Arginine- or Lysine-catalyzed Michael Addition of Nitromethane to α
... conversion for 24 h. More polar solvents probably maintain near the pKa of a compound and thus nitromethane is more easily deprotonated to be an activated form in alcohols. Although, the conversions are similar in both reactions in ethanol and 2-propanol, ethanol was chosen as a co-solvent for furth ...
... conversion for 24 h. More polar solvents probably maintain near the pKa of a compound and thus nitromethane is more easily deprotonated to be an activated form in alcohols. Although, the conversions are similar in both reactions in ethanol and 2-propanol, ethanol was chosen as a co-solvent for furth ...
Questions
... A tablet of ibuprofen contains a very small quantity of the drug and the remainder of the tablet material is unreactive. In an analysis 50 tablets were reacted with 100.0 cm3 of 1.00 mol dm–3 aqueous sodium hydroxide, an excess. The ibuprofen reacted as a weak acid. When the reaction was complete, t ...
... A tablet of ibuprofen contains a very small quantity of the drug and the remainder of the tablet material is unreactive. In an analysis 50 tablets were reacted with 100.0 cm3 of 1.00 mol dm–3 aqueous sodium hydroxide, an excess. The ibuprofen reacted as a weak acid. When the reaction was complete, t ...
Coordination compounds :
... A complex is a structure composed of a central metal atom or ion, generally a cation, surrounded by a number of negatively charged ions or neutral molecules possessing lone pairs. A complex may also be called a coordination compound or metal complex. The ions or molecules surrounding the metal are ...
... A complex is a structure composed of a central metal atom or ion, generally a cation, surrounded by a number of negatively charged ions or neutral molecules possessing lone pairs. A complex may also be called a coordination compound or metal complex. The ions or molecules surrounding the metal are ...
Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization of Norbornene by Cp
... presence of water is known to increase the activity of certain catalysts such as OsCl3. Methods to control molecular weight and polydispersity of polynorbornenes generated in aqueous solvents are continually being developed.27-30 It is generally accepted that the resting state in ROMP reactions is e ...
... presence of water is known to increase the activity of certain catalysts such as OsCl3. Methods to control molecular weight and polydispersity of polynorbornenes generated in aqueous solvents are continually being developed.27-30 It is generally accepted that the resting state in ROMP reactions is e ...
Oxidation - Sciencemadness
... • Requires less vigorous oxidation conditions. • We can try to remove the aldehyde from the reaction medium as quickly as it is formed – Generally, the aldehyde has a lower boiling point than either the corresponding alcohol or carboxylic acid ...
... • Requires less vigorous oxidation conditions. • We can try to remove the aldehyde from the reaction medium as quickly as it is formed – Generally, the aldehyde has a lower boiling point than either the corresponding alcohol or carboxylic acid ...
functional group review
... • p-nitrophenol is > acidic then phenol due to EWG nitro and p-ethylphenol is less acidic due to ERG ethyl. • When phenolic drugs needed to dissolve in aq-environment then they are treated with aq-bases to form salt. See next slide ...
... • p-nitrophenol is > acidic then phenol due to EWG nitro and p-ethylphenol is less acidic due to ERG ethyl. • When phenolic drugs needed to dissolve in aq-environment then they are treated with aq-bases to form salt. See next slide ...
Hydrocarbon Derivatives:
... Hydrocarbons • Contain only carbon & hydrogen • But carbon can also form strong covalent bonds with other elements such as: O, N, F, Cl, Br, I, S, & P ...
... Hydrocarbons • Contain only carbon & hydrogen • But carbon can also form strong covalent bonds with other elements such as: O, N, F, Cl, Br, I, S, & P ...
Practice Final Answers
... MnO4- + 8H+ + 5e- → Mn2+ + 4H2O PbO2 (s) + 4H+ + 2e- → Pb2+ + 2H2O Cl2 (g) + 2e- → 2ClCr2O72- + 14H+ + 6e- → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O O2 (g) + 4H+ + 4e- → 2H2O Br2 (g) + 2e- → 2BrNO3- + 4H+ + 3e- → NO (g) + 2H2O Hg2+ + 2e- → Hg (l) Ag+ + e- → Ag (s) Fe3+ + e- → Fe2+ O2 (g) + 2 H+ + 2 e- → Η2O2 I2 (s) + 2e- → 2I ...
... MnO4- + 8H+ + 5e- → Mn2+ + 4H2O PbO2 (s) + 4H+ + 2e- → Pb2+ + 2H2O Cl2 (g) + 2e- → 2ClCr2O72- + 14H+ + 6e- → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O O2 (g) + 4H+ + 4e- → 2H2O Br2 (g) + 2e- → 2BrNO3- + 4H+ + 3e- → NO (g) + 2H2O Hg2+ + 2e- → Hg (l) Ag+ + e- → Ag (s) Fe3+ + e- → Fe2+ O2 (g) + 2 H+ + 2 e- → Η2O2 I2 (s) + 2e- → 2I ...
