomenclature of Benzene Derivatives ...
American-Journal-of-Oil-and-Chemical-Technologies
... 3. Conclusion In conclusion, continuing with our previous works on synthesizing supramolecular compounds containing pyridinedicarboxylic acid N-oxides [9-11], two new coordination complexes have been synthesized and characterized. The red shift of bands ʋas(COO−), ʋs(COO−), and ʋas(COO−) and ʋ(NO) ...
... 3. Conclusion In conclusion, continuing with our previous works on synthesizing supramolecular compounds containing pyridinedicarboxylic acid N-oxides [9-11], two new coordination complexes have been synthesized and characterized. The red shift of bands ʋas(COO−), ʋs(COO−), and ʋas(COO−) and ʋ(NO) ...
Bulent Terem - CH324 - Syllabus | Chaminade
... and homework assignments. Approximately half of the questions in the midterm exams will be identical to those assigned previously. Course Grade (all grades in percentages): = + .22 (average of the three midterms) + .22 (average of the two highest midterms) + .15 (average of the quizzes/presentations ...
... and homework assignments. Approximately half of the questions in the midterm exams will be identical to those assigned previously. Course Grade (all grades in percentages): = + .22 (average of the three midterms) + .22 (average of the two highest midterms) + .15 (average of the quizzes/presentations ...
AP Chemistry
... 4. reduction half reactions of common oxidizing agents a. MnO4- + 8 H+ + 5 e- Mn2+ + 4 H2O b. Cr2O72- + 14 H+ + 6 e- 2 Cr3+ + 7 H2O 5. oxidation of reactive metals a. metal ion takes electron from metal listed lower on the Standard Potential Chart (see section B) metal + salt salt of metal + n ...
... 4. reduction half reactions of common oxidizing agents a. MnO4- + 8 H+ + 5 e- Mn2+ + 4 H2O b. Cr2O72- + 14 H+ + 6 e- 2 Cr3+ + 7 H2O 5. oxidation of reactive metals a. metal ion takes electron from metal listed lower on the Standard Potential Chart (see section B) metal + salt salt of metal + n ...
revised hydrocarbons alkenes cycloalkenes
... 6. Pyrolysis of esters Thermal cleavage of an ester usually acetate, involves the formation of cyclic transition state leading to the elimination of an acid leaving behind alkene as a product. ...
... 6. Pyrolysis of esters Thermal cleavage of an ester usually acetate, involves the formation of cyclic transition state leading to the elimination of an acid leaving behind alkene as a product. ...
Chromatographic and Spectroscopic Methods of Identification for the
... and analytical toxicology must depend heavily upon chromatographic methods as well as mass spectrometry (MS). When other compounds exist that have the potential to produce the same or nearly identical mass spectrum as the drug of interest, the identification by gas chromatography (GC)–MS must be bas ...
... and analytical toxicology must depend heavily upon chromatographic methods as well as mass spectrometry (MS). When other compounds exist that have the potential to produce the same or nearly identical mass spectrum as the drug of interest, the identification by gas chromatography (GC)–MS must be bas ...
Presentation
... 5) Reduction of aldehyde, RCHO with sodium and ethanol gives (A) 1° alcohol (B) 2° alcohol (C) 3° alcohol (D) alkane ...
... 5) Reduction of aldehyde, RCHO with sodium and ethanol gives (A) 1° alcohol (B) 2° alcohol (C) 3° alcohol (D) alkane ...
1442 Final Review
... 36. If the concentration of hydroxide ion in a certain solution is 5.8 x 10-3 M, what is the pH of the solution? a) 3.58 b) 10.42 *c) 11.76 d) 11.42 e) 2.24 37. What is the pH of 0.035 M HClO4? a) 2.65 b) 3.52 c) 2.35 *d) 1.46 e) 1.65 38. What is the pH of 0.025 M barium hydroxide? a) 1.30 b) 1.60 c ...
