CHAPTER 22 ORGANIC AND BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES 1
... relatively strong hydrogen-bonding interaction. These compounds have an OH or NH bond, which is a requirement for Hbonding. Reference the isomers of C3H8O in Review question 6. The alcohol can Hbond, the ether cannot (no OH bonds exist in the ether). Because the alcohol has the ability to Hbon ...
... relatively strong hydrogen-bonding interaction. These compounds have an OH or NH bond, which is a requirement for Hbonding. Reference the isomers of C3H8O in Review question 6. The alcohol can Hbond, the ether cannot (no OH bonds exist in the ether). Because the alcohol has the ability to Hbon ...
Complete Solution Manual
... relatively strong hydrogen-bonding interaction. These compounds have an OH or NH bond, which is a requirement for Hbonding. Reference the isomers of C3H8O in Review question 6. The alcohol can Hbond, the ether cannot (no OH bonds exist in the ether). Because the alcohol has the ability to Hbon ...
... relatively strong hydrogen-bonding interaction. These compounds have an OH or NH bond, which is a requirement for Hbonding. Reference the isomers of C3H8O in Review question 6. The alcohol can Hbond, the ether cannot (no OH bonds exist in the ether). Because the alcohol has the ability to Hbon ...
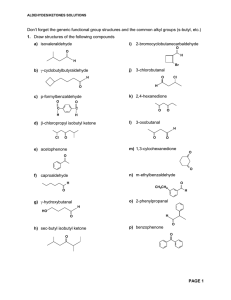
Aldehydes/Ketones Solutions
... The aldehyde is more easily reduced than the ketone so you must first add a protecting group to the aldehyde; reduce the ketone; and finally remove the protecting group to regenerate the aldehyde. ...
... The aldehyde is more easily reduced than the ketone so you must first add a protecting group to the aldehyde; reduce the ketone; and finally remove the protecting group to regenerate the aldehyde. ...
Asymmetric Synthesis: Substrate and Auxiliary Control
... reagent, catalyst, etc.). This is an absolute requirement when creating a chiral molecule from achiral starting ...
... reagent, catalyst, etc.). This is an absolute requirement when creating a chiral molecule from achiral starting ...
Transition Metal Reagents and Catalysts
... ®rst by giving a simple mechanistic explanation in chapter 2. Then a number of important types of reactions classi®ed mainly by representative substrates such as organic halides and allylic derivatives are surveyed with pertinent examples. For this purpose, I cited many references; these were select ...
... ®rst by giving a simple mechanistic explanation in chapter 2. Then a number of important types of reactions classi®ed mainly by representative substrates such as organic halides and allylic derivatives are surveyed with pertinent examples. For this purpose, I cited many references; these were select ...
8.1 Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers 8.2 Naming Alcohols
... Methyl Alcohol (CH3OH, methanol) Methyl alcohol is the simplest (smallest) alcohol and is commonly known as wood alcohol because it was once prepared by heating wood in the absence of air. Ethyl Alcohol (CH3CH2OH, ethanol) Ethyl alcohol is one of the oldest known pure organic compounds. Ethyl alcoho ...
... Methyl Alcohol (CH3OH, methanol) Methyl alcohol is the simplest (smallest) alcohol and is commonly known as wood alcohol because it was once prepared by heating wood in the absence of air. Ethyl Alcohol (CH3CH2OH, ethanol) Ethyl alcohol is one of the oldest known pure organic compounds. Ethyl alcoho ...
BIORANSFORMATION
... The mechanism of S-Dealkylation of thioethers is analogous to N-dealkylation .IT proceed via α-carbon hydroxylation. The C-S bond cleavage results in formation of a thiol and a carbonyl product. E.g. 6-Methyl mercaptopurine. SCH2OH ...
... The mechanism of S-Dealkylation of thioethers is analogous to N-dealkylation .IT proceed via α-carbon hydroxylation. The C-S bond cleavage results in formation of a thiol and a carbonyl product. E.g. 6-Methyl mercaptopurine. SCH2OH ...
chapter 4 -aromatic compounds
... • Substituent group present in the benzene ring can influence the rate of reaction of further substitutions. • Electron-donating groups make the ring more reactive (called activating groups) thus influence the reaction ...
