10. Alkyl Halides - faculty at Chemeketa
... Alkyl halide from addition of HCl, HBr, HI to alkenes ...
... Alkyl halide from addition of HCl, HBr, HI to alkenes ...
Carbonyl Compounds I. Aldehydes and Ketones
... Compared to carboxylic and carbonic acid derivatives, the less highly oxidized carbonyl compounds such as aldehydes and ketones are not so widespread in nature. That is not to say that they are unimportant. To the contrary. Aldehydes and ketones are of great importance both in biological chemistry a ...
... Compared to carboxylic and carbonic acid derivatives, the less highly oxidized carbonyl compounds such as aldehydes and ketones are not so widespread in nature. That is not to say that they are unimportant. To the contrary. Aldehydes and ketones are of great importance both in biological chemistry a ...
102 Lecture Ch14a
... • Cyclic ethers are generally named by their common names (we will not study the IUPAC names) • A cyclic ether containing two carbons is called ethylene oxide (generally known as epoxides) • A cyclic ether containing 4 carbons (with 2 double bonds) is called a furan • A cyclic ether containing 5 car ...
... • Cyclic ethers are generally named by their common names (we will not study the IUPAC names) • A cyclic ether containing two carbons is called ethylene oxide (generally known as epoxides) • A cyclic ether containing 4 carbons (with 2 double bonds) is called a furan • A cyclic ether containing 5 car ...
Exam 1 Review Sheet Chapter 15 Chemistry 110b
... composition and reaction (review the mechanism). Ozonolysis of alkenes (review from first semester). DIBAL reduction of esters; know the structure of the reagent and mechanism of reaction. Extend your mechanistic insights to the DIBAL reduction of nitriles. Li(Ot-Bu)3AlH reduction of acid chlorides ...
... composition and reaction (review the mechanism). Ozonolysis of alkenes (review from first semester). DIBAL reduction of esters; know the structure of the reagent and mechanism of reaction. Extend your mechanistic insights to the DIBAL reduction of nitriles. Li(Ot-Bu)3AlH reduction of acid chlorides ...
Chapter 1-
... “Straight-chain” alkanes have a zig-zag orientation when they are in their most straight orientation ...
... “Straight-chain” alkanes have a zig-zag orientation when they are in their most straight orientation ...
DME Rate Equations
... using one of two methods: 1) a two-step procedure consisting of methanol formation from synthesis gas followed by dehydration or 2) a single-step process involving the direct formation of DME from synthesis gas. The single-step procedure is attracting increasingly more attention for its dramatic eco ...
... using one of two methods: 1) a two-step procedure consisting of methanol formation from synthesis gas followed by dehydration or 2) a single-step process involving the direct formation of DME from synthesis gas. The single-step procedure is attracting increasingly more attention for its dramatic eco ...
(cobalamin)-dependent enzymes
... into three sub-groups dependent upon the nature of the substrate. First, there are those that catalyse the migration of hydroxy or amino groups in vicinal diols or amino alcohols, followed by dehydration or deamination to yield aldehydes. Second, there are the aminomutases, which catalyse the 1,2 mi ...
... into three sub-groups dependent upon the nature of the substrate. First, there are those that catalyse the migration of hydroxy or amino groups in vicinal diols or amino alcohols, followed by dehydration or deamination to yield aldehydes. Second, there are the aminomutases, which catalyse the 1,2 mi ...
Stockholm University
... (dr) (anti/syn); ao = anti isomer only; so = syn isomer only. [c] Enantiomeric excess. The major enantiomer is depicted in the product column. [d] Isolated yield. [e] In DMSO solvent. ...
... (dr) (anti/syn); ao = anti isomer only; so = syn isomer only. [c] Enantiomeric excess. The major enantiomer is depicted in the product column. [d] Isolated yield. [e] In DMSO solvent. ...
Name chemistry Unit 8 worksheet 1. Why do
... 22. The reaction C6H5N2Cl (aq) + H2O (l) → C6H5OH (aq) + N2 (g) + HCl (aq) is first order in C6H5N2Cl and zero order in H2O. What is the rate law expression? Rate = k[C6H5N2Cl] 23. For the reaction 2 NO (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2 NOCl (g) If the concentration of NO is tripled, the rate of the reaction increa ...
... 22. The reaction C6H5N2Cl (aq) + H2O (l) → C6H5OH (aq) + N2 (g) + HCl (aq) is first order in C6H5N2Cl and zero order in H2O. What is the rate law expression? Rate = k[C6H5N2Cl] 23. For the reaction 2 NO (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2 NOCl (g) If the concentration of NO is tripled, the rate of the reaction increa ...
Chapter 1: Fundamental Concepts
... increases going down in a group e.g. D is greater in Ru(NH3)63+ than in Fe(NH3)63+ Colors of metal complexes are due to electronic transition between the t2g and eg energy levels ...
... increases going down in a group e.g. D is greater in Ru(NH3)63+ than in Fe(NH3)63+ Colors of metal complexes are due to electronic transition between the t2g and eg energy levels ...
Chapter 16: Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides
... The sulfur atom of sulfides is much more nucleophilic than the oxygen atom of ethers, and will react with alkyl halides to give stable sulfonium salts. H3C ...
... The sulfur atom of sulfides is much more nucleophilic than the oxygen atom of ethers, and will react with alkyl halides to give stable sulfonium salts. H3C ...
Ch. 3 Sections 3.9-3.10 Notes
... In this reaction, N2 is the limiting reactant, it limited the amount of NH3 that was formed. Example: In an industrial process for making nitric acid, the first step is the reaction of ammonia with oxygen at high temperature in the presence of a platinum gauze. Nitrogen monoxide forms as follows: 4N ...
