EXPLORING ORGANIC CHEMISTRY FOR TEACHERS (CHMY 591
... Organic chemistry is an organized study of the myriad ways that carbon compounds form and interact. These interactions are often familiar to us in everyday applications. Indeed, it is often said that life on this planet is carbon-based. The intent of our course is to familiarize you with how the att ...
... Organic chemistry is an organized study of the myriad ways that carbon compounds form and interact. These interactions are often familiar to us in everyday applications. Indeed, it is often said that life on this planet is carbon-based. The intent of our course is to familiarize you with how the att ...
ppt
... Alkyl ammonium ions, R3NH+ X-, have pKa values in the range of 10-11 (ammonium ion, H4N+ X-, has a pKa ~ 9.3) The ammonium ions of aryl amines and heterocyclic aromatic amines are considerably more acidic than alkyl amines (pKa < 5). The nitrogen lone pair is less basic if it is in an sp2 hybridized ...
... Alkyl ammonium ions, R3NH+ X-, have pKa values in the range of 10-11 (ammonium ion, H4N+ X-, has a pKa ~ 9.3) The ammonium ions of aryl amines and heterocyclic aromatic amines are considerably more acidic than alkyl amines (pKa < 5). The nitrogen lone pair is less basic if it is in an sp2 hybridized ...
File - need help with revision notes?
... Aldehydes the lowest. This is because carboxylic acids have hydrogen bonds, dipole-dipole interactions and Secondary alcohols have two carbons bonded to the C-OH Van der Waals’ forces. Alcohols have hydrogen bonding and Van der Butan-2-ol Waals’ and Aldehydes have only dipole-dipole and Van der Waal ...
... Aldehydes the lowest. This is because carboxylic acids have hydrogen bonds, dipole-dipole interactions and Secondary alcohols have two carbons bonded to the C-OH Van der Waals’ forces. Alcohols have hydrogen bonding and Van der Butan-2-ol Waals’ and Aldehydes have only dipole-dipole and Van der Waal ...
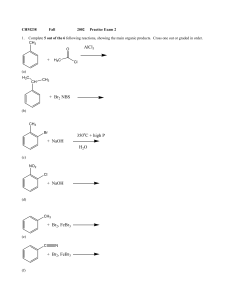
+ NaOH 350 C + high P H2O + H3C AlCl3 + NaOH + Br2, FeBr3
... Starting with toluene, design syntheses, providing the correct reagents for the following transformations. Both processes can be accomplished with 2 steps, but there is more than one correct answer for each. Assume that ortho and para isomers can be separated. OH O CH3 ...
... Starting with toluene, design syntheses, providing the correct reagents for the following transformations. Both processes can be accomplished with 2 steps, but there is more than one correct answer for each. Assume that ortho and para isomers can be separated. OH O CH3 ...
Ch04-04-alkenes-2
... the hydrogen adds to the carbon that has the greater number of hydrogen substituents, and the halogen adds to the carbon that has the fewer hydrogen substituents. ...
... the hydrogen adds to the carbon that has the greater number of hydrogen substituents, and the halogen adds to the carbon that has the fewer hydrogen substituents. ...
104 Chapter 22: Amines. Organic derivatives of ammonia, NH3
... Alkyl ammonium ions, R3NH+ X-, have pKa values in the range of 10-11 (ammonium ion, H4N+ X-, has a pKa ~ 9.3) The ammonium ions of aryl amines and heterocyclic aromatic amines are considerably more acidic than alkyl amines (pKa < 5). The nitrogen lone pair is less basic if it is in an sp2 hybridized ...
... Alkyl ammonium ions, R3NH+ X-, have pKa values in the range of 10-11 (ammonium ion, H4N+ X-, has a pKa ~ 9.3) The ammonium ions of aryl amines and heterocyclic aromatic amines are considerably more acidic than alkyl amines (pKa < 5). The nitrogen lone pair is less basic if it is in an sp2 hybridized ...
CHM230 OXIDATION OF CYCLOHEXANOL TO CYCLOHEXANONE
... graduated cylinder. The distillate should be a mixture of cyclohexanone and water that contains excess acetic acid. Transfer the distillate to a separatory funnel or beaker. 6. Add 3.5 grams of sodium carbonate to neutralize any excess acetic acid, and then add a small amount, about 3 grams of sodiu ...
... graduated cylinder. The distillate should be a mixture of cyclohexanone and water that contains excess acetic acid. Transfer the distillate to a separatory funnel or beaker. 6. Add 3.5 grams of sodium carbonate to neutralize any excess acetic acid, and then add a small amount, about 3 grams of sodiu ...
CHEM 202_ Part 2
... Aldehydes and ketones can be used to synthesis of many organic compounds. In all these reactions, carbonyl group can be retained (halogenation), or extended to more carbon skeleton (Grignard and Witting reaction), or converted to another functional group (reduction) ...