... • Substituent group present in the benzene ring can influence the rate of reaction of further substitutions. • Electron-donating groups make the ring more reactive (called activating groups) thus influence the reaction ...
Slide 1
... • Substituent group present in the benzene ring can influence the rate of reaction of further substitutions. • Electron-donating groups make the ring more reactive (called activating groups) thus influence the reaction ...
... • Substituent group present in the benzene ring can influence the rate of reaction of further substitutions. • Electron-donating groups make the ring more reactive (called activating groups) thus influence the reaction ...
Organic Chemistry: Introduction
... • study of carbon, the compounds it makes, and the reactions it undergoes • over 16 million carbon-containing compounds are known • because the C-C single bond (348 kJ mol-1) and the C-H bond (412 kJ mol-1) are strong, carbon compounds are stable • carbon can form chains and rings ...
... • study of carbon, the compounds it makes, and the reactions it undergoes • over 16 million carbon-containing compounds are known • because the C-C single bond (348 kJ mol-1) and the C-H bond (412 kJ mol-1) are strong, carbon compounds are stable • carbon can form chains and rings ...
Title The Cyanide-Ion Cleavage of Organic Disulfides
... alkyl aryl sulfides in high yields in the presence of cyanide ion. The results of this novel reaction are summarized in Table 4. It is expected that alkyl aryl sulfides would be derived from aryl thiocyanates. Thus, aryl thiocyanates were found to react with alcohols in the presence of cyanide ion t ...
... alkyl aryl sulfides in high yields in the presence of cyanide ion. The results of this novel reaction are summarized in Table 4. It is expected that alkyl aryl sulfides would be derived from aryl thiocyanates. Thus, aryl thiocyanates were found to react with alcohols in the presence of cyanide ion t ...
Colorimetric Assay of Alditols in Complex Biological Samples
... The formation of color was completed in 1 min at 100 °C and bleaching began after 3 min at that temperature. Thus, 2 min in boiling water was chosen as the optimal condition for the color reaction. On the other hand, changing the pH of the reaction medium from 2.0 to 7.0 had only a minor effect in t ...
... The formation of color was completed in 1 min at 100 °C and bleaching began after 3 min at that temperature. Thus, 2 min in boiling water was chosen as the optimal condition for the color reaction. On the other hand, changing the pH of the reaction medium from 2.0 to 7.0 had only a minor effect in t ...
university of london thesis
... The chapter covering results and discussion opens with a brief overview o f the investigational work previously carried out into the Sn I like ring opening o f a model molecule, 1-methylcyclohexene oxide. This is followed by a description o f how a new methodology for the acidic ring opening o f epo ...
... The chapter covering results and discussion opens with a brief overview o f the investigational work previously carried out into the Sn I like ring opening o f a model molecule, 1-methylcyclohexene oxide. This is followed by a description o f how a new methodology for the acidic ring opening o f epo ...
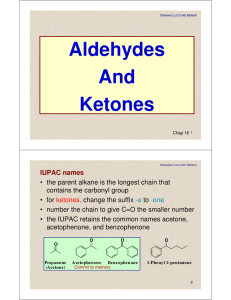
Aldehydes And Ketones
... Acidity of α-Hydrogens Hydrogens alpha to a carbonyl group are more acidic than hydrogens of alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes but less acidic than the hydroxyl hydrogen of alcohols ...
... Acidity of α-Hydrogens Hydrogens alpha to a carbonyl group are more acidic than hydrogens of alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes but less acidic than the hydroxyl hydrogen of alcohols ...
Chemistry of Fatty Acids
... with C18 most common. Naturally occurring fatty acids share a common biosynthesis. The chain is built from two carbon units, and cis double bonds are inserted by desaturase enzymes at specific positions relative to the carboxyl group. This results in even-chain-length fatty acids with a characterist ...
