슬라이드 1
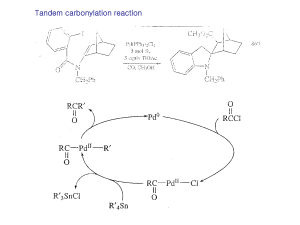
... These reactions are believed to involve Ni(I) and Ni(III) intermediates in a chain process which is initiated by formation of a small amount of a Ni(I) sepcies. ...
... These reactions are believed to involve Ni(I) and Ni(III) intermediates in a chain process which is initiated by formation of a small amount of a Ni(I) sepcies. ...
Properties of Hydrocarbons
... Insoluble in water Less dense than water and so will float on top of the water Dissolve in organic solvents (eg dry cleaning fluid) and in each other (eg Petrol is a mixture of alkanes) ...
... Insoluble in water Less dense than water and so will float on top of the water Dissolve in organic solvents (eg dry cleaning fluid) and in each other (eg Petrol is a mixture of alkanes) ...
Level 3: Organics Part I
... are soluble in water as they are ionised, but they have a carbon chain end that is soluble in fats and oils. This allows them to dissolve and break down dirt. Sodium laurate is the name of the soap molecule made from coconut oil made by boiling it with sodium hydroxide. ...
... are soluble in water as they are ionised, but they have a carbon chain end that is soluble in fats and oils. This allows them to dissolve and break down dirt. Sodium laurate is the name of the soap molecule made from coconut oil made by boiling it with sodium hydroxide. ...
Organic Reactions Note – Student.DOC
... Oxidation of a secondary (2°) alcohol produces a ketone ...
... Oxidation of a secondary (2°) alcohol produces a ketone ...
Organic Chemistry
... Nomenclature for Alkenes 1. Root hydrocarbon name ends in -ene C2H4 is ethene 2. With more than 3 carbons, double bond is indicated by the lowest numbered carbon atom in the bond. C=CCC is 1-butene ...
... Nomenclature for Alkenes 1. Root hydrocarbon name ends in -ene C2H4 is ethene 2. With more than 3 carbons, double bond is indicated by the lowest numbered carbon atom in the bond. C=CCC is 1-butene ...
Organo halides
... What Is an Alkylhlaide An organic compound containing at least one carbon-halogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain many C-X bonds Properties and some uses Fire-resistant solvents Refrigerants Pharmaceuticals and precursors ...
... What Is an Alkylhlaide An organic compound containing at least one carbon-halogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain many C-X bonds Properties and some uses Fire-resistant solvents Refrigerants Pharmaceuticals and precursors ...
Text questions - Corwin - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... 38. List three physical properties that organic halides have in common with alkanes. ...
... 38. List three physical properties that organic halides have in common with alkanes. ...
CHAPTER-6 DEHYDROHALOGENATION OF ALKYL HALIDES
... Dehydration of Alcohols to form Ethers • Simple, symmetrical ethers can be formed from the intermolecular acid‐catalyzed dehydration of 1° (or methyl) alcohols (a “substitution reaction”) • 2° and 3° alcohols can’t be used because they eliminate (intramolecular dehydration) to form alkenes ...
... Dehydration of Alcohols to form Ethers • Simple, symmetrical ethers can be formed from the intermolecular acid‐catalyzed dehydration of 1° (or methyl) alcohols (a “substitution reaction”) • 2° and 3° alcohols can’t be used because they eliminate (intramolecular dehydration) to form alkenes ...
Organic Reactions
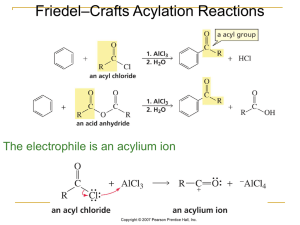
... • Reactions occur between electrophiles and nucleophiles. • Just about any part of a molecule can be either electrophilic or nucleophilic depending one what you are comparing it to ...
