FREE Sample Here
... Answer: Two carbon p atomic orbitals overlap side-to-side and in phase to form the p bond that is present. Rotation about the carbon-carbon bond axis requires quite a bit of energy because the p bond is broken as the overlap between the two p orbitals is disrupted. Diff: 2 Section: 2.7 72) Explain w ...
... Answer: Two carbon p atomic orbitals overlap side-to-side and in phase to form the p bond that is present. Rotation about the carbon-carbon bond axis requires quite a bit of energy because the p bond is broken as the overlap between the two p orbitals is disrupted. Diff: 2 Section: 2.7 72) Explain w ...
MS PowerPoint - Catalysis Eprints database
... C20 to C30+ Oil field Chemicals, Wax replacements ...
... C20 to C30+ Oil field Chemicals, Wax replacements ...
Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers
... (H2SO4) at 180°C removes the OH group and a H from an adjacent carbon to produce an alkene, with water as a by-product. Since water is “removed” from the alcohol, this reaction is known as a dehydration reaction (or an elimination reaction): ...
... (H2SO4) at 180°C removes the OH group and a H from an adjacent carbon to produce an alkene, with water as a by-product. Since water is “removed” from the alcohol, this reaction is known as a dehydration reaction (or an elimination reaction): ...
stoker-C15
... (1) The compound 4-oxopentanal contains both an aldehyde and an ether functional group. (2) An alkoxy group and a hydroxy group attached to the same carbon atom are present in both hemiacetals and acetals. (3) Cyclic aldehyde structures are possible but cyclic ketone structures are not possible. A) ...
... (1) The compound 4-oxopentanal contains both an aldehyde and an ether functional group. (2) An alkoxy group and a hydroxy group attached to the same carbon atom are present in both hemiacetals and acetals. (3) Cyclic aldehyde structures are possible but cyclic ketone structures are not possible. A) ...
Converting Glycerol to Higher Value Products
... www.BiodieselEducation.org [email protected] 208-885-7626 ...
... www.BiodieselEducation.org [email protected] 208-885-7626 ...
kinetic and thermodynamic studies of the oxidation of perfumery
... *E-mail: [email protected] ABSTRACT Oxidation is one of the most important industrial reactions as it yields useful products. Literature survey indicates the use of a variety of organic oxidants for the oxidation of alcohols to the corresponding carbonyl compounds but inorganic oxidants have rare ...
... *E-mail: [email protected] ABSTRACT Oxidation is one of the most important industrial reactions as it yields useful products. Literature survey indicates the use of a variety of organic oxidants for the oxidation of alcohols to the corresponding carbonyl compounds but inorganic oxidants have rare ...
13: Carbonyl Compounds: Ketones, Aldehydes, Carboxylic Acids
... The chain length remains the same during oxidation of aldehydes because the C=O group is at the very end of the chain. However, since most other chemical reactions of aldehydes and ketones are similar, it is likely that if they had been discovered recently they would not have been separated into two ...
... The chain length remains the same during oxidation of aldehydes because the C=O group is at the very end of the chain. However, since most other chemical reactions of aldehydes and ketones are similar, it is likely that if they had been discovered recently they would not have been separated into two ...
13: Carbonyl Compounds: Ketones, Aldehydes, Carboxylic Acids
... We systematically name aldehydes as "alkanals" and we show some simple examples in Figure 13.9. Figure 13.9 The systematic nomenclature for aldehydes derives from the systematic nomenclature for 1° alcohols because oxidation of 1° alcohols gives aldehydes. The ending "ol" in the name of the precurso ...
... We systematically name aldehydes as "alkanals" and we show some simple examples in Figure 13.9. Figure 13.9 The systematic nomenclature for aldehydes derives from the systematic nomenclature for 1° alcohols because oxidation of 1° alcohols gives aldehydes. The ending "ol" in the name of the precurso ...
Protection (and Deprotection) of Functional Groups in Organic
... Fine chemicals are complex and multifunctional molecules, often characterized by low volatility and limited thermal stability, whose manufacture generally is based on multistep synthesis performed in the liquid phase and frequently involving protectiondeprotection steps. The use of blocking function ...
... Fine chemicals are complex and multifunctional molecules, often characterized by low volatility and limited thermal stability, whose manufacture generally is based on multistep synthesis performed in the liquid phase and frequently involving protectiondeprotection steps. The use of blocking function ...
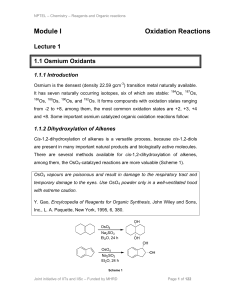
Module I Oxidation Reactions
... 2.1.3 Mn(IV) Reagents as an Oxidant MnO2 is a useful selective oxidizing reagent in organic synthesis. It is commercially available, and it can also be prepared by the reaction of MnSO4∙4H2O with KMnO4 in aqueous NaOH. G. Cahiez, M. Alami, Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis, John Wiley a ...
