Amines - ncert
... with three or more carbon atoms are liquid and still higher ones are solid. Aniline and other arylamines are usually colourless but get coloured on storage due to atmospheric oxidation. Lower aliphatic amines are soluble in water because they can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. However, so ...
... with three or more carbon atoms are liquid and still higher ones are solid. Aniline and other arylamines are usually colourless but get coloured on storage due to atmospheric oxidation. Lower aliphatic amines are soluble in water because they can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. However, so ...
amine cured-epoxy matrices
... aromatic amines require elevated temperature to effectively cure most epoxy resins. It should also be mentioned that catalysts can be added to increase the reaction rate of amines with epoxy resins but if used in excess oftentimes at the cost of a reduction in performance. The amine curing agent sel ...
... aromatic amines require elevated temperature to effectively cure most epoxy resins. It should also be mentioned that catalysts can be added to increase the reaction rate of amines with epoxy resins but if used in excess oftentimes at the cost of a reduction in performance. The amine curing agent sel ...
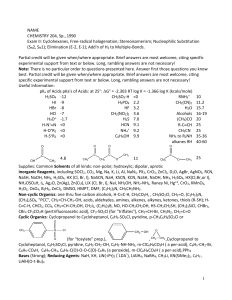
Problem Set Chapter 8: Introduction to Alkyl Halides, Alcohols
... (e) The equilibrium constant for the analogous reaction of ethanethiol is 0.004. Which forms stronger hydrogen bonds, thiols or alcohols? ...
... (e) The equilibrium constant for the analogous reaction of ethanethiol is 0.004. Which forms stronger hydrogen bonds, thiols or alcohols? ...
History of Organic Chemistry
... Which term describes this group of compounds? chloromethane, chloroethane, 1-chloropropane, 1-chlorobutane a. aldehydes c. functional isomers b. aromatics d. homologous series Alkanes/Straight chain alkanes Alkanes are: ...
... Which term describes this group of compounds? chloromethane, chloroethane, 1-chloropropane, 1-chlorobutane a. aldehydes c. functional isomers b. aromatics d. homologous series Alkanes/Straight chain alkanes Alkanes are: ...
13C NMR - Creighton Chemistry Webserver
... tells you the number of chemically nonequivalent CH 3 , CH2 , and CH carbons C do not appear–they must be identifed by comparison with the normal 13C NMR spectrum ways to present a DEPT 13C NMR spectrum: ...
... tells you the number of chemically nonequivalent CH 3 , CH2 , and CH carbons C do not appear–they must be identifed by comparison with the normal 13C NMR spectrum ways to present a DEPT 13C NMR spectrum: ...
1990-Spring-Exam-2-student
... What feature would you study experimentally to establish that this step is indeed "SN2"? Briefly describe an experimental study and what the outcome would be to confirm the S N2 designation. (There are at least two features that could be studied; recall lecture and text) ...
... What feature would you study experimentally to establish that this step is indeed "SN2"? Briefly describe an experimental study and what the outcome would be to confirm the S N2 designation. (There are at least two features that could be studied; recall lecture and text) ...
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44, 2202--2220 - RSC Publishing
... Nyhlén and Privalov a few years ago.30 Just recently, this gap was closed by the groups of Stephan31 and Ashley.32 Stephan and co-workers had already found that 1,1-diphenylethylene is reduced to the corresponding alkane when treated with dihydrogen in the presence of catalytic amounts of B(C6F5)3 ...
... Nyhlén and Privalov a few years ago.30 Just recently, this gap was closed by the groups of Stephan31 and Ashley.32 Stephan and co-workers had already found that 1,1-diphenylethylene is reduced to the corresponding alkane when treated with dihydrogen in the presence of catalytic amounts of B(C6F5)3 ...
Chapter 12
... Select as the parent compound the longest chain of carbon atoms that contains the functional group. For ketones, change the suffix –e of the parent name to –one. Number the chain so that the ketone group gets the lowest number. Chapter 12 ...
