chemical equilibrium type 1
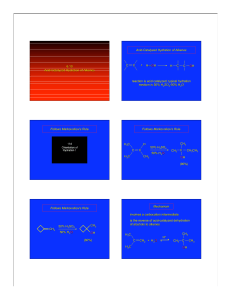
... N2(g) + 3H2(g) l 2 NH3 , KC has unit (mol/L)–2 and KP has unit bar–2 or N2O4 (g) l 2NO2, KC has unit mol / L and KP has unit bar However, these days we express equilibrium constants in dimensionless quantities by specifying the standard state of the reactants and the products. The standard state for ...
... N2(g) + 3H2(g) l 2 NH3 , KC has unit (mol/L)–2 and KP has unit bar–2 or N2O4 (g) l 2NO2, KC has unit mol / L and KP has unit bar However, these days we express equilibrium constants in dimensionless quantities by specifying the standard state of the reactants and the products. The standard state for ...
Acid-Catalyzed Hydration of Alkenes
... transition state for attack of water on bromonium ion has carbocation character; more stable transition state (left) has positive charge on more highly substituted carbon ...
... transition state for attack of water on bromonium ion has carbocation character; more stable transition state (left) has positive charge on more highly substituted carbon ...
Ch14b: Carboxylic Acids
... ‣ Carboxylic Acids have many interesting properties. ‣ Many of the sharp flavors we enjoy in food (vinegar, grapefruit, lemon…) are produced by simple substances of the carboxylic acid family of organic substances. ‣ These organic molecules are acids. Like the simple binary acids you’re already fami ...
... ‣ Carboxylic Acids have many interesting properties. ‣ Many of the sharp flavors we enjoy in food (vinegar, grapefruit, lemon…) are produced by simple substances of the carboxylic acid family of organic substances. ‣ These organic molecules are acids. Like the simple binary acids you’re already fami ...
Chapter 9 Stoichiometry
... The first step in the industrial manufacture of nitric acid is the catalytic oxidation of ammonia. 4 NH3 + 5 O2 4NO + 6H2O (unbalanced) The reaction is run using 824 g of NH3 and excess oxygen. a. How many moles of NO are formed? b. How many moles of H2O are formed? A. 824g NH3 X 1 mol X 4 mol NO ...
... The first step in the industrial manufacture of nitric acid is the catalytic oxidation of ammonia. 4 NH3 + 5 O2 4NO + 6H2O (unbalanced) The reaction is run using 824 g of NH3 and excess oxygen. a. How many moles of NO are formed? b. How many moles of H2O are formed? A. 824g NH3 X 1 mol X 4 mol NO ...
Celanese Emulsions GmbH
... known per se. Mineral wool mats incorporating crosslinked polymers as binders form part of the subject matter of a wide variety of patent documents. ...
... known per se. Mineral wool mats incorporating crosslinked polymers as binders form part of the subject matter of a wide variety of patent documents. ...
Chapter 12, Alkenes and Alkynes
... little import to biochemistry and will not be studied further in this course. Fig. 12.UN, p.314 ...
... little import to biochemistry and will not be studied further in this course. Fig. 12.UN, p.314 ...
Camp 1 - TypePad
... Ethers are polar compounds in which oxygen bears a partial negative charge and each carbon bonded to it bears a partial positive charge. • However, only weak forces of attraction exist between ether molecules in the pure liquid. • Consequently, boiling points of ethers are close to those of hydrocar ...
... Ethers are polar compounds in which oxygen bears a partial negative charge and each carbon bonded to it bears a partial positive charge. • However, only weak forces of attraction exist between ether molecules in the pure liquid. • Consequently, boiling points of ethers are close to those of hydrocar ...
OChem1 Course Pack
... 12. (5 pts) Dehydration of a tertiary alcohol in the presence of catalytic acid through the E1 pathway is thermodynamically unfavourable since sigma bonds are swapped for a pi bond. Explain how this process is made viable such that the alkene is able to be formed and isolated in high yield. (Klein C ...
