Old Sample Exam #2
... a) oxygen b) iron c) hydrogen d) uranium e) helium _____ 5) Planetary nebulae are often shaped like a(n) a) hourglass b) Frisbee c) basketball d) coke can e) ice cream cone _____ 6) How long will Prox Centauri (M5 dwarf) spend on the main sequence? (years) a) 1000 b) 106 c) 109 d) 1012 e) 1015 _____ ...
... a) oxygen b) iron c) hydrogen d) uranium e) helium _____ 5) Planetary nebulae are often shaped like a(n) a) hourglass b) Frisbee c) basketball d) coke can e) ice cream cone _____ 6) How long will Prox Centauri (M5 dwarf) spend on the main sequence? (years) a) 1000 b) 106 c) 109 d) 1012 e) 1015 _____ ...
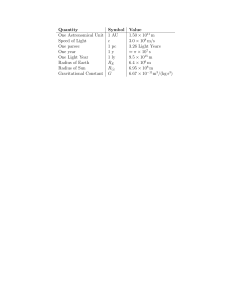
Quantity Symbol Value One Astronomical Unit 1 AU 1.50 × 10
... 3. A common unit of distance in Astronomy is a parsec. 1 pc ' 3.1 × 1016 m ' 3.3 ly (a) Explain how such a curious unit of measure came to be defined. Why is it called parsec? (b) What is the distance to the nearest stars and how was this distance measured? 4. Describe qualitatively what is the prec ...
... 3. A common unit of distance in Astronomy is a parsec. 1 pc ' 3.1 × 1016 m ' 3.3 ly (a) Explain how such a curious unit of measure came to be defined. Why is it called parsec? (b) What is the distance to the nearest stars and how was this distance measured? 4. Describe qualitatively what is the prec ...
Fact Sheet - NASA Spitzer Space Telescope
... Telescope will capture those celestial objects and phenomena that are too dim, distant or cool to study by other astronomical techniques. The Infrared 'Great Observatory' NASA's Great Observatories give astronomers an orbiting "toolbox" that provides multi-wavelength studies of the universe. The Hub ...
... Telescope will capture those celestial objects and phenomena that are too dim, distant or cool to study by other astronomical techniques. The Infrared 'Great Observatory' NASA's Great Observatories give astronomers an orbiting "toolbox" that provides multi-wavelength studies of the universe. The Hub ...
Chapter 5: Telescopes - University of Texas Astronomy Home Page
... There are a few reasons. The first is: Light-gathering power: Obviously bigger telescopes can collect more light, because the amount gathered just depends on the area of the telescope (diameter squared). This property determines the ability to see faint objects. Faint objects might not be nearby, bu ...
... There are a few reasons. The first is: Light-gathering power: Obviously bigger telescopes can collect more light, because the amount gathered just depends on the area of the telescope (diameter squared). This property determines the ability to see faint objects. Faint objects might not be nearby, bu ...
Solar System, Galaxy, and Universe (ES) V.4
... stars, star clusters, nebulas, and galaxies, observations of other potential planetary systems, accounts of possible travel to other star systems. ...
... stars, star clusters, nebulas, and galaxies, observations of other potential planetary systems, accounts of possible travel to other star systems. ...
Exploring Our Solar System
... would represent the mass of the sun. The other two grains of sand would represent the mass of the combination of all the planets, planetoids, moons, asteroids, meteors and comets. ...
... would represent the mass of the sun. The other two grains of sand would represent the mass of the combination of all the planets, planetoids, moons, asteroids, meteors and comets. ...
The Evolution of Massive Stars
... Neutron Stars: a brief history • Basic physics understood in the 1930s • At that time, no known counterparts • In the 1950s and 1960s, more and more strange objects found, but where were the neutrons stars, or did they even exist? • The case of the Crab Nebula (supernova of 1054 AD) ...
... Neutron Stars: a brief history • Basic physics understood in the 1930s • At that time, no known counterparts • In the 1950s and 1960s, more and more strange objects found, but where were the neutrons stars, or did they even exist? • The case of the Crab Nebula (supernova of 1054 AD) ...
IYA2009 Theme .(English)
... telescope for astronomy Illustrate the cultural influence astronomy over time and connect science and culture Show that astronomy is one of most captivating branches of natural science and excellently suited to show the fascinating aspects of science, especially to young people Remind humanity ...
... telescope for astronomy Illustrate the cultural influence astronomy over time and connect science and culture Show that astronomy is one of most captivating branches of natural science and excellently suited to show the fascinating aspects of science, especially to young people Remind humanity ...
