Fundamental properties of the Sun - University of Iowa Astronomy
... • A wind past the Earth at 400 km/sec • The Sun is “melting away” • Density 19 orders of magnitude less than atmosphere • A medium for solar events • May have “sandblasted” the early atmosphere of Mars ...
... • A wind past the Earth at 400 km/sec • The Sun is “melting away” • Density 19 orders of magnitude less than atmosphere • A medium for solar events • May have “sandblasted” the early atmosphere of Mars ...
Document
... • Light rays are refracted many times (by small amounts) • When they reach telescope they are no longer parallel • Hence rays can’t be focused to a point: ...
... • Light rays are refracted many times (by small amounts) • When they reach telescope they are no longer parallel • Hence rays can’t be focused to a point: ...
A105 Stars and Galaxies
... 84 ft. dish antenna at Harvard Univ. connected to supercomputers that look for nonrandom patterns in the signals (most of the signals come from natural sources such as stars) 250 megabytes of data each second ...
... 84 ft. dish antenna at Harvard Univ. connected to supercomputers that look for nonrandom patterns in the signals (most of the signals come from natural sources such as stars) 250 megabytes of data each second ...
Mode of Travel
... 1. Would it be practical to travel to Sirius by any of the modes of travel listed on the Activity chart? Why or why not? 2. "Star Trek" is a TV show in which a starship goes to other star systems in our Galaxy. Can you think of any practical problems with this idea? 3. Do you think that it is possib ...
... 1. Would it be practical to travel to Sirius by any of the modes of travel listed on the Activity chart? Why or why not? 2. "Star Trek" is a TV show in which a starship goes to other star systems in our Galaxy. Can you think of any practical problems with this idea? 3. Do you think that it is possib ...
astro20 telescopes - Las Positas College
... – if telescope #1 is ten times the diameter of telescope #2, telescope #1 will collect the same number of photons 100 times faster than telescope #2 – telescope observations are given in terms of the ...
... – if telescope #1 is ten times the diameter of telescope #2, telescope #1 will collect the same number of photons 100 times faster than telescope #2 – telescope observations are given in terms of the ...
Science CRCT Jeopardy 1
... A. The stars in a constellation revolve around the Earth together. B. The stars in a constellation rotate very slowly on their axes. C. Earth’s gravity attracts the stars and holds them in place. D. Stars appear not to move because they are so far away from the Earth. ...
... A. The stars in a constellation revolve around the Earth together. B. The stars in a constellation rotate very slowly on their axes. C. Earth’s gravity attracts the stars and holds them in place. D. Stars appear not to move because they are so far away from the Earth. ...
VLBI: connecting national radio telescopes into a global array
... eEVN: a real-time connected radio telescope as large as Europe plans to use the “Grid infrastructure” for - transporting raw data-streams from the telescopes to the central data processor at JIVE (via GÉANT) - real-time control of the distributed observing process - distributing processed data to s ...
... eEVN: a real-time connected radio telescope as large as Europe plans to use the “Grid infrastructure” for - transporting raw data-streams from the telescopes to the central data processor at JIVE (via GÉANT) - real-time control of the distributed observing process - distributing processed data to s ...
A Faint Star Orbiting the Big Dipper’s Alcor Discovered
... technique is powerful and much faster than the usual way of confirming that objects in the sky are physically related.” The more typical method involves observing the pair of objects over much longer periods of time, even years, to show that the two are moving through space together. Alcor and its n ...
... technique is powerful and much faster than the usual way of confirming that objects in the sky are physically related.” The more typical method involves observing the pair of objects over much longer periods of time, even years, to show that the two are moving through space together. Alcor and its n ...
radio telescope
... • To study X-rays, NASA uses the Chandra X-Ray Observatory. This space telescope was launched in 1999. • Another space telescope, the Compton GammaRay Observatory, was used to study both visible light and gamma rays. • In 2011, NASA plans to launch the James Webb Space Telescope to study infrared ra ...
