E. Explain
... A. You are given a mixture of precipitated copper hydroxide and zinc hydroxide. Name a solvent in each case which will dissolve [1] Copper hydoxide only [2] Coper hyhdroxide and Zinc hydroxide both. B. Name the property of the sulphuric acid which is made use in each of the following reactions. Give ...
... A. You are given a mixture of precipitated copper hydroxide and zinc hydroxide. Name a solvent in each case which will dissolve [1] Copper hydoxide only [2] Coper hyhdroxide and Zinc hydroxide both. B. Name the property of the sulphuric acid which is made use in each of the following reactions. Give ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment THIS
... help each other but do not copy someone else’s work. If you do not know how to do a problem, ask a friend to explain it to you. You will be doing him/her a favor because the ability to explain a concept to someone else is a test of that person’s true understanding. I look forward to working with you ...
... help each other but do not copy someone else’s work. If you do not know how to do a problem, ask a friend to explain it to you. You will be doing him/her a favor because the ability to explain a concept to someone else is a test of that person’s true understanding. I look forward to working with you ...
Unit 6 – Chemical Reactions: Particles and Energy
... rearrangement process of a chemical reaction requires that all atoms from the reactant molecules MUST become part of one of the products. The conservation of mass we observed at the beginning of the course is evident during chemical reactions; coefficients describe how many whole particles of each ...
... rearrangement process of a chemical reaction requires that all atoms from the reactant molecules MUST become part of one of the products. The conservation of mass we observed at the beginning of the course is evident during chemical reactions; coefficients describe how many whole particles of each ...
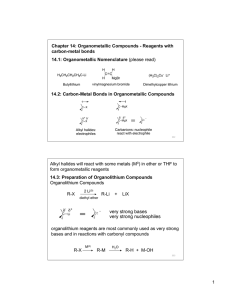
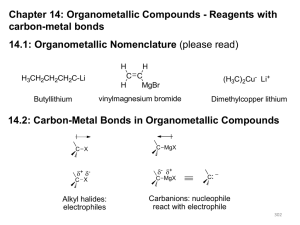
Organometallic Compounds - Reagents
... Disconnection: the reverse operation to a synthetic reaction; the hypothetical cleavage of a bond back to precursors of the target molecule. Functional Group Interconversion (FGI): the process of converting one functional group into another by substitution, addition, elimination, reduction, or oxida ...
... Disconnection: the reverse operation to a synthetic reaction; the hypothetical cleavage of a bond back to precursors of the target molecule. Functional Group Interconversion (FGI): the process of converting one functional group into another by substitution, addition, elimination, reduction, or oxida ...
(1) and New York University (2)
... stereochemical approach which systematically employs chiral podand, piperidine bearing ligands sulfur atoms; • Improve Hg(II) sensing sensitivity by using circularly polarized fluorescence excitation (CPE); • Systematically develope Fe(II) complexes of TPA-based chiral podands, piperidines and quinu ...
... stereochemical approach which systematically employs chiral podand, piperidine bearing ligands sulfur atoms; • Improve Hg(II) sensing sensitivity by using circularly polarized fluorescence excitation (CPE); • Systematically develope Fe(II) complexes of TPA-based chiral podands, piperidines and quinu ...
Week # 3 Homework doc
... For example, methyl alcohol dissolves in water because the hydrogen bonds between water molecules and those between alcohol molecules are of roughly equal strength. The hydrogen bonds between similar molecules can be broken and replaced by hydrogen bonds between alcohol and water molecules. Alcohol ...
... For example, methyl alcohol dissolves in water because the hydrogen bonds between water molecules and those between alcohol molecules are of roughly equal strength. The hydrogen bonds between similar molecules can be broken and replaced by hydrogen bonds between alcohol and water molecules. Alcohol ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC)
... Extraction and isolation of embelin compound A quantity of 1.2 kg of the bark powder of Embelia Schimperi was soaked in two litres of ethyl acetate in the cold for 48 hours while mechanically stirring. The extract was then filtered under suction and concentrated to dryness using a rotary evaporator ...
