Chapter 28 Vocabulary
... Absolute Magnitude – The measure of how bright a star would be if it were located 10 parsecs from Earth. ...
... Absolute Magnitude – The measure of how bright a star would be if it were located 10 parsecs from Earth. ...
Name Date Period ______ 30.1 Characteristics of Stars Definitions
... 19. What are circumpolar stars? What is one example? ...
... 19. What are circumpolar stars? What is one example? ...
100 X size of Sun - East Penn School District
... • In the magnitude scale, lower numbers are associated with brighter stars. • Star A has an apparent magnitude = 5.4 and star B has an apparent magnitude = 2.4. Which star is brighter? • We can't actually move stars around, but we can calculate how bright a star would be if placed at the agreed-upon ...
... • In the magnitude scale, lower numbers are associated with brighter stars. • Star A has an apparent magnitude = 5.4 and star B has an apparent magnitude = 2.4. Which star is brighter? • We can't actually move stars around, but we can calculate how bright a star would be if placed at the agreed-upon ...
Astronomy
... Polaris: the North Star, which is located almost directly above Earth’s geographic North Pole. Red shift: as a source of visible light moves away from the observer, the wavelengths increase, creating a shift toward the red end of the visible spectrum. Star: a fixed luminous point in the night sky th ...
... Polaris: the North Star, which is located almost directly above Earth’s geographic North Pole. Red shift: as a source of visible light moves away from the observer, the wavelengths increase, creating a shift toward the red end of the visible spectrum. Star: a fixed luminous point in the night sky th ...
Study Guide for Astronomy
... The United States launched its first satellite, Explorer 1, in 1958. Geosynchronous orbit – a satellite orbits at the same speed as the Earth rotates Space probe- an uncrewed vehicle that carries scientific instruments to planets or other bodies in space. The first space probe, Luna 1, was launched ...
... The United States launched its first satellite, Explorer 1, in 1958. Geosynchronous orbit – a satellite orbits at the same speed as the Earth rotates Space probe- an uncrewed vehicle that carries scientific instruments to planets or other bodies in space. The first space probe, Luna 1, was launched ...
here - University of Toronto Astronomy
... of stars moving towards or away can be studied; shift in wavelength divided by the wavelength at rest equals approach or recession speed divided by the velocity of light; can determine the following basic properties of stars- rotation, atmospheric motions, circumstellar material and motion; evidence ...
... of stars moving towards or away can be studied; shift in wavelength divided by the wavelength at rest equals approach or recession speed divided by the velocity of light; can determine the following basic properties of stars- rotation, atmospheric motions, circumstellar material and motion; evidence ...
Astrophysics
... If galaxies are moving away from us, they must have been closer together millions of years ago. If Hubble’s graph is used, the origin of this movement = approx. 10 000 million years old ...
... If galaxies are moving away from us, they must have been closer together millions of years ago. If Hubble’s graph is used, the origin of this movement = approx. 10 000 million years old ...
Document
... After this, my salary was also kept back from me, and scholars of most eminent rank were violently kept from me, contrary to their own wills, the masters persuading them that their brains were not able to endure it." ...
... After this, my salary was also kept back from me, and scholars of most eminent rank were violently kept from me, contrary to their own wills, the masters persuading them that their brains were not able to endure it." ...
MCERLEAN_2007 - Armagh Observatory
... • The angle was found to be 15.7°. One method of measuring the resolution of the lens is to measure the Modulation Transfer Function (MTF). This describes the response of an optical system to an image decomposed into sine waves. It is also known as the Spatial Frequency Response. MTF quantifies the ...
... • The angle was found to be 15.7°. One method of measuring the resolution of the lens is to measure the Modulation Transfer Function (MTF). This describes the response of an optical system to an image decomposed into sine waves. It is also known as the Spatial Frequency Response. MTF quantifies the ...
Spectroscopy in stellar astrophysics
... ASTROPHYSICS : studies the physics of stars, stellar systems and interstellar material. ...
... ASTROPHYSICS : studies the physics of stars, stellar systems and interstellar material. ...
Review 3 - Physics and Astronomy
... Mirrors are better: - Lenses don’t produce clear image - Lenses absorb some light - Lenses are heavier - Lenses change shape with time ...
... Mirrors are better: - Lenses don’t produce clear image - Lenses absorb some light - Lenses are heavier - Lenses change shape with time ...
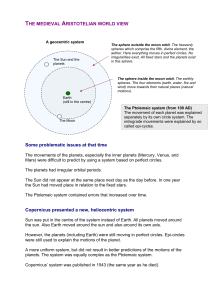
THE MEDIEVAL ARISTOTELIAN WORLD VIEW Some
... spheres. The four elements (earth, water, fire and wind) move towards their natural places (natural motions). Earth (still in the centre) ...
... spheres. The four elements (earth, water, fire and wind) move towards their natural places (natural motions). Earth (still in the centre) ...
Red Shift, Blue Shift
... If a star is moving toward Earth, each light wave that it emits will be released closer to Earth than the previous wave. To an observer on Earth, the distance between wave crests will be smaller than if the star were at rest relative to Earth. The observer would see light that has a shorter waveleng ...
