CHEM 203 Material
... Example: the C atom in CH4 has formally acquired 4 electrons, thereby assuming the oxidation state of –4. This produces a significant concentration of electronic density around the C atom. One may predict that the C atom in methane will behave as an electron donor in its reactions; that is, it will ...
... Example: the C atom in CH4 has formally acquired 4 electrons, thereby assuming the oxidation state of –4. This produces a significant concentration of electronic density around the C atom. One may predict that the C atom in methane will behave as an electron donor in its reactions; that is, it will ...
Chapter 1--Title
... Leaving group ability is inversely related to basicity Chloride is the weakest base and the best leaving group Amines are the strongest bases and the worst leaving groups ...
... Leaving group ability is inversely related to basicity Chloride is the weakest base and the best leaving group Amines are the strongest bases and the worst leaving groups ...
Chemistry Notes for class 12 Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and
... Relative reactivities of aldehydes and ketones in nucleophilic addition reactions is due the positive charge on carbonyl carbon. Greater positive charge means greater reactivity. Electron releasing power of two alkyl groups in ketones is more than one in aldehyde. Therefore positive charge is reduce ...
... Relative reactivities of aldehydes and ketones in nucleophilic addition reactions is due the positive charge on carbonyl carbon. Greater positive charge means greater reactivity. Electron releasing power of two alkyl groups in ketones is more than one in aldehyde. Therefore positive charge is reduce ...
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
... • Acyl chloride is used in place of alkyl chloride. • The acylium ion intermediate is resonance stabilized and does not rearrange like a carbocation. • The product is a phenyl ketone that is less reactive than benzene. ...
... • Acyl chloride is used in place of alkyl chloride. • The acylium ion intermediate is resonance stabilized and does not rearrange like a carbocation. • The product is a phenyl ketone that is less reactive than benzene. ...
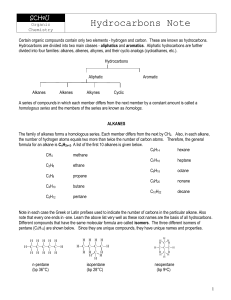
Hydrocarbons Note
... The characteristics of organic compounds (boiling point, odour, reactivity etc.) depend on the composition and arrangement of atoms. For example the properties of alkanes depend greatly on the number of carbon atoms in the hydrocarbon chain due to the increased strength of the van der Waal attractio ...
... The characteristics of organic compounds (boiling point, odour, reactivity etc.) depend on the composition and arrangement of atoms. For example the properties of alkanes depend greatly on the number of carbon atoms in the hydrocarbon chain due to the increased strength of the van der Waal attractio ...
organic sample test
... 19. The pulp and paper industry is a major employer in many small towns in Northern Ontario and other provinces. Some of the by-products of the pulp process include short chain carboxylic acids such as propanoic and butanoic acid. These are produced in quantities large enough that the strong odour p ...
... 19. The pulp and paper industry is a major employer in many small towns in Northern Ontario and other provinces. Some of the by-products of the pulp process include short chain carboxylic acids such as propanoic and butanoic acid. These are produced in quantities large enough that the strong odour p ...
communication - Kyushu University Library
... substrates, the former condition gave slightly better ers in every cases (Table 2, entries 2-7), therefore the 10 mol% condition was used for other substrates. Among them, the er of 95:5 was observed with 3 substrates. As an application of this reaction, we conducted a formal total synthesis of (R)- ...
... substrates, the former condition gave slightly better ers in every cases (Table 2, entries 2-7), therefore the 10 mol% condition was used for other substrates. Among them, the er of 95:5 was observed with 3 substrates. As an application of this reaction, we conducted a formal total synthesis of (R)- ...
Aldehydes can react with alcohols to form hemiacetals
... the formation of a cyclic acetal, two molecules go in (ketone plus diol) and two molecules come out (acetal plus water), so the usually unfavourable ∆S° factor is no longer against us. And, as for hemiacetals (see the explanation above), equilibrium tends to lie to the acetal side because the intram ...
... the formation of a cyclic acetal, two molecules go in (ketone plus diol) and two molecules come out (acetal plus water), so the usually unfavourable ∆S° factor is no longer against us. And, as for hemiacetals (see the explanation above), equilibrium tends to lie to the acetal side because the intram ...
Handout V
... The mechanism of chromic acid oxidation probably involves the formation of a chromate ester. In the elimination, the carbinol carbon retains its oxygen atom but loses its hydrogen and makes the second bond to oxygen (Scheme 6). One can follow the progress of a chromic acid oxidation by observing the ...
... The mechanism of chromic acid oxidation probably involves the formation of a chromate ester. In the elimination, the carbinol carbon retains its oxygen atom but loses its hydrogen and makes the second bond to oxygen (Scheme 6). One can follow the progress of a chromic acid oxidation by observing the ...