... 36. If the concentration of hydroxide ion in a certain solution is 5.8 x 10-3 M, what is the pH of the solution? a) 3.58 b) 10.42 *c) 11.76 d) 11.42 e) 2.24 37. What is the pH of 0.035 M HClO4? a) 2.65 b) 3.52 c) 2.35 *d) 1.46 e) 1.65 38. What is the pH of 0.025 M barium hydroxide? a) 1.30 b) 1.60 c ...
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY ERT 108 Semester II 2010
... (the same elements produced by the decomposition of the reactants will form the products) ...
... (the same elements produced by the decomposition of the reactants will form the products) ...
GCSE ADDITIONAL CHEMISTRY (C2) REVISION BOOKLET
... The rate of a chemical reaction can be found by measuring how ........................ the reactants are ............................ or how quickly the products are ....................... . An example of a chemical reaction is the reaction between calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid: CaCO3(s) ...
... The rate of a chemical reaction can be found by measuring how ........................ the reactants are ............................ or how quickly the products are ....................... . An example of a chemical reaction is the reaction between calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid: CaCO3(s) ...
Chapter 21: Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives
... LG = Cl (acid chloride), R'C(=O)O (acid anhydride), or R'O (ester) ...
... LG = Cl (acid chloride), R'C(=O)O (acid anhydride), or R'O (ester) ...
AL COS #
... What type of solution contains more hydrogen ions than it does Acidic hydroxide ions? Know the pH Scale. What is the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration pH known as? What are the substances produced when KOH (aq) neutralizes HCl (aq) ? H2O (l) and KCl (aq) NaOH Given: H2O, NaOH, HC2 ...
... What type of solution contains more hydrogen ions than it does Acidic hydroxide ions? Know the pH Scale. What is the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration pH known as? What are the substances produced when KOH (aq) neutralizes HCl (aq) ? H2O (l) and KCl (aq) NaOH Given: H2O, NaOH, HC2 ...
A New Method for Halodecarboxylation of Acids Using Lead(IV
... were dealing with a hydrate; this fact is supported by the published8 infrared spectrum of their tropone starting material. This tropone was clearly wet, as it contains a strong band at 3400 cm.-’ which is found in wet tropone, but not in material which has been rigorously dried. l 3 The above spect ...
... were dealing with a hydrate; this fact is supported by the published8 infrared spectrum of their tropone starting material. This tropone was clearly wet, as it contains a strong band at 3400 cm.-’ which is found in wet tropone, but not in material which has been rigorously dried. l 3 The above spect ...
M_ScOrganic_Chemistr..
... Organic synthesis: Reterosynthsis, synthons and synthetic equivalents, functional group interconversion, Synthesis of amines, regiospecific, chemospecific and stereospecific reactions, umpolung methods. principles and applications of protective groups in protection of hydroxyl, amino, carbonyl and c ...
... Organic synthesis: Reterosynthsis, synthons and synthetic equivalents, functional group interconversion, Synthesis of amines, regiospecific, chemospecific and stereospecific reactions, umpolung methods. principles and applications of protective groups in protection of hydroxyl, amino, carbonyl and c ...
haloalkanes 2013
... (i) C2H5Br + NH3 (aq / alc) ——> C2H5NH2 + HBr (ii) HBr + NH3 (aq / alc) ——> NH4Br ...
... (i) C2H5Br + NH3 (aq / alc) ——> C2H5NH2 + HBr (ii) HBr + NH3 (aq / alc) ——> NH4Br ...
Chemistry 1: Second Semester Practice Exam Read each question
... ___ C2H5OH + __ O2 Æ __ H2O + __ CO2 A. 3 B. 5 C. 7 D. 9 52. A double replacement reaction is likely to occur when A. a metal, such as zinc is placed in a concentrated acid B. a hydrocarbon is burned in the presence of oxygen C. a compound breaks down into its elemental components D. two ionic compo ...