... If a star is moving toward Earth, each light wave that it emits will be released closer to Earth than the previous wave. To an observer on Earth, the distance between wave crests will be smaller than if the star were at rest relative to Earth. The observer would see light that has a shorter waveleng ...
Satellite Communication - univ
... • ALOHA: • Every station can transmit any time • Very low efficiency 18- 36 %. ...
... • ALOHA: • Every station can transmit any time • Very low efficiency 18- 36 %. ...
Name
... 17) X-rays differ from visible light in that they … A) travel faster through empty space. B) travel slower through empty space. C) have a shorter wavelength D) are not electromagnetic waves like visible light is. E) have less energy per photon An infrared photon has a frequency of 1 x 1014 Hz. What ...
... 17) X-rays differ from visible light in that they … A) travel faster through empty space. B) travel slower through empty space. C) have a shorter wavelength D) are not electromagnetic waves like visible light is. E) have less energy per photon An infrared photon has a frequency of 1 x 1014 Hz. What ...
(1) Why is the Pleiades star cluster visible all night around
... These two charts of the orbits of the planets, one showing Mercury through Mars, and the other Mercury through Saturn, depict the view as seen from the north side, or “above” the solar system. In these views, the direction of revolution of the planets about the Sun is counterclockwise. The outer cir ...
... These two charts of the orbits of the planets, one showing Mercury through Mars, and the other Mercury through Saturn, depict the view as seen from the north side, or “above” the solar system. In these views, the direction of revolution of the planets about the Sun is counterclockwise. The outer cir ...
Name - MIT
... 30) Why can the Hubble Telescope observe fainter galaxies than can be observed on Earth? A) the Hubble Telescope is closer to the galaxies B) the Hubble Telescope can observe gamma rays C) the Hubble Telescope can observe X-rays D) the Hubble Telescope can observe radio waves E) the Hubble Telescope ...
... 30) Why can the Hubble Telescope observe fainter galaxies than can be observed on Earth? A) the Hubble Telescope is closer to the galaxies B) the Hubble Telescope can observe gamma rays C) the Hubble Telescope can observe X-rays D) the Hubble Telescope can observe radio waves E) the Hubble Telescope ...
Name
... 30) During its main sequence lifetime, the sun fuses __________ into ____________. A) hydrogen; helium B) hydrogen; carbon C) hydrogen; iron D) helium; carbon E) helium; iron 31) If it is 150 degrees Celsius, what is the temperature in Kelvin? A) 123.15 Kelvin B) 373.15 Kelvin C) 423.15 Kelvin D) -1 ...
... 30) During its main sequence lifetime, the sun fuses __________ into ____________. A) hydrogen; helium B) hydrogen; carbon C) hydrogen; iron D) helium; carbon E) helium; iron 31) If it is 150 degrees Celsius, what is the temperature in Kelvin? A) 123.15 Kelvin B) 373.15 Kelvin C) 423.15 Kelvin D) -1 ...
Name
... 4) A planet is 4 Astronomical Units from the Sun. What is the planet’s orbital period around the Sun? A) the square of 4, which equals 16 years B) the square root of 4, which equals 2 years C) the square root of 64, which equals 8 years D) the square of 9, which equals 81 years E) the cube of 4, whi ...
... 4) A planet is 4 Astronomical Units from the Sun. What is the planet’s orbital period around the Sun? A) the square of 4, which equals 16 years B) the square root of 4, which equals 2 years C) the square root of 64, which equals 8 years D) the square of 9, which equals 81 years E) the cube of 4, whi ...
Teachers Notes - Edinburgh International Science Festival
... Observations in the sky Geocentric and Heliocentric models During the day the sun can be seen rising from the horizon in the east, progressing across the sky and setting at the horizon in the west. At night stars can also be seen moving across the sky. Before space exploration, the only way to under ...
... Observations in the sky Geocentric and Heliocentric models During the day the sun can be seen rising from the horizon in the east, progressing across the sky and setting at the horizon in the west. At night stars can also be seen moving across the sky. Before space exploration, the only way to under ...
International Ultraviolet Explorer

The International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) was an astronomical observatory satellite primarily designed to take ultraviolet spectra. The satellite was a collaborative project between NASA, the UK Science Research Council and the European Space Agency (ESA). The mission was first proposed in early 1964, by a group of scientists in the United Kingdom, and was launched on January 26, 1978 aboard a NASA Delta rocket. The mission lifetime was initially set for 3 years, but in the end it lasted almost 18 years, with the satellite being shut down in 1996. The switch-off occurred for financial reasons, while the telescope was still functioning at near original efficiency.It was the first space observatory to be operated in real time by astronomers who visited the groundstations in the United States and Europe. Astronomers made over 104,000 observations using the IUE, of objects ranging from solar system bodies to distant quasars. Among the significant scientific results from IUE data were the first large scale studies of stellar winds, accurate measurements of the way interstellar dust absorbs light, and measurements of the supernova SN1987A which showed that it defied stellar evolution theories as they then stood. When the mission ended, it was considered the most successful astronomical satellite ever.