... 2.1.3 Mn(IV) Reagents as an Oxidant MnO2 is a useful selective oxidizing reagent in organic synthesis. It is commercially available, and it can also be prepared by the reaction of MnSO4∙4H2O with KMnO4 in aqueous NaOH. G. Cahiez, M. Alami, Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis, John Wiley a ...
Rhenium- and molybdenum-catalyzed dehydration reactions
... ratio close to one and are highly functionalized with hydroxyl groups. Therefore a completely different type of chemistry is required to acquire building blocks from lignocellulosic biomass suitable for the chemical industry: while in the case of fossil feedstocks functionality must be added, functi ...
... ratio close to one and are highly functionalized with hydroxyl groups. Therefore a completely different type of chemistry is required to acquire building blocks from lignocellulosic biomass suitable for the chemical industry: while in the case of fossil feedstocks functionality must be added, functi ...
Penny Commons - Chemistry Education Association
... Study Design they are provided as pdfs with support materials etc for Lab technicians at pearsonplaces.com.au SW refer to the Heinemann Student Workbook 2 – the worksheets listed are useful homework and revision. Fully worked solutions are available at peardonplaces.com.au The Research and Pract ...
... Study Design they are provided as pdfs with support materials etc for Lab technicians at pearsonplaces.com.au SW refer to the Heinemann Student Workbook 2 – the worksheets listed are useful homework and revision. Fully worked solutions are available at peardonplaces.com.au The Research and Pract ...
120 Chapter 24: Phenols. Alcohols contain an OH group bonded to
... tosylates afford aryl ethers (Williamson ether synthesis) OH ...
... tosylates afford aryl ethers (Williamson ether synthesis) OH ...
Chapter 4 Alcohols and Alkyl Halides
... We cannot actually isolate the transition state to study its structure. It has a very short lifetime and is an unstable structure that is literally making the transition from starting material to product. It is very important to understanding the full mechanism to have some sense of the structure of ...
... We cannot actually isolate the transition state to study its structure. It has a very short lifetime and is an unstable structure that is literally making the transition from starting material to product. It is very important to understanding the full mechanism to have some sense of the structure of ...
aa-2005-38-71-negishi - University of Windsor
... propargyl, alkyl, or acyl. Use of other related carbon groups as R1 and/or R2 is not only conceivable, but also known in the literature. Even if only those nine types of organometals (R1M) and eight types of organic electrophiles (R2X) mentioned above are considered, their binary combinations lead t ...
... propargyl, alkyl, or acyl. Use of other related carbon groups as R1 and/or R2 is not only conceivable, but also known in the literature. Even if only those nine types of organometals (R1M) and eight types of organic electrophiles (R2X) mentioned above are considered, their binary combinations lead t ...
State the main methods used to prepare polymers?
... Which of the following is true about reaction of benzene with nitric acid in presence of sulphuric acid ? a- The product is benzene sulfonic acid b- The product is nitrobenzene c- The type of reaction is nucleophilic substitution d- The nucleophile is NO2+ ion ...
... Which of the following is true about reaction of benzene with nitric acid in presence of sulphuric acid ? a- The product is benzene sulfonic acid b- The product is nitrobenzene c- The type of reaction is nucleophilic substitution d- The nucleophile is NO2+ ion ...
Aldehydes and Ketones The Carbonyl Group
... Other Nomenclature Rules • In cyclic ketones, the carbonyl group is always numbered “1”; this does not need to be included in the name. The numbering continues clockwise or counterclockwise to give the lowest number for the next substituent. • Molecules with more than one ketone group are named by p ...
... Other Nomenclature Rules • In cyclic ketones, the carbonyl group is always numbered “1”; this does not need to be included in the name. The numbering continues clockwise or counterclockwise to give the lowest number for the next substituent. • Molecules with more than one ketone group are named by p ...
PHENOL - Gneet's
... The above reaction is laboratory method for preparation of phenol 2. Hydrolysis of diazonium salt ...
... The above reaction is laboratory method for preparation of phenol 2. Hydrolysis of diazonium salt ...
Alcohols phenols
... CH3 tert-Butyl alcohol (ii) From carbonyl compounds by reduction. Aldehydes and ketones can be reduced to primary and secondary alcohols respectively either by catalytic hydrogenation (H2, Ni) or by the use of chemical reducing agents like sodium and ethanol, lithium aluminium hydride (LiAlH4) in et ...
... CH3 tert-Butyl alcohol (ii) From carbonyl compounds by reduction. Aldehydes and ketones can be reduced to primary and secondary alcohols respectively either by catalytic hydrogenation (H2, Ni) or by the use of chemical reducing agents like sodium and ethanol, lithium aluminium hydride (LiAlH4) in et ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.