... 12. (5 pts) Dehydration of a tertiary alcohol in the presence of catalytic acid through the E1 pathway is thermodynamically unfavourable since sigma bonds are swapped for a pi bond. Explain how this process is made viable such that the alkene is able to be formed and isolated in high yield. (Klein C ...
Topical KCSE Mock-Chemistry Answers(15 Schools)
... it is hygroscopic a)i)Ethanol, acetone (any organic solvent) ii) Its most soluble in the solvent and less sticky iii) - Cut out the yellow pigment - put in organic solvent to dissolve the pigment - filter and evaporate the filtrate to get the pigment iv)Above the red pigment and below the edge. b)-H ...
... it is hygroscopic a)i)Ethanol, acetone (any organic solvent) ii) Its most soluble in the solvent and less sticky iii) - Cut out the yellow pigment - put in organic solvent to dissolve the pigment - filter and evaporate the filtrate to get the pigment iv)Above the red pigment and below the edge. b)-H ...
1 Chapter 21: Organic and Biochemical Molecules
... Use a ring for the root name if the ring has more carbons than any of the other chains. The root name is formed by adding the prefix cyclo- to the core name (indicating the number of carbons). If only single bonds exist in the ring, the suffix –ane is added to the core name. If double bonds exist in ...
... Use a ring for the root name if the ring has more carbons than any of the other chains. The root name is formed by adding the prefix cyclo- to the core name (indicating the number of carbons). If only single bonds exist in the ring, the suffix –ane is added to the core name. If double bonds exist in ...
mod-5-revision-guide-4-transition-metals
... It cannot be nitric acid as it is an oxidising agent. It oxidises Fe2+ to Fe3+ as Eo NO3-/HNO2> Eo Fe3+/Fe2+ NO3- (aq) + 3H+(aq) + 2e– HNO2(aq) + H2O(l) Eo +0.94V Fe3+ (aq)+e– Fe2+ (aq) Eo +0.77 V This would lead to a smaller volume of manganate being used. ...
... It cannot be nitric acid as it is an oxidising agent. It oxidises Fe2+ to Fe3+ as Eo NO3-/HNO2> Eo Fe3+/Fe2+ NO3- (aq) + 3H+(aq) + 2e– HNO2(aq) + H2O(l) Eo +0.94V Fe3+ (aq)+e– Fe2+ (aq) Eo +0.77 V This would lead to a smaller volume of manganate being used. ...
15: Carbonyl Compounds: Esters, Amides, and Related Molecules
... various R-C(=O)-Z and R-C≡N compounds in the following sections. While we group all these classes together because they interconvert by nucleophilic acyl substitution reactions, you will see that nomenclature rules are signifcantly different for each class. Before we present systematic names for the ...
... various R-C(=O)-Z and R-C≡N compounds in the following sections. While we group all these classes together because they interconvert by nucleophilic acyl substitution reactions, you will see that nomenclature rules are signifcantly different for each class. Before we present systematic names for the ...
Multiple-choice questions : 1. Which of the following solutions
... Each question below consists of two separate statements. Decide whether each of the two statements is true or false; if both are true, then decide whether or not the second statement is a correct explanation of the first statement. Then select one option from A to D according to the following table ...
... Each question below consists of two separate statements. Decide whether each of the two statements is true or false; if both are true, then decide whether or not the second statement is a correct explanation of the first statement. Then select one option from A to D according to the following table ...
File - Chemistry Workshop
... A secondary carbon is directly bonded to two other C’s. A tertiary carbon is directly bonded to three other C’s. Multivalent atoms are 1º, 2º, or 3º by bonding to C’s. Univalent atom or group not really 1º, 2º, or 3º on its own - ID depends on type of carbon it is bonded to. ...
... A secondary carbon is directly bonded to two other C’s. A tertiary carbon is directly bonded to three other C’s. Multivalent atoms are 1º, 2º, or 3º by bonding to C’s. Univalent atom or group not really 1º, 2º, or 3º on its own - ID depends on type of carbon it is bonded to. ...
19.7 Reversible Addition Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones
... 19.6 Basicity of Aldehydes and Ketones 19.7 Reversible Addition Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones 19.8 Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones to Alcohols 19.9 Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones with Grignard and ...
