Polymer Synthesis by In Vitro Enzyme Catalysis
... Richard A Gross received his B.S. in Chemistry from SUNY at Albany in 1979. In 1986, he received his Ph.D. in Organic-Polymer Chemistry under the supervision of Professor Mark M. Green at the Polytechnic University (Brooklyn, NY). His doctoral work focused on macromolecular stereochemistry, and his ...
... Richard A Gross received his B.S. in Chemistry from SUNY at Albany in 1979. In 1986, he received his Ph.D. in Organic-Polymer Chemistry under the supervision of Professor Mark M. Green at the Polytechnic University (Brooklyn, NY). His doctoral work focused on macromolecular stereochemistry, and his ...
Complexes Of 5,7,7,12,14,14 - European Scientific Journal
... Proper weight (1.0 mmol) of Cadmium(II) salts (CdI2, Cd(NO3)2.4H2O, CdCl2.2H2O or Cd(ClO4)2.6H2O) and ligands (1.0 mmol) (L.2HClO4, ‘tet-a‘ or ‘tet-b’) were suspended/dissolved separately in 25 mL of hot methanol. The ligand solution/suspension was added as soon as possible to the salt solution whil ...
... Proper weight (1.0 mmol) of Cadmium(II) salts (CdI2, Cd(NO3)2.4H2O, CdCl2.2H2O or Cd(ClO4)2.6H2O) and ligands (1.0 mmol) (L.2HClO4, ‘tet-a‘ or ‘tet-b’) were suspended/dissolved separately in 25 mL of hot methanol. The ligand solution/suspension was added as soon as possible to the salt solution whil ...
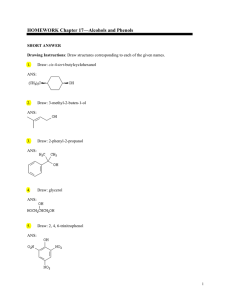
HOMEWORK Chapter 17—Alcohols and Phenols
... In m-nitrophenol, the inductive effect of the electron-withdrawing nitro group helps to stabilize the negative charge on oxygen. However, when the nitro group is para to the oxygen, direct conjugation of the negative charge on oxygen with the nitro group can occur. p-Nitrophenolate ion is, thus, mor ...
... In m-nitrophenol, the inductive effect of the electron-withdrawing nitro group helps to stabilize the negative charge on oxygen. However, when the nitro group is para to the oxygen, direct conjugation of the negative charge on oxygen with the nitro group can occur. p-Nitrophenolate ion is, thus, mor ...
A Simple and Advantageous Protocol for the Oxidation of Alcohols
... higher yields and shorter reaction times, but required chromatographic purification. The oxidation proceeds well with as few as 1.1 equiv of IBX, but an increased reaction rate is observed with excess oxidant. As a matter of convenience, we settled on 3 equiv to examine the solvent and substrate sco ...
... higher yields and shorter reaction times, but required chromatographic purification. The oxidation proceeds well with as few as 1.1 equiv of IBX, but an increased reaction rate is observed with excess oxidant. As a matter of convenience, we settled on 3 equiv to examine the solvent and substrate sco ...
Abstract Isomorphous substitution of Al or Si in zeolites/molecular
... Three different sources of vanadium .with different oxidation states viz. VC1 3 (III), VOSO 4 (IV) and NH 4 VO 3 (V) were tested in the 'synthesis of vanadium silicates. The gels containing VOSO 4 and NH 4 VO 3 were clear solution aifc that with VCl 3 was slightly turbid. The chemical analysis of th ...
... Three different sources of vanadium .with different oxidation states viz. VC1 3 (III), VOSO 4 (IV) and NH 4 VO 3 (V) were tested in the 'synthesis of vanadium silicates. The gels containing VOSO 4 and NH 4 VO 3 were clear solution aifc that with VCl 3 was slightly turbid. The chemical analysis of th ...
Handout 3
... rearrangement ).(hydride or methyl shift) Oxymercuration reaction is anti addition of H, OH that follows Mark.Rule (However, no rearrangement occurs). Hydroboration Method For the preparation of all types of alcohols 1°, 2°, 3° -Syn addition i.e. both H and OH are added to the same face of double bo ...
... rearrangement ).(hydride or methyl shift) Oxymercuration reaction is anti addition of H, OH that follows Mark.Rule (However, no rearrangement occurs). Hydroboration Method For the preparation of all types of alcohols 1°, 2°, 3° -Syn addition i.e. both H and OH are added to the same face of double bo ...
as a PDF
... The results of the two speciation methods applied to test solutions and theoretically computed inorganic speciations are shown in Fig. 3. The speciation of the 10 -2 M CaCI 2 solution gave the expected results. The ED method determined 100% low molecular weight Cd. This is in accordance with the fac ...
... The results of the two speciation methods applied to test solutions and theoretically computed inorganic speciations are shown in Fig. 3. The speciation of the 10 -2 M CaCI 2 solution gave the expected results. The ED method determined 100% low molecular weight Cd. This is in accordance with the fac ...
Lecture 10 -Further Consequences of d-Orbital
... 2. Factors Determining the Stability of a Metal Complex i. ...
... 2. Factors Determining the Stability of a Metal Complex i. ...
TRANSITION METALS
... A support medium is often used to maximise the surface area and minimise the cost (e.g. Rh on a ceramic support in catalytic converters). • It is obvious that the larger the surface area of these catalysts, the less quantity of catalyst that is needed to produce the same effect. • Many surface catal ...
... A support medium is often used to maximise the surface area and minimise the cost (e.g. Rh on a ceramic support in catalytic converters). • It is obvious that the larger the surface area of these catalysts, the less quantity of catalyst that is needed to produce the same effect. • Many surface catal ...