... • To study X-rays, NASA uses the Chandra X-Ray Observatory. This space telescope was launched in 1999. • Another space telescope, the Compton GammaRay Observatory, was used to study both visible light and gamma rays. • In 2011, NASA plans to launch the James Webb Space Telescope to study infrared ra ...
radio telescope
... • To study X-rays, NASA uses the Chandra X-Ray Observatory. This space telescope was launched in 1999. • Another space telescope, the Compton GammaRay Observatory, was used to study both visible light and gamma rays. • In 2011, NASA plans to launch the James Webb Space Telescope to study infrared ra ...
... • To study X-rays, NASA uses the Chandra X-Ray Observatory. This space telescope was launched in 1999. • Another space telescope, the Compton GammaRay Observatory, was used to study both visible light and gamma rays. • In 2011, NASA plans to launch the James Webb Space Telescope to study infrared ra ...
High-Resolution Optical Spectrometer (HROS)
... HROS concepts (Figure 2). These studies were completed and externally reviewed in March 2006. The University of California – Santa Cruz team led by Steve Vogt has proposed a classical Moderate- to High-Resolution Spectrometer (“MTHR”) echelle concept, and the University of Colorado team led by Cynth ...
... HROS concepts (Figure 2). These studies were completed and externally reviewed in March 2006. The University of California – Santa Cruz team led by Steve Vogt has proposed a classical Moderate- to High-Resolution Spectrometer (“MTHR”) echelle concept, and the University of Colorado team led by Cynth ...
Review Questions for Chp 2
... 56. Why can radio telescopes be so large? 57. What is the main problem with the atmosphere and ground based telescopes? 58. Who came up with the idea that planets move in an elliptical orbit? 59. Which type of electromagnetic radiation could cause cancer in the skin of humans? 60. If a star is 2.2 m ...
... 56. Why can radio telescopes be so large? 57. What is the main problem with the atmosphere and ground based telescopes? 58. Who came up with the idea that planets move in an elliptical orbit? 59. Which type of electromagnetic radiation could cause cancer in the skin of humans? 60. If a star is 2.2 m ...
Chapter 15 Study Guide
... 3. Who said that the Earth was the center of the universe? PTOLEMY 4. Who proved the ideas of Copernicus to be correct? KEPLER 5. What work did Harvey do? THE HEART AND THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6. Who created the word electricity? GILBERT 7. Which scientist explained the force of Gravity? NEWTON 8. Who inve ...
... 3. Who said that the Earth was the center of the universe? PTOLEMY 4. Who proved the ideas of Copernicus to be correct? KEPLER 5. What work did Harvey do? THE HEART AND THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6. Who created the word electricity? GILBERT 7. Which scientist explained the force of Gravity? NEWTON 8. Who inve ...
Space Study Guide
... A satellite is an object that orbits a larger object. Thousands are now in orbit around Earth, and others orbit the Moon, Sun, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn. Natural objects in orbit are called natural satellites. Human-made objects in orbit are called artificial satellites. Name a natural and an ...
... A satellite is an object that orbits a larger object. Thousands are now in orbit around Earth, and others orbit the Moon, Sun, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn. Natural objects in orbit are called natural satellites. Human-made objects in orbit are called artificial satellites. Name a natural and an ...
Space Key Word Search
... of a super-massive star. CELESTIAL SPHERE - system of mapping the space around the Earth; an imaginary sphere surrounding Earth. CIRCUMPOLAR - circling the pole star (Polaris). COMET - chunk of dirty, dark ice mixed with dust, rocks, and gases which revolves around the Sun in an elliptical orbit; em ...
... of a super-massive star. CELESTIAL SPHERE - system of mapping the space around the Earth; an imaginary sphere surrounding Earth. CIRCUMPOLAR - circling the pole star (Polaris). COMET - chunk of dirty, dark ice mixed with dust, rocks, and gases which revolves around the Sun in an elliptical orbit; em ...
Introduction
... meant it was on CS • more accurate predictions require better observations • prolific instrument maker ...
... meant it was on CS • more accurate predictions require better observations • prolific instrument maker ...