... Aldehydes and ketones can be used to synthesis of many organic compounds. In all these reactions, carbonyl group can be retained (halogenation), or extended to more carbon skeleton (Grignard and Witting reaction), or converted to another functional group (reduction) ...
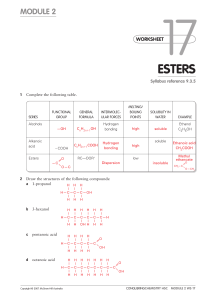
Module 02.indd
... A student was given three containers labelled A, B and C. The student was told they were pentanoic acid, hexane and 1-pentanol but not necessarily in that order. The student tested the boiling point and found the following: Boiling point ...
... A student was given three containers labelled A, B and C. The student was told they were pentanoic acid, hexane and 1-pentanol but not necessarily in that order. The student tested the boiling point and found the following: Boiling point ...
Alkane
... For RX compound, when X = Cl or F ,the b.p. will be higher than alkane which have the same molecular mass due to the dipole-dipole interaction between the molecules. Solubility As the interaction between water and RX are quite different, (H-bond and dipole-dipole),they are only sightly soluble in wa ...
... For RX compound, when X = Cl or F ,the b.p. will be higher than alkane which have the same molecular mass due to the dipole-dipole interaction between the molecules. Solubility As the interaction between water and RX are quite different, (H-bond and dipole-dipole),they are only sightly soluble in wa ...
Suggest a reason for the large difference in the boiling points of
... is 8.0K kg/mol.Calculate the molar mass of the unknown solute. 4 Calculate the boiling point of a solution containing 0.61g of benzoic acid in 5 g of CS2 .Assuming 84% dimerisation of acid. The boiling point and Kb of CS2 are 46.2 0C and 2.3 K Kg mol-1 respectively. 5 A metal crystallizes into fcc w ...
... is 8.0K kg/mol.Calculate the molar mass of the unknown solute. 4 Calculate the boiling point of a solution containing 0.61g of benzoic acid in 5 g of CS2 .Assuming 84% dimerisation of acid. The boiling point and Kb of CS2 are 46.2 0C and 2.3 K Kg mol-1 respectively. 5 A metal crystallizes into fcc w ...
Year 1 Foundation course, section B2
... Year 1 Foundation course, section B2; Structure and reactivity of specific functional groups Alkanes - the most basic of all organic compounds, composed of only C and H, with no functional groups. General formulae CnH2n+2 (unless cyclic in which case it is CnH2n). Alkanes are generally quite unreac ...
... Year 1 Foundation course, section B2; Structure and reactivity of specific functional groups Alkanes - the most basic of all organic compounds, composed of only C and H, with no functional groups. General formulae CnH2n+2 (unless cyclic in which case it is CnH2n). Alkanes are generally quite unreac ...
Electophilic Aromatic Substituion - Towson University
... Controlled by electronegativity and the polarity of bonds in functional groups, i.e. halogens, C=O, CN, and NO2 withdraw electrons through s bond connected to ring. Alkyl group inductive effect is to donate electrons. ...
... Controlled by electronegativity and the polarity of bonds in functional groups, i.e. halogens, C=O, CN, and NO2 withdraw electrons through s bond connected to ring. Alkyl group inductive effect is to donate electrons. ...
Principles of Organic and Biochemistry
... Amides contain carbon double bonded to oxygen plus an NH group ...
... Amides contain carbon double bonded to oxygen plus an NH group ...
chemistry ch4 - The Student Room
... Give the shortened structural formula of the compound produced when Compound G reacts with hydrogen gas in the presence of a nickel catalyst. ...
... Give the shortened structural formula of the compound produced when Compound G reacts with hydrogen gas in the presence of a nickel catalyst. ...
N - Dr. May Notes
... Alkenes Alkenes have one or more double bond between two or more of the carbons. The carbons are sharing two pairs of electrons. Alkenes are unsaturated meaning that they can hold more hydrogens or that all the carbons do not have as much hydrogen around it as it could have. If hydrogen gas (plus a ...
... Alkenes Alkenes have one or more double bond between two or more of the carbons. The carbons are sharing two pairs of electrons. Alkenes are unsaturated meaning that they can hold more hydrogens or that all the carbons do not have as much hydrogen around it as it could have. If hydrogen gas (plus a ...
Esters are reduced by hydride reagents to give alcohols or aldehydes.
... Lipids are biomolecules soluble in non-polar solvents. Non-polar solvent extracts a wide range of non-polar substances from biological materials: terpenes, steroids, fats, oils and other lipids, such as phospholipids. Phospholipids are important components of cell membranes. Lecithin is a phosphogl ...