... Select as the parent compound the longest chain of carbon atoms that contains the functional group. For ketones, change the suffix –e of the parent name to –one. Number the chain so that the ketone group gets the lowest number. Chapter 12 ...
C−C, C−O, C−N Bond Formation on sp2 Carbon by Pd(II)
... Being electrophilic species, palladium(II) salts tend to react with π-nucleophiles such as olefins, alkynes, and arenes. The mechanisms of these processes have been extensively studied. A typical reaction with alkenes starts with the complexation of the olefin by the Pd(II) salt, as shown in Scheme ...
... Being electrophilic species, palladium(II) salts tend to react with π-nucleophiles such as olefins, alkynes, and arenes. The mechanisms of these processes have been extensively studied. A typical reaction with alkenes starts with the complexation of the olefin by the Pd(II) salt, as shown in Scheme ...
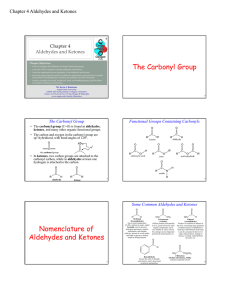
The Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones
... • Number the chain starting with the end closest to the ketone group (the carbonyl carbon should have the lowest possible number). The location # for the ketone group precedes the name for the longest chain. ...
... • Number the chain starting with the end closest to the ketone group (the carbonyl carbon should have the lowest possible number). The location # for the ketone group precedes the name for the longest chain. ...
Derivatization Reagents - Sigma
... Pentafluorobenzylbromide is convenient for making esters and ethers, and has been used in trace analyses. This strong lachrymator should be used in a hood. Hexacyclooctadecane and pentafluorobenzylbromide are used to prepare pentafluorobenzyldilute with 50mL 2-propanol. 1mL of this reagent will deri ...
... Pentafluorobenzylbromide is convenient for making esters and ethers, and has been used in trace analyses. This strong lachrymator should be used in a hood. Hexacyclooctadecane and pentafluorobenzylbromide are used to prepare pentafluorobenzyldilute with 50mL 2-propanol. 1mL of this reagent will deri ...
Boron and Metal Catalyzed CC and CH Bond Formation
... of these novel reactions have been developed. These include alternate routes to diphenylmethanes and 1,4-diynes from easily prepared dialkynylboron chlorides. In addition, E and Z alkenyl halides can now be prepared using boron trichloride without the use of butyllithium. The stereochemistry of the ...
... of these novel reactions have been developed. These include alternate routes to diphenylmethanes and 1,4-diynes from easily prepared dialkynylboron chlorides. In addition, E and Z alkenyl halides can now be prepared using boron trichloride without the use of butyllithium. The stereochemistry of the ...
Chapter 23 SG5e
... 1. The nitro group withdraws the lone pair electron from the amine, primarily via induction, making the N atom sp2 hybridized and hence trigonal planar. 2. The nitro group withdraws the lone pair electrons from the amine, primarily via resonance, making the N atom sp2 hybridized and hence trigonal p ...
... 1. The nitro group withdraws the lone pair electron from the amine, primarily via induction, making the N atom sp2 hybridized and hence trigonal planar. 2. The nitro group withdraws the lone pair electrons from the amine, primarily via resonance, making the N atom sp2 hybridized and hence trigonal p ...
Polymerization Synthesis of Nylon 6,10 C11-5
... The amine is dissolved in water, and the diacid chloride in an organic solvent. The two solutions are placed in the same beaker. Of course, the two solutions are immiscible, so there will be two phases in the beaker. At the interface of the two phases, the diacid chloride and diamine can meet each o ...
... The amine is dissolved in water, and the diacid chloride in an organic solvent. The two solutions are placed in the same beaker. Of course, the two solutions are immiscible, so there will be two phases in the beaker. At the interface of the two phases, the diacid chloride and diamine can meet each o ...