Amines
... • The basicity of the amines depends on the ability of the lone pair none bonding electrons at nitrogen atom to form bond with an acid. • The more easier the lone pair electrons formed bond with the acid, will make the amines a stronger base. • Factors that effect the basicity of the amines: i) sub ...
... • The basicity of the amines depends on the ability of the lone pair none bonding electrons at nitrogen atom to form bond with an acid. • The more easier the lone pair electrons formed bond with the acid, will make the amines a stronger base. • Factors that effect the basicity of the amines: i) sub ...
© John Congleton, Orange Coast College Organic Chemistry 220
... Be able to predict whether a reaction will proceed via o SN1 and E1 o S N2 o SN2 and E2 o E2 What makes a good nucleophile? What makes a good base? What makes a good leaving group? What is meant by high and low polarizability? Allylic bromination Understand, be able to predict, and be able to comple ...
... Be able to predict whether a reaction will proceed via o SN1 and E1 o S N2 o SN2 and E2 o E2 What makes a good nucleophile? What makes a good base? What makes a good leaving group? What is meant by high and low polarizability? Allylic bromination Understand, be able to predict, and be able to comple ...
Chapter 24 Chemistry of Coordination Compounds • Transition
... • Color of a complex depends on the metal, its oxidation state, and its ligands. • Pale blue [Cu(H2O)4]2+ can be converted into dark blue [Cu(NH3)4]2+ by adding NH3(aq). • A partially filled set of d orbitals is usually required for a complex to be colored. • So, d0 metal ions are usually colorless. ...
... • Color of a complex depends on the metal, its oxidation state, and its ligands. • Pale blue [Cu(H2O)4]2+ can be converted into dark blue [Cu(NH3)4]2+ by adding NH3(aq). • A partially filled set of d orbitals is usually required for a complex to be colored. • So, d0 metal ions are usually colorless. ...
ch23 lecture 7e
... SOLUTION: (b) There are two monodentate H2O ligands, each forming one bond to the metal ion; since the two C2O42− ligands are bidentate, each of these ligands forms two bonds to the metal ion, for a total of four bonds. The coordination number is 6. Since the K+ counter ion has a charge of 1+, the c ...
... SOLUTION: (b) There are two monodentate H2O ligands, each forming one bond to the metal ion; since the two C2O42− ligands are bidentate, each of these ligands forms two bonds to the metal ion, for a total of four bonds. The coordination number is 6. Since the K+ counter ion has a charge of 1+, the c ...
Lecture 10 -Further Consequences of d
... iv. The crystal field stabilization energy (CFSE). It is possible to calculate CFSE's CFSE s in any geometry in terms of the octahedral splitting energy o; we've seen how to do it for three common geometries: octahedral, tetrahedral, and square planar. Clearly, the CFSE is important, and it depends ...
... iv. The crystal field stabilization energy (CFSE). It is possible to calculate CFSE's CFSE s in any geometry in terms of the octahedral splitting energy o; we've seen how to do it for three common geometries: octahedral, tetrahedral, and square planar. Clearly, the CFSE is important, and it depends ...
Unit 13: Organic Chemistry
... Objective: What are Alkenes, and how do they function in chemistry? Alkene Family: 1. The alkene family, also known as the olefin family, differ from their related alkanes by having one carbon to carbon double bond (C=C) somewhere along the longest chain. 2. Ethane (C2H4) and propene (C3H6) are the ...
... Objective: What are Alkenes, and how do they function in chemistry? Alkene Family: 1. The alkene family, also known as the olefin family, differ from their related alkanes by having one carbon to carbon double bond (C=C) somewhere along the longest chain. 2. Ethane (C2H4) and propene (C3H6) are the ...
View/Open
... © 2008 Thomson Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Thomson Learning WebTutorTM is a trademark of Thomson Learning, Inc. Library of Congress Control Number: 2006938700 ...
... © 2008 Thomson Learning, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Thomson Learning WebTutorTM is a trademark of Thomson Learning, Inc. Library of Congress Control Number: 2006938700 ...
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
... • Unlike alkanes, alkenes cannot rotate freely about the double bond. Side-to-side overlap makes this impossible without breaking -bond. ...
... • Unlike alkanes, alkenes cannot rotate freely about the double bond. Side-to-side overlap makes this impossible without breaking -bond. ...
Unit 13: Organic Chemistry
... Objective: What are Alkenes, and how do they function in chemistry? Alkene Family: 1. The alkene family, also known as the olefin family, differ from their related alkanes by having one carbon to carbon double bond (C=C) somewhere along the longest chain. 2. Ethane (C2H4) and propene (C3H6) are the ...
... Objective: What are Alkenes, and how do they function in chemistry? Alkene Family: 1. The alkene family, also known as the olefin family, differ from their related alkanes by having one carbon to carbon double bond (C=C) somewhere along the longest chain. 2. Ethane (C2H4) and propene (C3H6) are the ...
Fragmentations Associated with Organic Functional Groups
... It is known that fragmentation of n-alkyl ions occurs by loss of ethene (C2H4), so that the ion of m/z 57 in the mass spectrum of n-octane, above, is probably derived from two pathways, as shown below. ...
... It is known that fragmentation of n-alkyl ions occurs by loss of ethene (C2H4), so that the ion of m/z 57 in the mass spectrum of n-octane, above, is probably derived from two pathways, as shown below. ...
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
... • Unlike alkanes, alkenes cannot rotate freely about the double bond. Side-to-side overlap makes this impossible without breaking -bond. ...
... • Unlike alkanes, alkenes cannot rotate freely about the double bond. Side-to-side overlap makes this impossible without breaking -bond. ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.