... In this reaction, N2 is the limiting reactant, it limited the amount of NH3 that was formed. Example: In an industrial process for making nitric acid, the first step is the reaction of ammonia with oxygen at high temperature in the presence of a platinum gauze. Nitrogen monoxide forms as follows: 4N ...
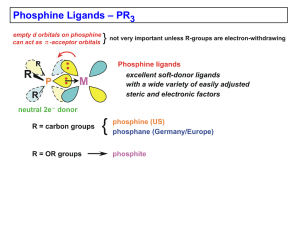
Chapter 4 (Phosphines)
... Tolman’s Cone Angle and Electronic Parameter The electron-donating ability of a phosphine ligand was determined by measuring the nCO of a Ni(CO)3(PR3) complex: Lowest CO stretching frequency: ...
... Tolman’s Cone Angle and Electronic Parameter The electron-donating ability of a phosphine ligand was determined by measuring the nCO of a Ni(CO)3(PR3) complex: Lowest CO stretching frequency: ...
Ch 10- Alcohols and Ethers
... • List the two alkyl groups in alphabetical order, followed with ether – example ...
... • List the two alkyl groups in alphabetical order, followed with ether – example ...
La chimica del carbonio
... hydrogen atoms with one or more different atoms (or different groups of atoms); ■■ addition reactions are reactions in which two atoms (or groups of atoms) bind to the carbon atoms with double or triple bonds. All hydrocarbons can be involved in combustion reactions and substitution reactions while ...
... hydrogen atoms with one or more different atoms (or different groups of atoms); ■■ addition reactions are reactions in which two atoms (or groups of atoms) bind to the carbon atoms with double or triple bonds. All hydrocarbons can be involved in combustion reactions and substitution reactions while ...
Lecture 18
... to be reasonable soluble in water so that it can be transported through the blood. Since amines are weak bases, they are often converted to salts with some acid and therefore may oral drugs have amine salts as part of their structure. One reason for their presence is that they confer some water solu ...
... to be reasonable soluble in water so that it can be transported through the blood. Since amines are weak bases, they are often converted to salts with some acid and therefore may oral drugs have amine salts as part of their structure. One reason for their presence is that they confer some water solu ...
Lectures 29-31
... •Some co-ordination complexes and complex salts contain extra water molecules which were trapped during crystallization. These complexes are also hydrates. Water of hydration can be removed by heating a complex salt in a dry oven. •If 5.00 grams of K3[Fe(C2O4)3].3H2O is heated until all of the water ...
... •Some co-ordination complexes and complex salts contain extra water molecules which were trapped during crystallization. These complexes are also hydrates. Water of hydration can be removed by heating a complex salt in a dry oven. •If 5.00 grams of K3[Fe(C2O4)3].3H2O is heated until all of the water ...
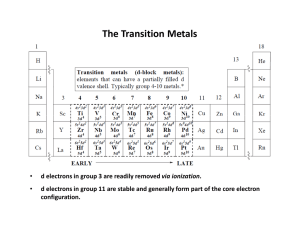
The Transition Metals
... It's these non-bonding d orbitals that give TM complexes many of their unique properties ...
... It's these non-bonding d orbitals that give TM complexes many of their unique properties ...
Homework set 1: Biological Molecules
... There are 5 carbon sugars such as ribose: Five carbon sugars are not used for energy, but are used within the structure of DNA and RNA. The carbohydrates shown above are drawn in what is known as the "chain form" of these monosaccharides. In solution (which is where we find them in living cells) the ...
... There are 5 carbon sugars such as ribose: Five carbon sugars are not used for energy, but are used within the structure of DNA and RNA. The carbohydrates shown above are drawn in what is known as the "chain form" of these monosaccharides. In solution (which is where we find them in living cells) the ...
polymer - MrSimonPorter
... Ethanoic acid C2H3OOH Propanoic acid C3H5OOH Butanoic acid C4H7OOH Pentanoic acid C5H9OOH Hexanoic acid C6H11OOH ...
... Ethanoic acid C2H3OOH Propanoic acid C3H5OOH Butanoic acid C4H7OOH Pentanoic acid C5H9OOH Hexanoic acid C6H11OOH ...
polymer - MrSimonPorter
... Ethanoic acid C2H3OOH Propanoic acid C3H5OOH Butanoic acid C4H7OOH Pentanoic acid C5H9OOH Hexanoic acid C6H11OOH ...
... Ethanoic acid C2H3OOH Propanoic acid C3H5OOH Butanoic acid C4H7OOH Pentanoic acid C5H9OOH Hexanoic acid C6H11OOH ...
04_Lecture_Presentation
... Concept 4.1: Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds • Organic chemistry is the study of compounds that contain carbon • Organic compounds range from simple molecules to colossal ones • Most organic compounds contain hydrogen atoms in addition to carbon atoms ...
... Concept 4.1: Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds • Organic chemistry is the study of compounds that contain carbon • Organic compounds range from simple molecules to colossal ones • Most organic compounds contain hydrogen atoms in addition to carbon atoms ...
AP® Chemistry 2009 Free-Response Questions - AP Central
... The data for the experiment are shown in the table below. Volume of sealed flask 843 mL Mass of sealed flask and dry air 157.70 g Mass of sealed flask and unknown gas 158.08 g (a) Calculate the mass, in grams, of the dry air that was in the sealed flask. (The density of dry air is 1.18 g L−1 at 23.0 ...
... The data for the experiment are shown in the table below. Volume of sealed flask 843 mL Mass of sealed flask and dry air 157.70 g Mass of sealed flask and unknown gas 158.08 g (a) Calculate the mass, in grams, of the dry air that was in the sealed flask. (The density of dry air is 1.18 g L−1 at 23.0 ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.