Pressemitteilung - Micro
... technology - just as Galileo did 400 years ago, when he was the first to turn a telescope towards the sky. The telescope may help to answer some major scientific challenges of our time. Do other Earth-like planets exist that we could live and survive on? What are the characteristics of the first sta ...
... technology - just as Galileo did 400 years ago, when he was the first to turn a telescope towards the sky. The telescope may help to answer some major scientific challenges of our time. Do other Earth-like planets exist that we could live and survive on? What are the characteristics of the first sta ...
View Presentation Slides
... Our Place in the Galaxy • The Sun is the only star in the SOLAR SYSTEM, but it is one of over 100 billion stars in the GALAXY we call the Milky Way. • Our Solar System is located about 2/3 of the way out from the galaxy’s center. • Astronomers think that most of the stars in the Milky Way galaxy co ...
... Our Place in the Galaxy • The Sun is the only star in the SOLAR SYSTEM, but it is one of over 100 billion stars in the GALAXY we call the Milky Way. • Our Solar System is located about 2/3 of the way out from the galaxy’s center. • Astronomers think that most of the stars in the Milky Way galaxy co ...
DOC
... 1. I can describe the differences between the relative sizes of various bodies in space (planetary systems, stars, star clusters, galaxies). 2. I can recall that the universe is made up of interacting bodies (planets, stars, etc.) that behave in a predictable way. 3. I can recall that our sola ...
... 1. I can describe the differences between the relative sizes of various bodies in space (planetary systems, stars, star clusters, galaxies). 2. I can recall that the universe is made up of interacting bodies (planets, stars, etc.) that behave in a predictable way. 3. I can recall that our sola ...
Solar System Unit Review - Parma City School District
... What is a chunk of rock or iron that is less than 1,000 km in diameter that orbits the sun? ...
... What is a chunk of rock or iron that is less than 1,000 km in diameter that orbits the sun? ...
L The James Webb Space Telescope
... both be used to probe the Universe at the time of its own ‘first light’ — the birth of the first stars and galaxies. The radio array will map the large-scale structure of the Universe, elucidating the role in that structure of ‘dark matter’ and ‘dark energy’, as will studies of the faintest galaxies ...
... both be used to probe the Universe at the time of its own ‘first light’ — the birth of the first stars and galaxies. The radio array will map the large-scale structure of the Universe, elucidating the role in that structure of ‘dark matter’ and ‘dark energy’, as will studies of the faintest galaxies ...
Microsoft Word Document
... 9. When massive stars go supernova, they can leave behind a neutron star. These stars are so dense that a teaspoon of their material would weigh ______ million tons! ...
... 9. When massive stars go supernova, they can leave behind a neutron star. These stars are so dense that a teaspoon of their material would weigh ______ million tons! ...
pptx
... The first telescopes were refractors, but they have limitations: • A larger lens collects more light and allows one to see fainter objects. However, it is difficult to physically support a big lens because it must be held at the edges. • Lenses focus different wavelengths of light at different locat ...
... The first telescopes were refractors, but they have limitations: • A larger lens collects more light and allows one to see fainter objects. However, it is difficult to physically support a big lens because it must be held at the edges. • Lenses focus different wavelengths of light at different locat ...
Our SOlar System
... 1) If the Earth actually spun on an axis -- as required in a heliocentric system to explain the diurnal motion (day/night)of the sky-- why didn't objects fly off the spinning Earth? ...
... 1) If the Earth actually spun on an axis -- as required in a heliocentric system to explain the diurnal motion (day/night)of the sky-- why didn't objects fly off the spinning Earth? ...
Jeopardy Review
... Describe two ways that light is separated out into its component colors for spectroscopy ...
... Describe two ways that light is separated out into its component colors for spectroscopy ...
International Ultraviolet Explorer

The International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) was an astronomical observatory satellite primarily designed to take ultraviolet spectra. The satellite was a collaborative project between NASA, the UK Science Research Council and the European Space Agency (ESA). The mission was first proposed in early 1964, by a group of scientists in the United Kingdom, and was launched on January 26, 1978 aboard a NASA Delta rocket. The mission lifetime was initially set for 3 years, but in the end it lasted almost 18 years, with the satellite being shut down in 1996. The switch-off occurred for financial reasons, while the telescope was still functioning at near original efficiency.It was the first space observatory to be operated in real time by astronomers who visited the groundstations in the United States and Europe. Astronomers made over 104,000 observations using the IUE, of objects ranging from solar system bodies to distant quasars. Among the significant scientific results from IUE data were the first large scale studies of stellar winds, accurate measurements of the way interstellar dust absorbs light, and measurements of the supernova SN1987A which showed that it defied stellar evolution theories as they then stood. When the mission ended, it was considered the most successful astronomical satellite ever.