Identification of Aldehydes and Ketones
... * The b.p.s of aldehydes & ketones are lower than those of the alcohols from which they are derived i.e.: isopropyl alcohol boils at 82.5˚C while its oxidation product acetone, boils at 56˚C ; ethanol boils at 78˚C while its oxidation product, acetaldehyde, boils at 21˚C. ...
... * The b.p.s of aldehydes & ketones are lower than those of the alcohols from which they are derived i.e.: isopropyl alcohol boils at 82.5˚C while its oxidation product acetone, boils at 56˚C ; ethanol boils at 78˚C while its oxidation product, acetaldehyde, boils at 21˚C. ...
alcohols03
... such as methyl lithium (:CH3- Li+) and Grignard reagents (RMgX) such as methyl magnesium bromide (:CH3- +MgBr). Metal alkoxides themselves are strong bases that are frequently used in organic chemistry. Phenols are ca. 106 times more acidic than alcohols. They are soluble in dilute aq. NaOH soln. Th ...
... such as methyl lithium (:CH3- Li+) and Grignard reagents (RMgX) such as methyl magnesium bromide (:CH3- +MgBr). Metal alkoxides themselves are strong bases that are frequently used in organic chemistry. Phenols are ca. 106 times more acidic than alcohols. They are soluble in dilute aq. NaOH soln. Th ...
benzene - 固体表面物理化学国家重点实验室
... 13.2 Naming Alcohols • Alkyl alcohols can be named as alkanols, a name derived by dropping the e from alkane and adding ol. • For instance, the name of the alcohol derived from the simplest alkane comes from changing the methane to methanol (CH3OH). • Ethanol is a two-carbon alcohol: CH3CH2OH. • To ...
... 13.2 Naming Alcohols • Alkyl alcohols can be named as alkanols, a name derived by dropping the e from alkane and adding ol. • For instance, the name of the alcohol derived from the simplest alkane comes from changing the methane to methanol (CH3OH). • Ethanol is a two-carbon alcohol: CH3CH2OH. • To ...
Alkene complexes - Dewar/Chatt/Duncanson model
... Conveniently classed together because bonding to TM is very similar in all cases - involves synergic bonding also called backbonding Evidence for back-bonding (E/Salzer pp 226-231) bond lengths increases the strength, hence reduces the length of M-C bond but decreases the strength, hence increases ...
... Conveniently classed together because bonding to TM is very similar in all cases - involves synergic bonding also called backbonding Evidence for back-bonding (E/Salzer pp 226-231) bond lengths increases the strength, hence reduces the length of M-C bond but decreases the strength, hence increases ...
Reduction Reactions
... Reactions are normally carried out in ethereal solvents (e.g. THF, Et2O); LiAlH4 reacts ...
... Reactions are normally carried out in ethereal solvents (e.g. THF, Et2O); LiAlH4 reacts ...
Organic Chemistry Lecture Outline Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids
... a. The parent name is derived from the corresponding alkane based on the number of carbon atoms in the chain including the carbon atom of the carboxylic acid. b. The "e" ending of the alkane is replaced with "oic acid". c. The carbon atom of the acid is the #1 carbon atom when numbering the chain. 2 ...
... a. The parent name is derived from the corresponding alkane based on the number of carbon atoms in the chain including the carbon atom of the carboxylic acid. b. The "e" ending of the alkane is replaced with "oic acid". c. The carbon atom of the acid is the #1 carbon atom when numbering the chain. 2 ...
Chapter 22: Phenols. Alcohols contain an OH group bonded to an
... Chapter 22: Phenols. Alcohols contain an OH group bonded to an sp3-hybridized carbon. Phenols contain an OH group bonded to an sp2-hybridized carbon of a benzene ring 22.1: Nomenclature (please read) 22.2: Structure and Bonding (please read) 22.3: Physical Properties (please read). Like other alcoho ...
... Chapter 22: Phenols. Alcohols contain an OH group bonded to an sp3-hybridized carbon. Phenols contain an OH group bonded to an sp2-hybridized carbon of a benzene ring 22.1: Nomenclature (please read) 22.2: Structure and Bonding (please read) 22.3: Physical Properties (please read). Like other alcoho ...
1012_4th Exam_1020619 - NTOU-Chem
... 27) Define "conformation". A) Conformations are different structural representations of the same molecule. B) Conformations are different arrangements of bonds in space C) Conformations are two enantiomers. D) Conformations are all possible structural isomers for a given molecular formula E) Conform ...
... 27) Define "conformation". A) Conformations are different structural representations of the same molecule. B) Conformations are different arrangements of bonds in space C) Conformations are two enantiomers. D) Conformations are all possible structural isomers for a given molecular formula E) Conform ...
