Chemistry_
... Synthetic means artificial (man-made), TeflonTM is an example of another synthetic substance 3. Can you list three properties of KevlarTM that make it so useful? Properties include fire resistance, high tensile strength, lightweight(ness) and flexibility ...
... Synthetic means artificial (man-made), TeflonTM is an example of another synthetic substance 3. Can you list three properties of KevlarTM that make it so useful? Properties include fire resistance, high tensile strength, lightweight(ness) and flexibility ...
The collision theory of reactions
... It is important for chemists to know which reaction (6 or 7) is happening fastest, to understand whether oxygen atoms or chlorine atoms are responsible for the removal of ozone. In fact, Cl atoms react 1500 faster with ozone, compared to O atoms. Even though Cl atoms have a much lower concentration ...
... It is important for chemists to know which reaction (6 or 7) is happening fastest, to understand whether oxygen atoms or chlorine atoms are responsible for the removal of ozone. In fact, Cl atoms react 1500 faster with ozone, compared to O atoms. Even though Cl atoms have a much lower concentration ...
C. Branched Chains and Substitute Groups
... -Carbon has 4 valence electrons and likes to share electrons with other atoms (including itself) to make four stable covalent bonds. -Most common partners are hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. -Hydrocarbons are a group which have only carbon and hydrogen. These are what we use as fuel because of the h ...
... -Carbon has 4 valence electrons and likes to share electrons with other atoms (including itself) to make four stable covalent bonds. -Most common partners are hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. -Hydrocarbons are a group which have only carbon and hydrogen. These are what we use as fuel because of the h ...
Chem 400 Review Chem 350 JJ.S17
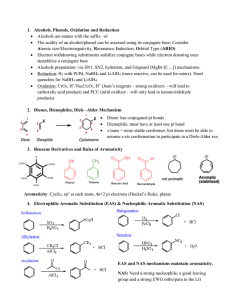
... Atomic size/Electronegativity, Resonance, Induction, Orbital Type (ARIO) Electron withdrawing substituents stabilize conjugate bases while electron donating ones destabilize a conjugate base Alcohols preparation: via SN1, SN2, hydration, and Grignard (MgBr-[C…]) mechanisms Reduction: H2 with P ...
... Atomic size/Electronegativity, Resonance, Induction, Orbital Type (ARIO) Electron withdrawing substituents stabilize conjugate bases while electron donating ones destabilize a conjugate base Alcohols preparation: via SN1, SN2, hydration, and Grignard (MgBr-[C…]) mechanisms Reduction: H2 with P ...
Organic Chemistry
... – The carbon chain must be numbered from the end that will give the lowest numbers for the branches Example: 2, 2, 3 – trimethyl pentane ...
... – The carbon chain must be numbered from the end that will give the lowest numbers for the branches Example: 2, 2, 3 – trimethyl pentane ...
Organic Chemistry
... This designates the parent chain and the root word of the molecule. • 2. Number the parent chain such that the branch (substituent) falls on the lowest carbon number. • 3. Count the number of carbons in the branched chain. Use the same set of root words EXCEPT add the suffix –yl. ...
... This designates the parent chain and the root word of the molecule. • 2. Number the parent chain such that the branch (substituent) falls on the lowest carbon number. • 3. Count the number of carbons in the branched chain. Use the same set of root words EXCEPT add the suffix –yl. ...
Chapter 12- Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds, Redox Reactions
... • They are normally used in the same they are prepared in • The ether solvent is very important in that it forms a diether complex with the grignard reagent that provides its solubility and stabilizes the reagent. ...
... • They are normally used in the same they are prepared in • The ether solvent is very important in that it forms a diether complex with the grignard reagent that provides its solubility and stabilizes the reagent. ...
CHEM1102 Worksheet 7: Reactions of Carbonyls and Acid
... Grignard reagents (RMgBr) are excellent nucleophiles, and are a very good way to form new carbon-carbon bonds. ...
... Grignard reagents (RMgBr) are excellent nucleophiles, and are a very good way to form new carbon-carbon bonds. ...
Organic Reactions
... 1. To what class of organic compounds does reactant 1 belong? 2. To what class of organic compounds does reactant 2 belong? 3. To what class of organic compounds does the product (not water) belong? ...
... 1. To what class of organic compounds does reactant 1 belong? 2. To what class of organic compounds does reactant 2 belong? 3. To what class of organic compounds does the product (not water) belong? ...
Chapter 8 Lecture
... Inversion of Stereochemistry with SN2 The nucleophile attacks carbon from the side opposite the bond to the leaving group. The SN2 reaction at a chirality center proceeds with inversion of configuration at the carbon bearing the leaving group. ...
... Inversion of Stereochemistry with SN2 The nucleophile attacks carbon from the side opposite the bond to the leaving group. The SN2 reaction at a chirality center proceeds with inversion of configuration at the carbon bearing the leaving group. ...
