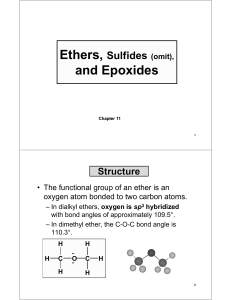
(omit), and Epoxides
... Name the OR group as an alkoxy substituent. • Common names: name the groups bonded to oxygen in alphabetical order followed by the word ether. OH ...
... Name the OR group as an alkoxy substituent. • Common names: name the groups bonded to oxygen in alphabetical order followed by the word ether. OH ...
CHAPTER 21 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... for cis-trans isomerism as outlined in Exercise 21.21. Only 4-methyl-1-pentyne does not exhibit cis-trans isomerism. Because of the triple bond in alkynes, the carbons with the restricted rotation only have one group bonded to them (not two groups, as is a necessity for geometric isomerism). See the ...
... for cis-trans isomerism as outlined in Exercise 21.21. Only 4-methyl-1-pentyne does not exhibit cis-trans isomerism. Because of the triple bond in alkynes, the carbons with the restricted rotation only have one group bonded to them (not two groups, as is a necessity for geometric isomerism). See the ...
Full file at http://testbanksolution.eu/Test-Bank-Bank-for
... Full file at http://testbanksolution.eu/Test-Bank-Bank-for-Organic-Chemistry-7-E-by-Anslyn d. C2sp3 + H1s ANS: D 61. Which atomic orbitals overlap to form the carbon-hydrogen bonding molecular orbitals of ethene, H2C=CH2? a. C2p + H1s b. C2sp + H1s c. C2sp2 + H1s d. C2sp3 + H1s ANS: C 62. Which a ...
... Full file at http://testbanksolution.eu/Test-Bank-Bank-for-Organic-Chemistry-7-E-by-Anslyn d. C2sp3 + H1s ANS: D 61. Which atomic orbitals overlap to form the carbon-hydrogen bonding molecular orbitals of ethene, H2C=CH2? a. C2p + H1s b. C2sp + H1s c. C2sp2 + H1s d. C2sp3 + H1s ANS: C 62. Which a ...
PowerPoint - Naming Hydrocarbons
... Branched Chain Alkanes Alkyl Groups -groups that are formed when one hydrogen atom is removed from an alkane - the suffix “-ane” is replaced by “-yl” ...
... Branched Chain Alkanes Alkyl Groups -groups that are formed when one hydrogen atom is removed from an alkane - the suffix “-ane” is replaced by “-yl” ...
Full Text
... functional groups is the hydroxyl group, which is present in a number of compounds of biological and synthetic interest, including nucleosides, carbohydrates, steroids, macrolides, polyethers, and the side chain of some amino acids or in large numbers of intermediates in total syntheses of complex n ...
... functional groups is the hydroxyl group, which is present in a number of compounds of biological and synthetic interest, including nucleosides, carbohydrates, steroids, macrolides, polyethers, and the side chain of some amino acids or in large numbers of intermediates in total syntheses of complex n ...
Reactions of Alcohols and Thiols
... Oxidation of Primary (1) Alcohols When a primary alcohol is oxidized, [O], • one H is removed from the –OH. • another H is removed from the carbon bonded to the OH. • an aldehyde is produced. [O] Primary alcohol ...
... Oxidation of Primary (1) Alcohols When a primary alcohol is oxidized, [O], • one H is removed from the –OH. • another H is removed from the carbon bonded to the OH. • an aldehyde is produced. [O] Primary alcohol ...
Chapter 12 Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers, Aldehydes, and Ketones
... Oxidation of Primary (1) Alcohols When a primary alcohol is oxidized, [O], • one H is removed from the –OH. • another H is removed from the carbon bonded to the OH. • an aldehyde is produced. [O] Primary alcohol ...
... Oxidation of Primary (1) Alcohols When a primary alcohol is oxidized, [O], • one H is removed from the –OH. • another H is removed from the carbon bonded to the OH. • an aldehyde is produced. [O] Primary alcohol ...
1 - TEST BANK 360
... Difficulty Level: Medium 70. Which of the following is not found in the following substance? CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2OH A) Ion-ion B) Dispersion forces C) Dipole-dipole D) Covalent bonding E) Hydrogen bonding Ans: A Topic: Intermolecular forces Section: 2.13 Difficulty Level: Medium 71. Which alkane is predi ...
... Difficulty Level: Medium 70. Which of the following is not found in the following substance? CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2OH A) Ion-ion B) Dispersion forces C) Dipole-dipole D) Covalent bonding E) Hydrogen bonding Ans: A Topic: Intermolecular forces Section: 2.13 Difficulty Level: Medium 71. Which alkane is predi ...
The story of V
... do not have left reactive groups in the matrix: no reactive end groups (-OH, -COOH), no unreacted carboncarbon double bonds (= unsaturated, (vinyl group = ethenyl group = unsaturated end-group)). Vinyl-Ester (VE) systems, like most resin systems, shrink during the curing (polymerisation). The volume ...
... do not have left reactive groups in the matrix: no reactive end groups (-OH, -COOH), no unreacted carboncarbon double bonds (= unsaturated, (vinyl group = ethenyl group = unsaturated end-group)). Vinyl-Ester (VE) systems, like most resin systems, shrink during the curing (polymerisation). The volume ...