... Extraction and isolation of embelin compound A quantity of 1.2 kg of the bark powder of Embelia Schimperi was soaked in two litres of ethyl acetate in the cold for 48 hours while mechanically stirring. The extract was then filtered under suction and concentrated to dryness using a rotary evaporator ...
Practice Exam-1A Fall 2016
... 12. Which of the following is not a correct match? (a) AlCl3, aluminum chloride (b) H2O dihydrogen monoxide (c) CrF3, chromium (III) fluoride (d) HNO3, nitrous acid (e) CuSO4.5H2O, copper (II) sulfate pentahydrate Hint: Follow the rules of naming the compounds. 13. Which of the following pairs is a ...
... 12. Which of the following is not a correct match? (a) AlCl3, aluminum chloride (b) H2O dihydrogen monoxide (c) CrF3, chromium (III) fluoride (d) HNO3, nitrous acid (e) CuSO4.5H2O, copper (II) sulfate pentahydrate Hint: Follow the rules of naming the compounds. 13. Which of the following pairs is a ...
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives 1. Background and Properties
... and halides consist of alkyl and/or aryl groups bonded to hydroxyl, alkoxyl, amino and halo substituents respectively. If these same functional groups are attached to an acyl group (RCO–) their properties are substantially changed, and they are designated ...
... and halides consist of alkyl and/or aryl groups bonded to hydroxyl, alkoxyl, amino and halo substituents respectively. If these same functional groups are attached to an acyl group (RCO–) their properties are substantially changed, and they are designated ...
Alcohols, Diols, and Thiols
... analogous to that of sodium borohydride except that the reduction and hydrolysis stages are independent operations. The reduction is carried out in diethyl ether, followed by a separate hydrolysis step when water is added to the reaction mixture. LiAlH4 diethyl Aldehyde or ketone ether ...
... analogous to that of sodium borohydride except that the reduction and hydrolysis stages are independent operations. The reduction is carried out in diethyl ether, followed by a separate hydrolysis step when water is added to the reaction mixture. LiAlH4 diethyl Aldehyde or ketone ether ...
Organic and Biological Molecules
... All alcohols contain the hydroxyl group, OH. This greatly changes the properties of the hydrocarbon to which it is attached. Hydrocarbons are non-polar, with low boiling points and poor solubility in polar solvents. The presence of an –OH group increases the polarity of the molecule, and provides a ...
... All alcohols contain the hydroxyl group, OH. This greatly changes the properties of the hydrocarbon to which it is attached. Hydrocarbons are non-polar, with low boiling points and poor solubility in polar solvents. The presence of an –OH group increases the polarity of the molecule, and provides a ...
Oxidation of Benzyl Ethers to Benzoate Esters Using a Novel
... enthalpically favored H-atom abstraction (Feray et. al., 2001) from the benzylic site produces the stable α-alkoxy radical, 5, which can be oxidized to benzaldehyde in one of two ways. A single electron transfer (SET) from 5 to the odd-electron species, 6, produces the benzylic carbocation 8 which c ...
... enthalpically favored H-atom abstraction (Feray et. al., 2001) from the benzylic site produces the stable α-alkoxy radical, 5, which can be oxidized to benzaldehyde in one of two ways. A single electron transfer (SET) from 5 to the odd-electron species, 6, produces the benzylic carbocation 8 which c ...
74 CHAPTER-IV "LEAD (IV) ACETATE OXIDATIONS"
... saturated hydrocarbons by lead (IV) acetate in presence of short chain alcohol is considered to proceed via alkoxy radicals as transient intermediates, which abstract a hydrogen atom from cyclohexane. 15 In the oxidation of mono and disubstituted acyclic olefins with lead (IV) acetate, three competi ...