... • Reactions occur between electrophiles and nucleophiles. • Just about any part of a molecule can be either electrophilic or nucleophilic depending one what you are comparing it to ...
halogen compounds organic chemistry
... The contribution of structures III, IV and V imparts a partial double bond character to the carbon-chlorine bond. The shortening of bond length imparts stability to aryl halides and as a result, the bond cleavage becomes rather difficult. The aryl halides are, therefore, less reactive than alkyl hal ...
... The contribution of structures III, IV and V imparts a partial double bond character to the carbon-chlorine bond. The shortening of bond length imparts stability to aryl halides and as a result, the bond cleavage becomes rather difficult. The aryl halides are, therefore, less reactive than alkyl hal ...
10. Alkyl Halides
... carbon or hydrogen that is connected to a carbon atom in a structure is replaced by oxygen, nitrogen, or halogen Not defined as loss of electrons by an atom as in inorganic chemistry Oxidation is a reaction that results in loss of electron density at carbon (as more electronegative atoms replace ...
... carbon or hydrogen that is connected to a carbon atom in a structure is replaced by oxygen, nitrogen, or halogen Not defined as loss of electrons by an atom as in inorganic chemistry Oxidation is a reaction that results in loss of electron density at carbon (as more electronegative atoms replace ...
(Q.3) Carbon completes its octet by
... (Q.6) The hydrocarbons having the general formula of CnH2n-2 , CnH2n+2 and CnH2n+1 are known as (Q.7) The next higher homologue of pentane and propylene is (Q.8) The IUPAC name of formaldehyde and acetaldehyde is ________and ________ (Q.9) What is meant by homologous series? State any four character ...
... (Q.6) The hydrocarbons having the general formula of CnH2n-2 , CnH2n+2 and CnH2n+1 are known as (Q.7) The next higher homologue of pentane and propylene is (Q.8) The IUPAC name of formaldehyde and acetaldehyde is ________and ________ (Q.9) What is meant by homologous series? State any four character ...
Organic Chemistry –Syllabus- one Semester Sackler faculty of
... Organic Compounds + Alkanes double bond equivalent, alkyl group, Nomenclature (IUPAC rules), intermolecular forces( van der Waals force, Dipole–dipole interaction, Hydrogen bonds), Solubility, Conformations of alkanes(staggered-eclipsd) , Cycloalkanes, geometric isomers, The chair conformation of cy ...
... Organic Compounds + Alkanes double bond equivalent, alkyl group, Nomenclature (IUPAC rules), intermolecular forces( van der Waals force, Dipole–dipole interaction, Hydrogen bonds), Solubility, Conformations of alkanes(staggered-eclipsd) , Cycloalkanes, geometric isomers, The chair conformation of cy ...
Combustion, Addition and Elimination Objective Combustion Example
... is weaker than the single bond, this bond can break and then we have free bonding electrons where another element or functional group can be added. In general: ...
... is weaker than the single bond, this bond can break and then we have free bonding electrons where another element or functional group can be added. In general: ...
Introduction to Organic Chemistry/Practical
... because it is hydrolysed to produce ethane-1,2 diol which is then used in the production of antifreeze and polyesters. ...
... because it is hydrolysed to produce ethane-1,2 diol which is then used in the production of antifreeze and polyesters. ...
Document
... CI 13.1 Halogenoalkanes Are man-made compounds with one or more halogen atoms (F, Cl, Br, I) attached to a carbon atom. The attached halogen changes the chemical properties of alkane chains…they are very unreactive, and so have been very useful to humans. Naming halogenoalkanes (haloalkanes) (simila ...
... CI 13.1 Halogenoalkanes Are man-made compounds with one or more halogen atoms (F, Cl, Br, I) attached to a carbon atom. The attached halogen changes the chemical properties of alkane chains…they are very unreactive, and so have been very useful to humans. Naming halogenoalkanes (haloalkanes) (simila ...
Review for Exam #1
... Naming Haloalkanes In a haloalkane, • halogen atoms replace hydrogen atoms. • substituents are numbered and arranged alphabetically. • alkanes with halogens can be named as alkyl halides; the carbon group is named as an alkyl group followed by the halide name. CH3—CH2—Cl CH3—Br IUPAC Name chloroeth ...