IGCSE Chemistry Definitions – LEARN THESE! Melting
... Base - A substance with a pH higher than 7, they react with acids to form a salt and water (called neutralization). Metal hydroxides, oxides and carbonates are all bases. Acid - They have a pH less than 7 and neutralize bases or alkalis to form salt and water. Acidity is caused by a high concentrati ...
... Base - A substance with a pH higher than 7, they react with acids to form a salt and water (called neutralization). Metal hydroxides, oxides and carbonates are all bases. Acid - They have a pH less than 7 and neutralize bases or alkalis to form salt and water. Acidity is caused by a high concentrati ...
Organic-IB-Short-Exam Questions-Answers
... Describe how chiral auxiliaries can be used to synthesize only the desired enantiomeric form of a drug from a non-chiral starting compound. Explain why it is important to use only the desired enantiomeric form of a drug and state an example of what can happen if a racemic mixture is used. ...
... Describe how chiral auxiliaries can be used to synthesize only the desired enantiomeric form of a drug from a non-chiral starting compound. Explain why it is important to use only the desired enantiomeric form of a drug and state an example of what can happen if a racemic mixture is used. ...
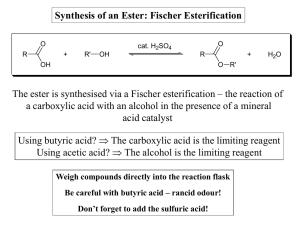
Synthesis of an Ester: Fischer Esterification The ester is synthesised
... - It speeds up the reaction rate, allowing equilibrium to be reached more quickly - It acts as a dehydrating agent, helping to shift the equilibrium towards products (alcohols are weak nucleophiles – protonation of the carbonyl group enhances the reactivity of the acid, meaning it is more readily at ...
... - It speeds up the reaction rate, allowing equilibrium to be reached more quickly - It acts as a dehydrating agent, helping to shift the equilibrium towards products (alcohols are weak nucleophiles – protonation of the carbonyl group enhances the reactivity of the acid, meaning it is more readily at ...
C h e m g u id e –... ESTERS: PREPARATION
... d) The ester phenyl benzoate can be made from a reaction starting from benzoyl chloride, C6H5COCl. However, in this case, the phenol is first converted into sodium phenoxide, C6H5O- Na+. (i) Why is it necessary to use sodium phenoxide rather than phenol itself? (ii) How do you convert phenol into so ...
... d) The ester phenyl benzoate can be made from a reaction starting from benzoyl chloride, C6H5COCl. However, in this case, the phenol is first converted into sodium phenoxide, C6H5O- Na+. (i) Why is it necessary to use sodium phenoxide rather than phenol itself? (ii) How do you convert phenol into so ...
Chemistry 201 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State University
... Amino acids have the ability to link together and form proteins. Amino acids have carboxylic acid groups Amino acids have a base and an acid in the same molecule There are about 20 amino acids each of which has a different sidechain that yield ...
... Amino acids have the ability to link together and form proteins. Amino acids have carboxylic acid groups Amino acids have a base and an acid in the same molecule There are about 20 amino acids each of which has a different sidechain that yield ...
Organic Tutorial 1st Year HT01
... 4. Carbonyl condensations: enolisation followed by attack at C=O; aldol condensation and its reverse, a,b-unsaturated carbonyls, ester condensation both acyclic and cyclic (Claisen and Dieckmann). Crossed condensations, such as Aldol and Claisen type. 5. α,β-Unsaturated carbonyl compounds. Michael-t ...
... 4. Carbonyl condensations: enolisation followed by attack at C=O; aldol condensation and its reverse, a,b-unsaturated carbonyls, ester condensation both acyclic and cyclic (Claisen and Dieckmann). Crossed condensations, such as Aldol and Claisen type. 5. α,β-Unsaturated carbonyl compounds. Michael-t ...
to get Period 1 8
... Scientists classify organic compounds into different categories. The simplest organic compounds are the hydrocarbons. A hydrocarbon is a compound that contains only the atoms of hydrogen and carbon. Methane is the main gas in metro gas. Its used to heat homes. Propane is used in portable stoves And ...
... Scientists classify organic compounds into different categories. The simplest organic compounds are the hydrocarbons. A hydrocarbon is a compound that contains only the atoms of hydrogen and carbon. Methane is the main gas in metro gas. Its used to heat homes. Propane is used in portable stoves And ...
Stereoselective Reduction of Ketones with Sodium Borohydride
... Many examples in chemistry In Organic Chemistry: – 2 main “classes” of organometallic compounds Organomagnesium reagents (“Grignards”) Organolithium reagents ...
... Many examples in chemistry In Organic Chemistry: – 2 main “classes” of organometallic compounds Organomagnesium reagents (“Grignards”) Organolithium reagents ...
Chemistry 210 - MiraCosta College
... constitutional isomers and instructed to rank them in order of increasing boiling points and explain the ranking trend. ...