... saturated hydrocarbons by lead (IV) acetate in presence of short chain alcohol is considered to proceed via alkoxy radicals as transient intermediates, which abstract a hydrogen atom from cyclohexane. 15 In the oxidation of mono and disubstituted acyclic olefins with lead (IV) acetate, three competi ...
1. When the reaction Cu + HNO3 → Cu2+ + NO + H2O is balanced
... D) 3 53. In the reaction MnO4– + H2O2 → Mn2+ + O2 , _____. A) 5 moles of H2O2 are oxidized by 2 moles of MnO4– B) 2 moles of H2O2 are oxidized by 5 moles of MnO4– C) 3 moles of H2O2 are oxidized by 1 mole of MnO4– D) 6 moles of H2O2 are oxidized by 4 moles of MnO4– 54. In a titration a 1.0 g sample ...
... D) 3 53. In the reaction MnO4– + H2O2 → Mn2+ + O2 , _____. A) 5 moles of H2O2 are oxidized by 2 moles of MnO4– B) 2 moles of H2O2 are oxidized by 5 moles of MnO4– C) 3 moles of H2O2 are oxidized by 1 mole of MnO4– D) 6 moles of H2O2 are oxidized by 4 moles of MnO4– 54. In a titration a 1.0 g sample ...
AP Chem Chapter 16 Review Packet
... harvesting the hydrogen for fuel. The free energy of this reaction is so positive that there is no hope of causing the reaction to occur without coupling it to another process. For example, it has been proposed that the reaction can be promoted by first reacting silver with water to produce hydrogen ...
... harvesting the hydrogen for fuel. The free energy of this reaction is so positive that there is no hope of causing the reaction to occur without coupling it to another process. For example, it has been proposed that the reaction can be promoted by first reacting silver with water to produce hydrogen ...
study material class X (science)
... (c) Zinc granules ,identify the type of reaction when marble chips and Zinc granules are added separately to acid taken in two test tubes . Ans. (a) marble chips react with dilute hydrochloric acid to form calcium chloride and carbon dioxide .it is a double displacement reaction CaCO3+2HCl CaCl2 + ...
... (c) Zinc granules ,identify the type of reaction when marble chips and Zinc granules are added separately to acid taken in two test tubes . Ans. (a) marble chips react with dilute hydrochloric acid to form calcium chloride and carbon dioxide .it is a double displacement reaction CaCO3+2HCl CaCl2 + ...
Chemistry II Exams and Keys 2014 Season
... values for the average bond strengths: Br-Br (193 kJ/mol) and Cl-Cl (233 kJ/mol). I. Blue light can break the bond between two chlorine atoms. II. Red light can break the bond between two chlorine atoms. III. Green light can break the bond between two bromine atoms. A. Only I and II B. Only II and I ...
... values for the average bond strengths: Br-Br (193 kJ/mol) and Cl-Cl (233 kJ/mol). I. Blue light can break the bond between two chlorine atoms. II. Red light can break the bond between two chlorine atoms. III. Green light can break the bond between two bromine atoms. A. Only I and II B. Only II and I ...
IMPORTANT CONCEPTS IN ALKYNE CHEMISTRY
... To be of use in synthesis, the electrophilic center of substrates containing sp3 carbon must be sterically accessible and contain a good leaving group. This is the type encountered in ch. 6 in Sn2 reactions. Examples are many primary and secondary halides. The outcome of the reaction between a nucle ...
... To be of use in synthesis, the electrophilic center of substrates containing sp3 carbon must be sterically accessible and contain a good leaving group. This is the type encountered in ch. 6 in Sn2 reactions. Examples are many primary and secondary halides. The outcome of the reaction between a nucle ...
Chapter 5: thermochemstry
... More on hess’ law • Hess' law allows ΔH rxn to be calculated even when it can’t be measured directly. • To do this, we perform arithmetic operations on chemical equations and known ΔH values. – Chemical equations may be multiplied or divided by a whole number. – When an equation is multiplied by a c ...