... Lipids are biomolecules soluble in non-polar solvents. Non-polar solvent extracts a wide range of non-polar substances from biological materials: terpenes, steroids, fats, oils and other lipids, such as phospholipids. Phospholipids are important components of cell membranes. Lecithin is a phosphogl ...
Slide 1 In this lesson, we will give you a general
... The shape of a tetrahedron is given here. The compound on this PowerPoint is methane. ...
... The shape of a tetrahedron is given here. The compound on this PowerPoint is methane. ...
Organic Chemistry Assignments Topic 1: Review
... Organic Chemistry Assignments Chapter 2: Week 4 (9/12 -16) Work Due by: Thursday, September 15 Learning Goal: To be able to write the mechanisms for the reactions of alkenes and be able to predict the products of alkene reactions. Topic ...
... Organic Chemistry Assignments Chapter 2: Week 4 (9/12 -16) Work Due by: Thursday, September 15 Learning Goal: To be able to write the mechanisms for the reactions of alkenes and be able to predict the products of alkene reactions. Topic ...
mc_ch22 - WordPress.com
... amount of hydrogen are referred to as unsaturated. • Unsaturated hydrocarbons are hydrocarbons in which not all carbon atoms have four single covalent bonds. • An unsaturated hydrocarbon has one or more double bonds or triple bonds between carbon atoms. • Carbon atoms can easily form multiple bonds ...
... amount of hydrogen are referred to as unsaturated. • Unsaturated hydrocarbons are hydrocarbons in which not all carbon atoms have four single covalent bonds. • An unsaturated hydrocarbon has one or more double bonds or triple bonds between carbon atoms. • Carbon atoms can easily form multiple bonds ...
Electrophilic Additions: Alkenes Addition of Hydrogen Halides
... the hydrogen adds to the carbon that has the greater number of hydrogen substituents, substituents, and the halogen adds to the carbon that has the fewer hydrogen substituents. substituents. ...
... the hydrogen adds to the carbon that has the greater number of hydrogen substituents, substituents, and the halogen adds to the carbon that has the fewer hydrogen substituents. substituents. ...
Esters
... perfumes. • Also, very good at dissolving organic compounds so often used as solvents. ...
... perfumes. • Also, very good at dissolving organic compounds so often used as solvents. ...
Chemistry 0310 - Organic Chemistry 1 Chapter 12. Reactions of
... Chapter 12. Reactions of Alkenes ...
... Chapter 12. Reactions of Alkenes ...
Haloalkane

The haloalkanes (also known, as halogenoalkanes or alkyl halides) are a group of chemical compounds derived from alkanes containing one or more halogens. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely used commercially and, consequently, are known under many chemical and commercial names. They are used as flame retardants, fire extinguishants, refrigerants, propellants, solvents, and pharmaceuticals. Subsequent to the widespread use in commerce, many halocarbons have also been shown to be serious pollutants and toxins. For example, the chlorofluorocarbons have been shown to lead to ozone depletion. Methyl bromide is a controversial fumigant. Only haloalkanes which contain chlorine, bromine, and iodine are a threat to the ozone layer, but fluorinated volatile haloalkanes in theory may have activity as greenhouse gases. Methyl iodide, a naturally occurring substance, however, does not have ozone-depleting properties and the United States Environmental Protection Agency has designated the compound a non-ozone layer depleter. For more information, see Halomethane. Haloalkane or alkyl halides are the compounds which have the general formula ″RX″ where R is an alkyl or substituted alkyl group and X is a halogen (F, Cl, Br, I).Haloalkanes have been known for centuries. Chloroethane was produced synthetically in the 15th century. The systematic synthesis of such compounds developed in the 19th century in step with the development of organic chemistry and the understanding of the structure of alkanes. Methods were developed for the selective formation of C-halogen bonds. Especially versatile methods included the addition of halogens to alkenes, hydrohalogenation of alkenes, and the conversion of alcohols to alkyl halides. These methods are so reliable and so easily implemented that haloalkanes became cheaply available for use in industrial chemistry because the halide could be further replaced by other functional groups.While most haloalkanes are human-produced, non-artificial-source haloalkanes do occur on Earth, mostly through enzyme-mediated synthesis by bacteria, fungi, and especially sea macroalgae (seaweeds). More than 1600 halogenated organics have been identified, with bromoalkanes being the most common haloalkanes. Brominated organics in biology range from biologically produced methyl bromide to non-alkane aromatics and unsaturates (indoles, terpenes, acetogenins, and phenols). Halogenated alkanes in land plants are more rare, but do occur, as for example the fluoroacetate produced as a toxin by at least 40 species of known plants. Specific dehalogenase enzymes in bacteria which remove halogens from haloalkanes, are also known.