Aromatic Compounds
... Even though benzene is highly unsaturated it does not undergo any of the regular reactions of alkenes such as addition or oxidation ...
... Even though benzene is highly unsaturated it does not undergo any of the regular reactions of alkenes such as addition or oxidation ...
Recent advances in homogeneous nickel catalysis
... (Fig. 1) is needed. Nickel is a relatively electropositive late transition metal. Therefore, oxidative addition5, which results in loss of electron density around nickel, tends to occur quite readily (though, conversely, reductive elimination is correspondingly more difficult)6. This facile oxidativ ...
... (Fig. 1) is needed. Nickel is a relatively electropositive late transition metal. Therefore, oxidative addition5, which results in loss of electron density around nickel, tends to occur quite readily (though, conversely, reductive elimination is correspondingly more difficult)6. This facile oxidativ ...
Solid-Phase Organic Synthesis: Creation of Carbon
... aldehydes and ketones. Subsequently, treatments with a variety of phosphorane ylides or phosphonate anions provided alkenes. Stabilized phosphoranes quantitatively transformed aliphatic and aromatic aldehydes (no starting materials remaining) and gave E-olefins in good yields, purities, and stereose ...
... aldehydes and ketones. Subsequently, treatments with a variety of phosphorane ylides or phosphonate anions provided alkenes. Stabilized phosphoranes quantitatively transformed aliphatic and aromatic aldehydes (no starting materials remaining) and gave E-olefins in good yields, purities, and stereose ...
topic 6 – hydrocarbons (general level)
... oil. Gas oil can be cracked to give more gasoline. (a) State two ways in which the molecules produced by cracking can be different from the molecules in the gas oil. 2 marks (KU) (b) Chart A shows the fractions supplied by distilling crude oil. Chart B shows the demand for these fractions. ...
... oil. Gas oil can be cracked to give more gasoline. (a) State two ways in which the molecules produced by cracking can be different from the molecules in the gas oil. 2 marks (KU) (b) Chart A shows the fractions supplied by distilling crude oil. Chart B shows the demand for these fractions. ...
this PDF file
... corresponding carbonyl compound was accomplished by the procedure reported in earlier papers. [9, 10]. The above procedure may be carried out on 1-100 g scales without any problem. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION TMAFC was used for the oxidation of some alcohols and polycyclic arenes under microwave irradiat ...
... corresponding carbonyl compound was accomplished by the procedure reported in earlier papers. [9, 10]. The above procedure may be carried out on 1-100 g scales without any problem. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION TMAFC was used for the oxidation of some alcohols and polycyclic arenes under microwave irradiat ...
Haloalkane

The haloalkanes (also known, as halogenoalkanes or alkyl halides) are a group of chemical compounds derived from alkanes containing one or more halogens. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely used commercially and, consequently, are known under many chemical and commercial names. They are used as flame retardants, fire extinguishants, refrigerants, propellants, solvents, and pharmaceuticals. Subsequent to the widespread use in commerce, many halocarbons have also been shown to be serious pollutants and toxins. For example, the chlorofluorocarbons have been shown to lead to ozone depletion. Methyl bromide is a controversial fumigant. Only haloalkanes which contain chlorine, bromine, and iodine are a threat to the ozone layer, but fluorinated volatile haloalkanes in theory may have activity as greenhouse gases. Methyl iodide, a naturally occurring substance, however, does not have ozone-depleting properties and the United States Environmental Protection Agency has designated the compound a non-ozone layer depleter. For more information, see Halomethane. Haloalkane or alkyl halides are the compounds which have the general formula ″RX″ where R is an alkyl or substituted alkyl group and X is a halogen (F, Cl, Br, I).Haloalkanes have been known for centuries. Chloroethane was produced synthetically in the 15th century. The systematic synthesis of such compounds developed in the 19th century in step with the development of organic chemistry and the understanding of the structure of alkanes. Methods were developed for the selective formation of C-halogen bonds. Especially versatile methods included the addition of halogens to alkenes, hydrohalogenation of alkenes, and the conversion of alcohols to alkyl halides. These methods are so reliable and so easily implemented that haloalkanes became cheaply available for use in industrial chemistry because the halide could be further replaced by other functional groups.While most haloalkanes are human-produced, non-artificial-source haloalkanes do occur on Earth, mostly through enzyme-mediated synthesis by bacteria, fungi, and especially sea macroalgae (seaweeds). More than 1600 halogenated organics have been identified, with bromoalkanes being the most common haloalkanes. Brominated organics in biology range from biologically produced methyl bromide to non-alkane aromatics and unsaturates (indoles, terpenes, acetogenins, and phenols). Halogenated alkanes in land plants are more rare, but do occur, as for example the fluoroacetate produced as a toxin by at least 40 species of known plants. Specific dehalogenase enzymes in bacteria which remove halogens from haloalkanes, are also known.