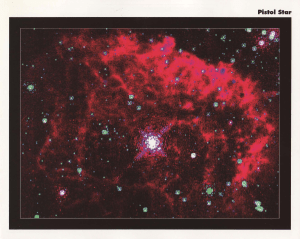
Pistol Star - TeacherLINK
... be the mos t lum inous star known a celestial ti tan tha t releases u p to 10 million times the power of the Sun and is big enough to fill th e d iameter o f Earth's orbit. The Pistol Star is invisible to the naked eye beca use it is hidd en 25,000 light-years away behind grea t dust clouds in the c ...
... be the mos t lum inous star known a celestial ti tan tha t releases u p to 10 million times the power of the Sun and is big enough to fill th e d iameter o f Earth's orbit. The Pistol Star is invisible to the naked eye beca use it is hidd en 25,000 light-years away behind grea t dust clouds in the c ...
TU Muscae and the Early-type Overcontact Binaries
... Binary orbital plane is oriented so that the two stars pass in front of one another as seen from Earth. The light curve is rich in information about the two stars. ...
... Binary orbital plane is oriented so that the two stars pass in front of one another as seen from Earth. The light curve is rich in information about the two stars. ...
Science 9 Test Review-Space Answers 1. pg 434 2a
... Orbital period – the period of time required for an orbiting object to complete one revolution Constellations – a group of stars that forms shapes or patterns Probe – an unmanned space craft sent into space to obtain data and complete research Satellite – a large natural object that travels in an or ...
... Orbital period – the period of time required for an orbiting object to complete one revolution Constellations – a group of stars that forms shapes or patterns Probe – an unmanned space craft sent into space to obtain data and complete research Satellite – a large natural object that travels in an or ...
The Danger of Deadly Cosmic Explosions
... • Narrow beam, confined over galactic distances. • We see GRB in distant galaxies that have most radiation at high energies…. penetrates even underground and underseas. • Equivalent to 1 kiloton TNT / km2 over earth surface, and clearly kills everything immediately exposed. • Longer term destroys at ...
... • Narrow beam, confined over galactic distances. • We see GRB in distant galaxies that have most radiation at high energies…. penetrates even underground and underseas. • Equivalent to 1 kiloton TNT / km2 over earth surface, and clearly kills everything immediately exposed. • Longer term destroys at ...
Peer Instruction/Active Learning
... b) HST uses a larger primary mirror. c) it gathers X-‐ray light. d) HST orbits above the atmosphere. e) it stays on the night-‐
... b) HST uses a larger primary mirror. c) it gathers X-‐ray light. d) HST orbits above the atmosphere. e) it stays on the night-‐
Jodrell Bank Discovery Centre Scouts
... Find the dome with two planets orbiting a star Exoplanets are planets outside our solar system, orbiting around other stars. 12. The amount of light from the star is being measured by a camera (in the red circle) and being shown on screen. What happens to the light level when a planet passes between ...
... Find the dome with two planets orbiting a star Exoplanets are planets outside our solar system, orbiting around other stars. 12. The amount of light from the star is being measured by a camera (in the red circle) and being shown on screen. What happens to the light level when a planet passes between ...
Exploring Space
... Looking from Earth Telescopes are used to see objects that are far away. The largest telescopes are up to 300m wide There are 3 types ...
... Looking from Earth Telescopes are used to see objects that are far away. The largest telescopes are up to 300m wide There are 3 types ...
International Ultraviolet Explorer

The International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) was an astronomical observatory satellite primarily designed to take ultraviolet spectra. The satellite was a collaborative project between NASA, the UK Science Research Council and the European Space Agency (ESA). The mission was first proposed in early 1964, by a group of scientists in the United Kingdom, and was launched on January 26, 1978 aboard a NASA Delta rocket. The mission lifetime was initially set for 3 years, but in the end it lasted almost 18 years, with the satellite being shut down in 1996. The switch-off occurred for financial reasons, while the telescope was still functioning at near original efficiency.It was the first space observatory to be operated in real time by astronomers who visited the groundstations in the United States and Europe. Astronomers made over 104,000 observations using the IUE, of objects ranging from solar system bodies to distant quasars. Among the significant scientific results from IUE data were the first large scale studies of stellar winds, accurate measurements of the way interstellar dust absorbs light, and measurements of the supernova SN1987A which showed that it defied stellar evolution theories as they then stood. When the mission ended, it was considered the most successful astronomical satellite ever.