Nickel Catalyzed Conversion of Cyclohexanol into Cyclohexylamine
... cyclohexylamine in water and two solvents with low boiling points: tetrahydrofuran and cyclohexane. Three catalysts, Raney Ni, Ni/Al2 O3 and Ni/C, were investigated and it is found that the base, hydrogen, the solvents and the support will affect the activity of the catalyst. In water, all the three ...
... cyclohexylamine in water and two solvents with low boiling points: tetrahydrofuran and cyclohexane. Three catalysts, Raney Ni, Ni/Al2 O3 and Ni/C, were investigated and it is found that the base, hydrogen, the solvents and the support will affect the activity of the catalyst. In water, all the three ...
Organic Chemistry
... Because of the relative stability of alkyl radical intermediates, selectivity in free radical halogenation favors tertiary over secondary over primary carbon radicals. Bromination, though, is more selective than chlorination, because the proton extraction step is more endothermic in bromination than ...
... Because of the relative stability of alkyl radical intermediates, selectivity in free radical halogenation favors tertiary over secondary over primary carbon radicals. Bromination, though, is more selective than chlorination, because the proton extraction step is more endothermic in bromination than ...
FREE Sample Here - We can offer most test bank and
... Answer: Two carbon p atomic orbitals overlap side-to-side and in phase to form the p bond that is present. Rotation about the carbon-carbon bond axis requires quite a bit of energy because the p bond is broken as the overlap between the two p orbitals is disrupted. Diff: 2 Section: 2.7 72) Explain w ...
... Answer: Two carbon p atomic orbitals overlap side-to-side and in phase to form the p bond that is present. Rotation about the carbon-carbon bond axis requires quite a bit of energy because the p bond is broken as the overlap between the two p orbitals is disrupted. Diff: 2 Section: 2.7 72) Explain w ...
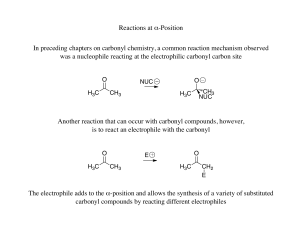
Reactions at α-Position In preceding chapters on carbonyl chemistry
... Once formed, each enolate could react with either carbonyl that is present to yield 4 different products (assuming the compounds don’t dehydrate to yield potentially more products) ...
... Once formed, each enolate could react with either carbonyl that is present to yield 4 different products (assuming the compounds don’t dehydrate to yield potentially more products) ...
06. Alcohols. Phenols. Ethers
... are called monohydric alcohols. These are further classified as primary (1'), secondary (2'), and tertiary (3') according as the ОН group is attached to primary, secondary and tertiary carbon atoms respectively. For example: ...
... are called monohydric alcohols. These are further classified as primary (1'), secondary (2'), and tertiary (3') according as the ОН group is attached to primary, secondary and tertiary carbon atoms respectively. For example: ...
23.2 Alcohols, Ethers, and Amines
... Halogenation Reactions The addition of bromine to carbon-carbon multiple bonds is often used as a chemical test for unsaturation in an organic molecule. • Bromine has an orange color, but most bromine-substituted organic compounds are colorless. After mixing, if the solution remains colorless, the c ...
... Halogenation Reactions The addition of bromine to carbon-carbon multiple bonds is often used as a chemical test for unsaturation in an organic molecule. • Bromine has an orange color, but most bromine-substituted organic compounds are colorless. After mixing, if the solution remains colorless, the c ...
Sample pages 6 PDF
... acids. On the other hand, Cella’s procedure involves the use of a peracid as secondary oxidant, which is a strong oxidant that interferes with many functional groups. In 1987, Anelli et al. published 3 a landmark paper in which they showed that primary alcohols can be oxidized either to aldehydes or ...
... acids. On the other hand, Cella’s procedure involves the use of a peracid as secondary oxidant, which is a strong oxidant that interferes with many functional groups. In 1987, Anelli et al. published 3 a landmark paper in which they showed that primary alcohols can be oxidized either to aldehydes or ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.