AQA A-level Chemistry
... and products in a chemical reaction. The vertical (y) axis is enthalpy but not ∆H. The horizontal (x) axis is progress of reaction, reaction coordinate or extent of reaction. Two horizontal lines are drawn and labelled with the names or formulae of reactants and products. These represent the enthalp ...
... and products in a chemical reaction. The vertical (y) axis is enthalpy but not ∆H. The horizontal (x) axis is progress of reaction, reaction coordinate or extent of reaction. Two horizontal lines are drawn and labelled with the names or formulae of reactants and products. These represent the enthalp ...
ALDEHYDES AND KETONES I. NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION TO …
... •At the end of the reaction, because imines come apart easily (remember the “unfavorable” equilibrium?), the modified substrate can dissociate from the enzyme and return to the solution. •As we can see, often biological substrates possess carbonyl groups so that they can act as a “handle” in enzyme- ...
... •At the end of the reaction, because imines come apart easily (remember the “unfavorable” equilibrium?), the modified substrate can dissociate from the enzyme and return to the solution. •As we can see, often biological substrates possess carbonyl groups so that they can act as a “handle” in enzyme- ...
chapter2
... bent toward each other • there are four sets of eclipsed C-H interactions and one flagpole interaction • a boat conformation is less stable than a chair ...
... bent toward each other • there are four sets of eclipsed C-H interactions and one flagpole interaction • a boat conformation is less stable than a chair ...
Molecular geometry, polarity MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
... 29. The number of unique open-chain structures corresponding to the molecular formula C3H5Cl is: A) 2 B) 3 C) 4 D) 5 E) 6 Ans: C Topic: Functional groups Section: 2.6 Difficulty Level: Easy 30. Which compound listed below is a secondary alcohol? A) CH3CHCH2CH3 OH ...
... 29. The number of unique open-chain structures corresponding to the molecular formula C3H5Cl is: A) 2 B) 3 C) 4 D) 5 E) 6 Ans: C Topic: Functional groups Section: 2.6 Difficulty Level: Easy 30. Which compound listed below is a secondary alcohol? A) CH3CHCH2CH3 OH ...
14A
... – 1° alcohols are the most difficult to dehydrate – 2° alcohols undergo acid-catalyzed dehydration at somewhat lower temperatures – 3° alcohols generally undergo acid-catalyzed dehydration at temperatures only slightly above room temperature ...
... – 1° alcohols are the most difficult to dehydrate – 2° alcohols undergo acid-catalyzed dehydration at somewhat lower temperatures – 3° alcohols generally undergo acid-catalyzed dehydration at temperatures only slightly above room temperature ...
Document
... First, he was fascinated by the chemistry of organocerium reagents in addition to easily enolizable electrophiles. Then he discovered that cerium was not a chelating metal and he stated the rules for the stereoselective reduction of functionalised ketones in the presence of a Lewis acid promoter. Re ...
... First, he was fascinated by the chemistry of organocerium reagents in addition to easily enolizable electrophiles. Then he discovered that cerium was not a chelating metal and he stated the rules for the stereoselective reduction of functionalised ketones in the presence of a Lewis acid promoter. Re ...
Alkenes 4 - ChemWeb (UCC)
... Long before anything was known about the mechanism of this reaction it was recognised that 'Addition of HX to an alkene will proceed in such a way as to attach hydrogen to the least substituted carbon and X to the most substituted carbon'. This is known as Markovnikov's Rule after the Russian chemis ...
... Long before anything was known about the mechanism of this reaction it was recognised that 'Addition of HX to an alkene will proceed in such a way as to attach hydrogen to the least substituted carbon and X to the most substituted carbon'. This is known as Markovnikov's Rule after the Russian chemis ...
Anionic rearrangement of 2-benzyloxypyridine derivatives and a synthetic approach to aldingenin B
... TABLE OF CONTENTS List of Tables .......................................................................................................... vii List of Figures ........................................................................................................ viii Abstract .................... ...
... TABLE OF CONTENTS List of Tables .......................................................................................................... vii List of Figures ........................................................................................................ viii Abstract .................... ...
Full-Text PDF
... stationary points were characterized as minima or transition state by analytical frequency calculations. The electronic configuration of the molecular systems was described with the standard split-valence basis set with a polarization function of Ahlrichs and co-workers for H, C, O, P, and Cl (SVP k ...
... stationary points were characterized as minima or transition state by analytical frequency calculations. The electronic configuration of the molecular systems was described with the standard split-valence basis set with a polarization function of Ahlrichs and co-workers for H, C, O, P, and Cl (SVP k ...
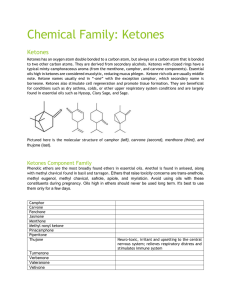
Chemical Family Ketones
... Ketones has an oxygen atom double bonded to a carbon atom, but always on a carbon atom that is bonded to two other carbon atoms. They are derived from secondary alcohols. Ketones with closed rings have a typical minty-camphoraceous aroma (from the menthone, camphor, and carvone components). Essentia ...
... Ketones has an oxygen atom double bonded to a carbon atom, but always on a carbon atom that is bonded to two other carbon atoms. They are derived from secondary alcohols. Ketones with closed rings have a typical minty-camphoraceous aroma (from the menthone, camphor, and carvone components). Essentia ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.