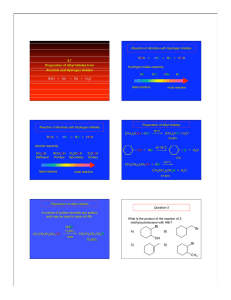
4.9 Preparation of Alkyl Halides from Alcohols and Hydrogen Halides
... bond can be shared by positively charged carbon because the s orbital can overlap with the empty 2p orbital of positively charged carbon ...
... bond can be shared by positively charged carbon because the s orbital can overlap with the empty 2p orbital of positively charged carbon ...
Living ring-opening metathesis polymerization
... olefin metathesis, a unique metal-mediated carbon– carbon double bond exchange process [4]. As a result, any unsaturation associated with the monomer is conserved as it is converted to polymer. This is an important feature that distinguishes ROMP from typical olefin addition polymerizations (e.g. ethy ...
... olefin metathesis, a unique metal-mediated carbon– carbon double bond exchange process [4]. As a result, any unsaturation associated with the monomer is conserved as it is converted to polymer. This is an important feature that distinguishes ROMP from typical olefin addition polymerizations (e.g. ethy ...
Scientific Jury of the 30th International
... your students need to show in Melbourne. We have tried to highlight the procedures in each exercise that need some particular caution, even for students of Olympiad level but our warnings cannot be comprehensive - your students will still need your careful supervision. We have also not included spec ...
... your students need to show in Melbourne. We have tried to highlight the procedures in each exercise that need some particular caution, even for students of Olympiad level but our warnings cannot be comprehensive - your students will still need your careful supervision. We have also not included spec ...
Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Photocatalytic Water Oxidation
... CAN because the rate of water oxidation was proportional to the square of the concentration of RuIII-OH2.[76] The formation of the radical superoxo intermediate [RuIV-O-O-RuIV]C3 + was indicated in the electrochemical experiments and supported by DFT calculations.[76] However, the direct detection o ...
... CAN because the rate of water oxidation was proportional to the square of the concentration of RuIII-OH2.[76] The formation of the radical superoxo intermediate [RuIV-O-O-RuIV]C3 + was indicated in the electrochemical experiments and supported by DFT calculations.[76] However, the direct detection o ...
Cyclam ``capa` POT.4` to ``capa` POT.3` denticity change
... linkers because they can form amide bonds with a desired material or relevant biomolecules such as proteins or antibodies. Whereas complex-modified solid materials may lead, for example, to sensors with potential analytical applications, the attachment of such compounds to biomolecules may form NO c ...
... linkers because they can form amide bonds with a desired material or relevant biomolecules such as proteins or antibodies. Whereas complex-modified solid materials may lead, for example, to sensors with potential analytical applications, the attachment of such compounds to biomolecules may form NO c ...
Reactions of Alcohols and Thiols
... Oxidation of Tertiary ( 3)Alcohols Tertiary 3alcohols do not readily oxidize. [O] Tertiary alcohol no reaction OH ...
... Oxidation of Tertiary ( 3)Alcohols Tertiary 3alcohols do not readily oxidize. [O] Tertiary alcohol no reaction OH ...
Chapter 12 Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers, Aldehydes, and Ketones
... Oxidation of Tertiary ( 3)Alcohols Tertiary 3alcohols do not readily oxidize. [O] Tertiary alcohol no reaction OH ...
... Oxidation of Tertiary ( 3)Alcohols Tertiary 3alcohols do not readily oxidize. [O] Tertiary alcohol no reaction OH ...
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions - An Introduction to Chemistry
... Oxidation-Reduction and Molecular Compounds The oxidation of nitrogen to form nitrogen monoxide is very similar to the oxidation of zinc to form zinc oxide. N2(g) + O2(g) → 2NO(g) 2Zn(s) + O2(g) → 2ZnO(s) The main difference between these reactions is that as the nitrogen monoxide forms, electrons a ...
... Oxidation-Reduction and Molecular Compounds The oxidation of nitrogen to form nitrogen monoxide is very similar to the oxidation of zinc to form zinc oxide. N2(g) + O2(g) → 2NO(g) 2Zn(s) + O2(g) → 2ZnO(s) The main difference between these reactions is that as the nitrogen monoxide forms, electrons a ...
Coordination Compounds - Madison Public Schools
... 1893 that metal ions exhibit what he called primary and secondary valences. Primary valences were the oxidation number for the metal (+3 on the cobalt at the right). Secondary valences were the coordination number, the number of atoms directly bonded to the metal (6 in the complex at the right). ...
... 1893 that metal ions exhibit what he called primary and secondary valences. Primary valences were the oxidation number for the metal (+3 on the cobalt at the right). Secondary valences were the coordination number, the number of atoms directly bonded to the metal (6 in the complex at the right). ...
coordination complexes
... surrounding molecules or ions. Ligand (ligare is Latin, to bind): A ligand is a molecule or ion that is directly bonded to a metal ion in a coordination complex A ligand uses a lone pair of electrons (Lewis base) to bond to the metal ion (Lewis acid) Coordination sphere: A metal and its surrounding ...
... surrounding molecules or ions. Ligand (ligare is Latin, to bind): A ligand is a molecule or ion that is directly bonded to a metal ion in a coordination complex A ligand uses a lone pair of electrons (Lewis base) to bond to the metal ion (Lewis acid) Coordination sphere: A metal and its surrounding ...
Chapter 24 Chemistry of Coordination Compounds
... 1893 that metal ions exhibit what he called primary and secondary valences. Primary valences were the oxidation number for the metal (+3 on the cobalt at the right). Secondary valences were the coordination number, the number of atoms directly bonded to the metal (6 in the complex at the right). ...