... 19.6 Basicity of Aldehydes and Ketones 19.7 Reversible Addition Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones 19.8 Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones to Alcohols 19.9 Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones with Grignard and ...
Chemical Reactions - 2012 Book Archive
... measurable quantity in the laboratory—a given mass of sample. The unit that provides this link is the mole (mol)6, from the Latin moles, meaning “pile” or “heap” (not from the small subterranean animal!). Many familiar items are sold in numerical quantities that have unusual names. For example, cans ...
... measurable quantity in the laboratory—a given mass of sample. The unit that provides this link is the mole (mol)6, from the Latin moles, meaning “pile” or “heap” (not from the small subterranean animal!). Many familiar items are sold in numerical quantities that have unusual names. For example, cans ...
Relevance of the Physicochemical Properties of Calcined Quail
... experiments can provide qualitative information about the strength of the basic sites obtained by thermal treatment of the quail eggshell. The results obtained, compiled in the Supplementary Material Table S2, indicated that the calcined quail eggshell has a basic character, in accordance with the c ...
... experiments can provide qualitative information about the strength of the basic sites obtained by thermal treatment of the quail eggshell. The results obtained, compiled in the Supplementary Material Table S2, indicated that the calcined quail eggshell has a basic character, in accordance with the c ...
here
... Draw the structures of the two compounds formed when CH3NH2 reacts with ethanoic anhydride. ...
... Draw the structures of the two compounds formed when CH3NH2 reacts with ethanoic anhydride. ...
Chemistry 1250 - Sp17 Solutions for Midterm 1
... parentheses in the name. In ionic compounds groups 5A, 6A and 7A have charges of !3, !2 and !1 respectively. You have to memorize some polyatomic ions (names, formulas and charges). For molecular compounds the less electronegative element is generally written first in the formula and is named first ...
... parentheses in the name. In ionic compounds groups 5A, 6A and 7A have charges of !3, !2 and !1 respectively. You have to memorize some polyatomic ions (names, formulas and charges). For molecular compounds the less electronegative element is generally written first in the formula and is named first ...
SMK RAJA PEREMPUAN, IPOH
... oxidant such as acidified KMnO4 will cause the carbon atoms which are joined directly to the benzene ring to become a carboxyl group, and the remaining alkyl chains will turn into water and CO2 21. determine the products of halogenation of methylbenzene (toluene) with Lewis acid catalysts such as Al ...
... oxidant such as acidified KMnO4 will cause the carbon atoms which are joined directly to the benzene ring to become a carboxyl group, and the remaining alkyl chains will turn into water and CO2 21. determine the products of halogenation of methylbenzene (toluene) with Lewis acid catalysts such as Al ...
Strychnine total synthesis

Strychnine total synthesis in chemistry describes the total synthesis of the complex biomolecule strychnine. The first reported method by the group of Robert Burns Woodward in 1954 is considered a classic in this research field. At the time it formed the natural conclusion to an elaborate process of molecular structure elucidation that started with the isolation of strychnine from the beans of Strychnos ignatii by Pierre Joseph Pelletier and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou in 1818. Major contributors to the entire effort were Sir Robert Robinson with over 250 publications and Hermann Leuchs with another 125 papers in a time span of 40 years. Robinson was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1947 for his work on alkaloids, strychnine included. The process of chemical identification was completed with publications in 1946 by Robinson and later confirmed by Woodward in 1947. X-ray structures establishing the absolute configuration became available between 1947 and 1951 with publications from J. M. Bijvoet and J.H. Robertson .Woodward published a very brief account on the strychnine synthesis in 1954 (just 3 pages) and a lengthy one (42 pages) in 1963.Many more methods exist and reported by the research groups of Magnus, Overman, Kuehne, Rawal, Bosch, Vollhardt, Mori, Shibasaki, Li, Fukuyama Vanderwal and MacMillan. Synthetic (+)-strychnine is also known. Racemic synthesises were published by Padwa in 2007 and in 2010 by Andrade and by Reissig.In his 1963 publication Woodward quoted Sir Robert Robinson who said for its molecular size it is the most complex substance known.