... ___ C2H5OH + __ O2 Æ __ H2O + __ CO2 A. 3 B. 5 C. 7 D. 9 52. A double replacement reaction is likely to occur when A. a metal, such as zinc is placed in a concentrated acid B. a hydrocarbon is burned in the presence of oxygen C. a compound breaks down into its elemental components D. two ionic compo ...
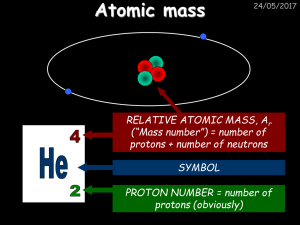
Atomic mass - drseemaljelani
... When a reversible reaction occurs in a closed system (Where nothing can escape), equilibrium is reached when both reactions occur at exactly the same rate in each direction. The relative amounts of all the reacting substances at equilibrium depend on the conditions of the reaction. ...
... When a reversible reaction occurs in a closed system (Where nothing can escape), equilibrium is reached when both reactions occur at exactly the same rate in each direction. The relative amounts of all the reacting substances at equilibrium depend on the conditions of the reaction. ...
CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDS
... 2. Alcohol drinking ruins the health of a person concerned. It damages the liver and makes the brain dull. 3. The drinking of adulterated alcohol containing methyl alcohol causes severe poisoning leading to blindness and even death. 4. The alcohol drinking by the head of the family has a very bad ef ...
... 2. Alcohol drinking ruins the health of a person concerned. It damages the liver and makes the brain dull. 3. The drinking of adulterated alcohol containing methyl alcohol causes severe poisoning leading to blindness and even death. 4. The alcohol drinking by the head of the family has a very bad ef ...
Class XI Chemistry Practics Paper
... (b) What is salt bridge. Write its application also Q25.(a) Give two properties of Water which are due to Hydrogen bonding. (b) Explain the Structure of H2O2. Q26.An org. compound contain 69% carbon and 4.8% Hydrogen, the remainder being oxygen, Calculate the masses of carbon dioxide and water produ ...
... (b) What is salt bridge. Write its application also Q25.(a) Give two properties of Water which are due to Hydrogen bonding. (b) Explain the Structure of H2O2. Q26.An org. compound contain 69% carbon and 4.8% Hydrogen, the remainder being oxygen, Calculate the masses of carbon dioxide and water produ ...
Organic Compounds
... • Fats and Oils are naturally occurring esters of long chain Carboxyillic acid ...
... • Fats and Oils are naturally occurring esters of long chain Carboxyillic acid ...
Strychnine total synthesis

Strychnine total synthesis in chemistry describes the total synthesis of the complex biomolecule strychnine. The first reported method by the group of Robert Burns Woodward in 1954 is considered a classic in this research field. At the time it formed the natural conclusion to an elaborate process of molecular structure elucidation that started with the isolation of strychnine from the beans of Strychnos ignatii by Pierre Joseph Pelletier and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou in 1818. Major contributors to the entire effort were Sir Robert Robinson with over 250 publications and Hermann Leuchs with another 125 papers in a time span of 40 years. Robinson was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1947 for his work on alkaloids, strychnine included. The process of chemical identification was completed with publications in 1946 by Robinson and later confirmed by Woodward in 1947. X-ray structures establishing the absolute configuration became available between 1947 and 1951 with publications from J. M. Bijvoet and J.H. Robertson .Woodward published a very brief account on the strychnine synthesis in 1954 (just 3 pages) and a lengthy one (42 pages) in 1963.Many more methods exist and reported by the research groups of Magnus, Overman, Kuehne, Rawal, Bosch, Vollhardt, Mori, Shibasaki, Li, Fukuyama Vanderwal and MacMillan. Synthetic (+)-strychnine is also known. Racemic synthesises were published by Padwa in 2007 and in 2010 by Andrade and by Reissig.In his 1963 publication Woodward quoted Sir Robert Robinson who said for its molecular size it is the most complex substance known.