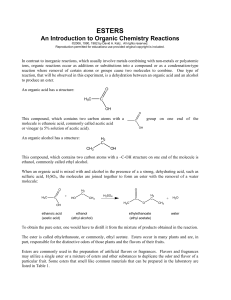
carboxylic acids
... Esters are produced by esterification reactions. These are condensation reactions involving an alcohol and a carboxylic acid (with conc, H2SO4 as catalyst) or an alcohol and an acid chloride. ...
... Esters are produced by esterification reactions. These are condensation reactions involving an alcohol and a carboxylic acid (with conc, H2SO4 as catalyst) or an alcohol and an acid chloride. ...
model paper-1 - WordPress.com
... b) What is the energy in joules, required to shift the electron of the hydrogen atom from the first Bohr orbit to the fifth Bohr orbit, and what is the wavelength of the light emitted when the electron returns to the \ground state? The ground state electron energy is -2.18x10-11 ergs. c) Assign the ...
... b) What is the energy in joules, required to shift the electron of the hydrogen atom from the first Bohr orbit to the fifth Bohr orbit, and what is the wavelength of the light emitted when the electron returns to the \ground state? The ground state electron energy is -2.18x10-11 ergs. c) Assign the ...
RxnTypesPrednotesIIAP
... Double replacement reaction generally fall under one of two categories - (1) acid-base neutralization reactions or (2) precipitation reactions. Many types of double replacement reactions are said to be reversible - that is, once the products are formed, they may turn back into the original reactants ...
... Double replacement reaction generally fall under one of two categories - (1) acid-base neutralization reactions or (2) precipitation reactions. Many types of double replacement reactions are said to be reversible - that is, once the products are formed, they may turn back into the original reactants ...
Asymmetric Catalytic Aldol
... achieved with Sn (II) complexes in the presence of chiral diamines. The reaction between aldehydes and Ketene silyl acetals are highly enantioselective with ee >98% Since then considerable interest has been paid to Titanium (IV) catalysts, along with copper (II) complexes, and Boron complexes. ...
... achieved with Sn (II) complexes in the presence of chiral diamines. The reaction between aldehydes and Ketene silyl acetals are highly enantioselective with ee >98% Since then considerable interest has been paid to Titanium (IV) catalysts, along with copper (II) complexes, and Boron complexes. ...
Organic Chemistry Boardwork
... The presence of the hydroxyl group with its electronegative oxygen atom means that alcohols are polar. They can therefore take part in hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonding between alcohol molecules means that an alcohol’s boiling point is higher than that of an alkane of similar molecular mass. For ex ...
... The presence of the hydroxyl group with its electronegative oxygen atom means that alcohols are polar. They can therefore take part in hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonding between alcohol molecules means that an alcohol’s boiling point is higher than that of an alkane of similar molecular mass. For ex ...
Changing Coordination Numbers: Nickel Complexes
... A complex ion is a metal ion with Lewis bases attached to it through coordinate covalent bonds. A complex or coordination compound is a compound consisting either of complex ions with other ions of opposite charge or of a neutral complex species. Ligands are the Lewis bases attached to the metal ato ...
... A complex ion is a metal ion with Lewis bases attached to it through coordinate covalent bonds. A complex or coordination compound is a compound consisting either of complex ions with other ions of opposite charge or of a neutral complex species. Ligands are the Lewis bases attached to the metal ato ...
FahadH. Ahmad (Contact: +92 323 509 4443)
... Emulsifier molecules have two different ends: a hydrophilic (water-loving) ‘head’ that forms chemical bonds with water but not with oils a hydrophobic (water-hating) ‘tail’ that forms chemical bonds with oils but not with water Lecithin is an emulsifier commonly used in foods. It is ...
... Emulsifier molecules have two different ends: a hydrophilic (water-loving) ‘head’ that forms chemical bonds with water but not with oils a hydrophobic (water-hating) ‘tail’ that forms chemical bonds with oils but not with water Lecithin is an emulsifier commonly used in foods. It is ...
Chapters 12 – 20 Practice Problems
... 30. Calculate the entropy change of the surroundings at 25C for the reaction below. C3H8(g) + 5 O2(g) 3 CO2(g) + 4 H2O(g) ∆Hrxn = −2044 kJ A) 1.30 kJ/K B) 15.5 kJ/K C) 6.86 kJ/K D) 10.4 kJ/K E) 20.5 kJ/K 31. The reaction CCl4(g) C(s, graphite) + 2 Cl2(g) has ∆H = +95.7 kJ and ∆S = +142.2 J/K at ...
... 30. Calculate the entropy change of the surroundings at 25C for the reaction below. C3H8(g) + 5 O2(g) 3 CO2(g) + 4 H2O(g) ∆Hrxn = −2044 kJ A) 1.30 kJ/K B) 15.5 kJ/K C) 6.86 kJ/K D) 10.4 kJ/K E) 20.5 kJ/K 31. The reaction CCl4(g) C(s, graphite) + 2 Cl2(g) has ∆H = +95.7 kJ and ∆S = +142.2 J/K at ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.