... 1893 that metal ions exhibit what he called primary and secondary valences. Primary valences were the oxidation number for the metal (+3 on the cobalt at the right). Secondary valences were the coordination number, the number of atoms directly bonded to the metal (6 in the complex at the right). ...
Synthesis, Characterization, and Luminescent Properties of
... Dinuclear Gold(I) Xanthate Complexes addition of about half of the CS2, the solution becomes light yellow. After the addition of more than 0.65 mL of CS2, the clear yellow solution turns cloudy. The cloudy yellow solution is then left to stir for 1 h, after which a yellow precipitate starts to form ...
... Dinuclear Gold(I) Xanthate Complexes addition of about half of the CS2, the solution becomes light yellow. After the addition of more than 0.65 mL of CS2, the clear yellow solution turns cloudy. The cloudy yellow solution is then left to stir for 1 h, after which a yellow precipitate starts to form ...
13: Carbonyl Compounds: Ketones, Aldehydes, Carboxylic Acids
... carboxylic acids of the same chain length. However, oxidation of ketones is very difficult, ...
... carboxylic acids of the same chain length. However, oxidation of ketones is very difficult, ...
review-rough
... 20. The last stage of the addition polymerization reaction when two unpaired electron ends combine is called: ...
... 20. The last stage of the addition polymerization reaction when two unpaired electron ends combine is called: ...
NOMENCLATURE OF ORGANOMETALLIC COMPOUNDS OF THE
... An organometallic compound is de®ned as any chemical species containing at least one bond between a carbon atom in an organic molecule, ion, or radical and a metal. By their very nature, the names of organometallic compounds should therefore incorporate the rules of organic chemistry as well as thos ...
... An organometallic compound is de®ned as any chemical species containing at least one bond between a carbon atom in an organic molecule, ion, or radical and a metal. By their very nature, the names of organometallic compounds should therefore incorporate the rules of organic chemistry as well as thos ...
Phenol - Macmillan Academy
... Sodium phenol reacts with sodium to form an ionic salt - sodium phenoxide hydrogen is also produced this reaction is similar to that with aliphatic alcohols such as ethanol 2C6H5OH(s) ...
... Sodium phenol reacts with sodium to form an ionic salt - sodium phenoxide hydrogen is also produced this reaction is similar to that with aliphatic alcohols such as ethanol 2C6H5OH(s) ...
Aspects of Coordination Chemistry (Part 2) Isomers in Coordination
... A number of examples of these types have been isolated and characterised and they show very different chemical and biological properties. Thus for example, cis-PtCl2(NH3)2 is an anti-cancer agent (cisplatin) whereas the trans- isomer is inactive against cancer (it is toxic), and so not useful in Che ...
... A number of examples of these types have been isolated and characterised and they show very different chemical and biological properties. Thus for example, cis-PtCl2(NH3)2 is an anti-cancer agent (cisplatin) whereas the trans- isomer is inactive against cancer (it is toxic), and so not useful in Che ...
HALO-ORGANICS – Fully functional fluorine 1
... variety of aromatic compounds. However, it is often much easier to use it in a hemiacetal form instead. This is precisely the strategy employed by a group at Gifu University in Japan, who found that trifluoroacetaldehyde required high temperatures or an excess of concentrated sulfuric acid to make t ...
... variety of aromatic compounds. However, it is often much easier to use it in a hemiacetal form instead. This is precisely the strategy employed by a group at Gifu University in Japan, who found that trifluoroacetaldehyde required high temperatures or an excess of concentrated sulfuric acid to make t ...
chapter27
... Alcohols and Phenols • The functional group in alcohols and phenols is the hydroxyl (-OH) group. • Alcohols and phenols can be considered derivatives of hydrocarbons in which one or more H atoms have been replaced by -OH groups. • Phenols are derivatives of benzene in which one H has been replaced ...
... Alcohols and Phenols • The functional group in alcohols and phenols is the hydroxyl (-OH) group. • Alcohols and phenols can be considered derivatives of hydrocarbons in which one or more H atoms have been replaced by -OH groups. • Phenols are derivatives of benzene in which one H has been replaced ...
Introduction to Organic Chemistry 2 ed William H. Brown
... 11 The Carbonyl Group • In this and three following chapters we study the physical and chemical properties of classes of compounds containing the carbonyl group, C=O ...
... 11 The Carbonyl Group • In this and three following chapters we study the physical and chemical properties of classes of compounds containing the carbonyl group, C=O ...
2007 Final Exam - Oregon State chemistry
... is cis-[CoCl3F3]3is trans-[CoCl3F3]3is mer-[CoCl3F3]3is fac-[CoCl3F3]3is college-world-series-[CoCl3F3]3- ...
... is cis-[CoCl3F3]3is trans-[CoCl3F3]3is mer-[CoCl3F3]3is fac-[CoCl3F3]3is college-world-series-[CoCl3F3]3- ...
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY, UNIVERSITY OF JYVÄSKYLÄ
... the formation of molecules with great accuracy, less is still known about what the molecules can do with their bonds. The reactivity of low-valent main group compounds is a primary example: at first, these species were thought to be inert in reactions toward small molecules, such as hydrogen and ole ...
... the formation of molecules with great accuracy, less is still known about what the molecules can do with their bonds. The reactivity of low-valent main group compounds is a primary example: at first, these species were thought to be inert in reactions toward small molecules, such as hydrogen and ole ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.