... Naming Haloalkanes In a haloalkane, • halogen atoms replace hydrogen atoms. • substituents are numbered and arranged alphabetically. • alkanes with halogens can be named as alkyl halides; the carbon group is named as an alkyl group followed by the halide name. CH3—CH2—Cl CH3—Br IUPAC Name chloroeth ...
Give reasons for the following.(one mark each)
... 1. Reaction of alcohol with thionyl chloride is the best preferred method for the preparation of alkyl halides. 2. Free radical chlorination or bromination of alkanes is not preferred for the preparation of alkyl halides. 3. Aryl fluorides are not prepared by the electrophilic substitution of arenes ...
... 1. Reaction of alcohol with thionyl chloride is the best preferred method for the preparation of alkyl halides. 2. Free radical chlorination or bromination of alkanes is not preferred for the preparation of alkyl halides. 3. Aryl fluorides are not prepared by the electrophilic substitution of arenes ...
Organic Reactions 1
... Condensation is an organic reaction when two molecules combine, usually in the presence of a catalyst, with the elimination of water or some other simple molecule. Catalysts commonly used in condensation reactions include acids and bases. The combination of two identical molecules is known as self-c ...
... Condensation is an organic reaction when two molecules combine, usually in the presence of a catalyst, with the elimination of water or some other simple molecule. Catalysts commonly used in condensation reactions include acids and bases. The combination of two identical molecules is known as self-c ...
$doc.title
... http://www.chem.wisc.edu/areas/clc (Resource page) Reactions of Alcohols #8: Reaction of a 1° Alcohol with Hydrogen Halides ...
... http://www.chem.wisc.edu/areas/clc (Resource page) Reactions of Alcohols #8: Reaction of a 1° Alcohol with Hydrogen Halides ...
Haloalkane

The haloalkanes (also known, as halogenoalkanes or alkyl halides) are a group of chemical compounds derived from alkanes containing one or more halogens. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely used commercially and, consequently, are known under many chemical and commercial names. They are used as flame retardants, fire extinguishants, refrigerants, propellants, solvents, and pharmaceuticals. Subsequent to the widespread use in commerce, many halocarbons have also been shown to be serious pollutants and toxins. For example, the chlorofluorocarbons have been shown to lead to ozone depletion. Methyl bromide is a controversial fumigant. Only haloalkanes which contain chlorine, bromine, and iodine are a threat to the ozone layer, but fluorinated volatile haloalkanes in theory may have activity as greenhouse gases. Methyl iodide, a naturally occurring substance, however, does not have ozone-depleting properties and the United States Environmental Protection Agency has designated the compound a non-ozone layer depleter. For more information, see Halomethane. Haloalkane or alkyl halides are the compounds which have the general formula ″RX″ where R is an alkyl or substituted alkyl group and X is a halogen (F, Cl, Br, I).Haloalkanes have been known for centuries. Chloroethane was produced synthetically in the 15th century. The systematic synthesis of such compounds developed in the 19th century in step with the development of organic chemistry and the understanding of the structure of alkanes. Methods were developed for the selective formation of C-halogen bonds. Especially versatile methods included the addition of halogens to alkenes, hydrohalogenation of alkenes, and the conversion of alcohols to alkyl halides. These methods are so reliable and so easily implemented that haloalkanes became cheaply available for use in industrial chemistry because the halide could be further replaced by other functional groups.While most haloalkanes are human-produced, non-artificial-source haloalkanes do occur on Earth, mostly through enzyme-mediated synthesis by bacteria, fungi, and especially sea macroalgae (seaweeds). More than 1600 halogenated organics have been identified, with bromoalkanes being the most common haloalkanes. Brominated organics in biology range from biologically produced methyl bromide to non-alkane aromatics and unsaturates (indoles, terpenes, acetogenins, and phenols). Halogenated alkanes in land plants are more rare, but do occur, as for example the fluoroacetate produced as a toxin by at least 40 species of known plants. Specific dehalogenase enzymes in bacteria which remove halogens from haloalkanes, are also known.