... More on hess’ law • Hess' law allows ΔH rxn to be calculated even when it can’t be measured directly. • To do this, we perform arithmetic operations on chemical equations and known ΔH values. – Chemical equations may be multiplied or divided by a whole number. – When an equation is multiplied by a c ...
AH 2015 incl MG
... made up to the mark with deionised water. 25·0 cm3 samples of this solution were titrated with 0·050 mol l−1 sulphuric acid. ...
... made up to the mark with deionised water. 25·0 cm3 samples of this solution were titrated with 0·050 mol l−1 sulphuric acid. ...
Wilson and Gisvold` s Textbook of Organic Medicinal and
... in which the hydroxyl group at C6 adds to the carbonyl gp at C9, forming a 6,9-hemiketal that undergoes irreversible dehydration (between 8&9) Participation of the hydroxyl group at C12 in a second intramolecular cyclization yields the 6,9, 9, 12 spiroketal, either through the intermediate anhydrohe ...
... in which the hydroxyl group at C6 adds to the carbonyl gp at C9, forming a 6,9-hemiketal that undergoes irreversible dehydration (between 8&9) Participation of the hydroxyl group at C12 in a second intramolecular cyclization yields the 6,9, 9, 12 spiroketal, either through the intermediate anhydrohe ...
Properties of amines
... (NH3), where one or more of the hydrogen atoms is replaced by a carbon chain. Thus R—NH2 is a primary amine, while R—NH—R’ is a secondary amine, and R—N(R’)—R’’ is a tertiary amine. You will only be asked to name primary amines. Note that 2-aminopropane, CH3—CH(NH2)—CH3, is a primary amine, yet the ...
... (NH3), where one or more of the hydrogen atoms is replaced by a carbon chain. Thus R—NH2 is a primary amine, while R—NH—R’ is a secondary amine, and R—N(R’)—R’’ is a tertiary amine. You will only be asked to name primary amines. Note that 2-aminopropane, CH3—CH(NH2)—CH3, is a primary amine, yet the ...
Unit 7 Packet
... When you heated sodium hydrogen carbonate, you decomposed it into sodium oxide, water vapor, and gaseous carbon dioxide. ...
... When you heated sodium hydrogen carbonate, you decomposed it into sodium oxide, water vapor, and gaseous carbon dioxide. ...
Chemistry 201 C Alkenes
... Breaking the πbond requires about 268 kJ/mol The rotational barrier in ethane is only 12 kJ/mole. ...
... Breaking the πbond requires about 268 kJ/mol The rotational barrier in ethane is only 12 kJ/mole. ...
Strychnine total synthesis

Strychnine total synthesis in chemistry describes the total synthesis of the complex biomolecule strychnine. The first reported method by the group of Robert Burns Woodward in 1954 is considered a classic in this research field. At the time it formed the natural conclusion to an elaborate process of molecular structure elucidation that started with the isolation of strychnine from the beans of Strychnos ignatii by Pierre Joseph Pelletier and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou in 1818. Major contributors to the entire effort were Sir Robert Robinson with over 250 publications and Hermann Leuchs with another 125 papers in a time span of 40 years. Robinson was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1947 for his work on alkaloids, strychnine included. The process of chemical identification was completed with publications in 1946 by Robinson and later confirmed by Woodward in 1947. X-ray structures establishing the absolute configuration became available between 1947 and 1951 with publications from J. M. Bijvoet and J.H. Robertson .Woodward published a very brief account on the strychnine synthesis in 1954 (just 3 pages) and a lengthy one (42 pages) in 1963.Many more methods exist and reported by the research groups of Magnus, Overman, Kuehne, Rawal, Bosch, Vollhardt, Mori, Shibasaki, Li, Fukuyama Vanderwal and MacMillan. Synthetic (+)-strychnine is also known. Racemic synthesises were published by Padwa in 2007 and in 2010 by Andrade and by Reissig.In his 1963 publication Woodward quoted Sir Robert Robinson who said for its molecular size it is the most complex substance known.