... with C18 most common. Naturally occurring fatty acids share a common biosynthesis. The chain is built from two carbon units, and cis double bonds are inserted by desaturase enzymes at specific positions relative to the carboxyl group. This results in even-chain-length fatty acids with a characterist ...
HIGHLY SELECTIVE RHODIUM–CATALYZED C–H BORYLATIONS IN
... List of Schemes Scheme 1-1. General process of directed ortho–Metalation (DoM).............................................. 3 Scheme 1-2. Sequential DoM/Suzuki–Miyaura cross–coupling for synthesis of 1,2–disubstituted biaryls by Snieckus and coworkers .............................................. ...
... List of Schemes Scheme 1-1. General process of directed ortho–Metalation (DoM).............................................. 3 Scheme 1-2. Sequential DoM/Suzuki–Miyaura cross–coupling for synthesis of 1,2–disubstituted biaryls by Snieckus and coworkers .............................................. ...
CHAPTER TWENTY-TWO ORGANIC AND BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES
... relatively strong hydrogen-bonding interaction. These compounds have an O−H or N−H bond, which is a requirement for H−bonding. Reference the isomers of C3H8O in Review question 6. The alcohol can H−bond, the ether cannot (no O−H bonds exist in the ether). Because the alcohol has the ability to H−bon ...
... relatively strong hydrogen-bonding interaction. These compounds have an O−H or N−H bond, which is a requirement for H−bonding. Reference the isomers of C3H8O in Review question 6. The alcohol can H−bond, the ether cannot (no O−H bonds exist in the ether). Because the alcohol has the ability to H−bon ...
Oxidative Alihatic Carbon-Carbon Bond Cleavage Reactions
... Dr. Lisa Berreau, for her continued advice and support, and for putting up with me telling her she was wrong (even when she was right). I’m especially grateful for the freedom she has given me in pursuing chemistry that is inherently interesting, even if it was not always the chemistry we had origin ...
... Dr. Lisa Berreau, for her continued advice and support, and for putting up with me telling her she was wrong (even when she was right). I’m especially grateful for the freedom she has given me in pursuing chemistry that is inherently interesting, even if it was not always the chemistry we had origin ...
cleavage of methyl ethers with iodotrimethylsilane
... trimethylphenysilane with iodine.7 The reagent has also been generated in situ by halide exchange between magnesium iodide and chlorotrimethylsilane.8 The present procedure is essentially that of Voronkov and Khudobin,3 modified by slowly adding iodine to a mixture of aluminum and hexamethyldisiloxa ...
... trimethylphenysilane with iodine.7 The reagent has also been generated in situ by halide exchange between magnesium iodide and chlorotrimethylsilane.8 The present procedure is essentially that of Voronkov and Khudobin,3 modified by slowly adding iodine to a mixture of aluminum and hexamethyldisiloxa ...
University of Groningen Manganese catalysts in
... substituents on the phenolate moieties are necessary in order stabilise the CuI-phenoxyl radical species. Benzyl alcohol and 1-phenyl ethanol are readily converted to the corresponding carbonyl compounds with the concomitant formation of H2O2, using O2 as oxidant at room temperature. Under neat reac ...
... substituents on the phenolate moieties are necessary in order stabilise the CuI-phenoxyl radical species. Benzyl alcohol and 1-phenyl ethanol are readily converted to the corresponding carbonyl compounds with the concomitant formation of H2O2, using O2 as oxidant at room temperature. Under neat reac ...
lec-3- 211( Elim+ Re..
... Oxidation is the beginning of the deterioration process. Think of how a slice of apple turns brown when exposed to air. Oxidation leads to the formation of free radicals which are unstable molecules in the body that have one unpaired electron. They can cause oxidation and damage to the cells. This ...
... Oxidation is the beginning of the deterioration process. Think of how a slice of apple turns brown when exposed to air. Oxidation leads to the formation of free radicals which are unstable molecules in the body that have one unpaired electron. They can cause oxidation and damage to the cells. This ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.