... constitutional isomers and instructed to rank them in order of increasing boiling points and explain the ranking trend. ...
Production of materials
... Ethylene (ethene) Although ethylene is a widely used raw material very little of it is found in either natural gas or crude oil. Instead it has to be produced from other hydrocarbons by a process called cracking. Cracking: process in which large hydrocarbons are broken down into smaller ones with t ...
... Ethylene (ethene) Although ethylene is a widely used raw material very little of it is found in either natural gas or crude oil. Instead it has to be produced from other hydrocarbons by a process called cracking. Cracking: process in which large hydrocarbons are broken down into smaller ones with t ...
Nomenclature - Clydebank High School
... Benzene is the simplest aromatic compound – C6 H6 Each carbon has 3 ½ filled electron clouds which bond with the nearest atom – delocalised electrons. When we replace one of the H atoms with another group we have a phenyl group C6 H5 Examples C6H5 – CH3 = methyl benzene (Toluene) C6H5 – OH = Phenol ...
... Benzene is the simplest aromatic compound – C6 H6 Each carbon has 3 ½ filled electron clouds which bond with the nearest atom – delocalised electrons. When we replace one of the H atoms with another group we have a phenyl group C6 H5 Examples C6H5 – CH3 = methyl benzene (Toluene) C6H5 – OH = Phenol ...
Organic Chem WS - mvhs
... position of the hydroxyl the lowest possible number on longest continuous chain. CH3-CH2-OH ethanol Carboxylic Acids: COOH group, carboxyl group. weak acids, ionize slightly in solution. -COOH <--> COO- + H+ to name: drop -e ending of parent alkane name and add oic acid CH3COOH ethanoic acid.(acetic ...
... position of the hydroxyl the lowest possible number on longest continuous chain. CH3-CH2-OH ethanol Carboxylic Acids: COOH group, carboxyl group. weak acids, ionize slightly in solution. -COOH <--> COO- + H+ to name: drop -e ending of parent alkane name and add oic acid CH3COOH ethanoic acid.(acetic ...
Lecture5
... Watson’s exchange reaction between a coordinated methyl group and free methane, via σ bond metathesis, discovered by 13C isotope labeling of the methane carbon. ...
... Watson’s exchange reaction between a coordinated methyl group and free methane, via σ bond metathesis, discovered by 13C isotope labeling of the methane carbon. ...
naming using more functional groups
... but I’m not going to test you on it. http://www.chem.ucalgary.ca/cou rses/351/orgnom/ethers/ethers01.html ...
... but I’m not going to test you on it. http://www.chem.ucalgary.ca/cou rses/351/orgnom/ethers/ethers01.html ...
Haloalkane

The haloalkanes (also known, as halogenoalkanes or alkyl halides) are a group of chemical compounds derived from alkanes containing one or more halogens. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely used commercially and, consequently, are known under many chemical and commercial names. They are used as flame retardants, fire extinguishants, refrigerants, propellants, solvents, and pharmaceuticals. Subsequent to the widespread use in commerce, many halocarbons have also been shown to be serious pollutants and toxins. For example, the chlorofluorocarbons have been shown to lead to ozone depletion. Methyl bromide is a controversial fumigant. Only haloalkanes which contain chlorine, bromine, and iodine are a threat to the ozone layer, but fluorinated volatile haloalkanes in theory may have activity as greenhouse gases. Methyl iodide, a naturally occurring substance, however, does not have ozone-depleting properties and the United States Environmental Protection Agency has designated the compound a non-ozone layer depleter. For more information, see Halomethane. Haloalkane or alkyl halides are the compounds which have the general formula ″RX″ where R is an alkyl or substituted alkyl group and X is a halogen (F, Cl, Br, I).Haloalkanes have been known for centuries. Chloroethane was produced synthetically in the 15th century. The systematic synthesis of such compounds developed in the 19th century in step with the development of organic chemistry and the understanding of the structure of alkanes. Methods were developed for the selective formation of C-halogen bonds. Especially versatile methods included the addition of halogens to alkenes, hydrohalogenation of alkenes, and the conversion of alcohols to alkyl halides. These methods are so reliable and so easily implemented that haloalkanes became cheaply available for use in industrial chemistry because the halide could be further replaced by other functional groups.While most haloalkanes are human-produced, non-artificial-source haloalkanes do occur on Earth, mostly through enzyme-mediated synthesis by bacteria, fungi, and especially sea macroalgae (seaweeds). More than 1600 halogenated organics have been identified, with bromoalkanes being the most common haloalkanes. Brominated organics in biology range from biologically produced methyl bromide to non-alkane aromatics and unsaturates (indoles, terpenes, acetogenins, and phenols). Halogenated alkanes in land plants are more rare, but do occur, as for example the fluoroacetate produced as a toxin by at least 40 species of known plants. Specific dehalogenase enzymes in bacteria which remove halogens from haloalkanes, are also known.